Erythropoietin Ameliorates Parent to F1 Murine Graft versus Host Disease by Inhibiting TFH
1Department of Medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 2Dipartimento di Medicina Specialistica, Diagnostica e Sperimentale (DIMES), Policlinico Sant'Orsola-Malpighi, Bologna, Italy
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 157
Keywords: Antibodies, T helper cells
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Lymphocyte Biology - Basic
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Location: Room 306
*Purpose: Building upon our previously generated evidence that erythropoietin (EPO) directly inhibits effector T cells (JASN 2015, 2017) and reduces autoantibody formation in murine lupus, we hypothesized that EPO affects also T follicular helper cells (TFH) function.
*Methods: We administered EPO or vehicle to (bxd)F1 mice given B6 T cells and quantified splenic TFH and germinal center (GC) B cells 2 weeks later. While this graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD) model allows to study alloreactive TFH cells, it is not associated with a clinical phenotype. Therefore, we next treated (dxb/d)F1 mice given DBA/2J spleen cells with EPO or vehicle and quantified anti-dsDNA IgG, proteinuria, renal histology, TFH and GC cells at 6 weeks thereafter. In vitro experiments tested the effect of EPO on B cells stimulated with anti-IgM, anti-CD40 or LPS.
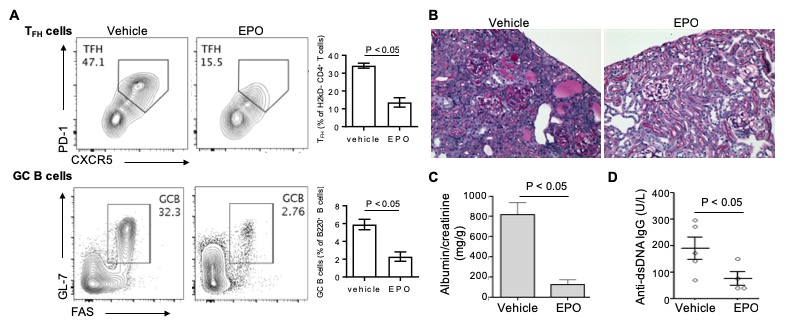
*Results: In the (bxd) parent to F1 model, EPO inhibited TFH and GC B cells formation (Fig 1A). Also in the (dxb/d) parent to F1 model, EPO-induced inhibition of TFH (-20.6±3.5%; p<0.01) and GC B cells (-3.6±0.8%; p<0.001) and this was associated with reduced autoantibodies, proteinuria and renal histological changes (Figure 1B-D). In vitro, EPO did not affect IgG class switch rate of stimulated B cells.
*Conclusions: EPO administration inhibits TFH and GC B cell formation, together reducing the clinical and histological expression of murine lupus nephritis in parent-to-F1 models. Together with our published evidence that EPO promotes human Treg, the data support safety/efficacy testing of rEPO as an immunemodulating agent in to inhibit TFH and alloantibody formation.
Figure 1: Percentages of splenic H2kD–CD4+PD1+CXCR5+ TFH and B220+GL7+Fas+ GC B cells in (bxd)F1 mice injected with B6 T cells 2 weeks prior and treated with vehicle or EPO (A). Representative renal histology (B), urinary albumin/creatinine (C), and anti-dsDNA IgG (D) in (dxb/d)F1 recipients of DBA/2J spleen cells and treated with vehicle or EPO for 6 weeks.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Angeletti A, Donadei C, Cumpelik A, Cantarelli C, Guglielmo C, Manna GLa, Heeger P, Cravedi P. Erythropoietin Ameliorates Parent to F1 Murine Graft versus Host Disease by Inhibiting TFH [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/erythropoietin-ameliorates-parent-to-f1-murine-graft-versus-host-disease-by-inhibiting-tfh/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress