Enhanced Hepatic Engraftment of Stem Cell Derivatives Using Magnetic Targeting into Structurally Normal Liver.
Surgery, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D14
Keywords: Liver transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Cellular & Bone Marrow Transplantation Session II
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Attaining consistent robust engraftment in the structurally normal liver is an obstacle for cellular transplantation. Until now, many therapies to increase engraftment after cellular transplantation involve recipient–centered deleterious methods such as irradiation. Here we present a cell-based strategy that increases engraftment into the structurally normal liver using a combination of magnetic targeting and putative endodermal precursors (PEPs). We used intracellular superparamagnetic particles (SPM) technology to create PEPs that were responsive to an external magnetic field in a noninvasive, targeted approach of cell transplantation to the hepatic parenchyma. We show that magnetic targeting has little effect on cell viability and can enhance initial engraftment of transplanted stem cell derivatives into normal liver parenchyma up to 4 folds 30 days after transplantation.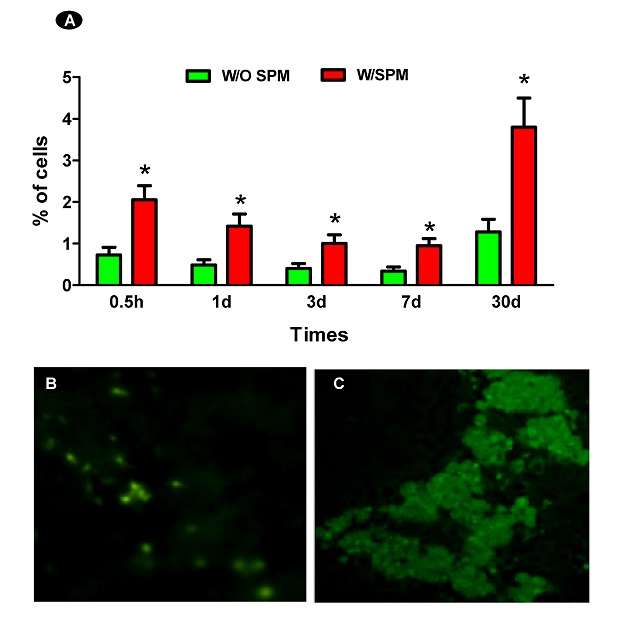 In addition, 3-D fluorescent microscopy confirmed that in mice exposed to magnets, there were substantially more labeled fluorescent cells in the liver, compared to mice not exposed to magnets [figure 1].Consequently, this increase in engraftment may reduce the burden of cellular emboli to the lungs, and reveals a novel method for efficient engraftment without liver damage.
In addition, 3-D fluorescent microscopy confirmed that in mice exposed to magnets, there were substantially more labeled fluorescent cells in the liver, compared to mice not exposed to magnets [figure 1].Consequently, this increase in engraftment may reduce the burden of cellular emboli to the lungs, and reveals a novel method for efficient engraftment without liver damage.
CITATION INFORMATION: Liu N, Fagg S, Fair J. Enhanced Hepatic Engraftment of Stem Cell Derivatives Using Magnetic Targeting into Structurally Normal Liver. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liu N, Fagg S, Fair J. Enhanced Hepatic Engraftment of Stem Cell Derivatives Using Magnetic Targeting into Structurally Normal Liver. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/enhanced-hepatic-engraftment-of-stem-cell-derivatives-using-magnetic-targeting-into-structurally-normal-liver/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
