Elevated Donor HbA1C Confers Impaired Overall Survival Following Renal Allotransplantation in Recipients of Allografts from Donors with Diabetes Mellitus: A National Analysis.
Surgery, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 436
Keywords: Allocation, Donors, Graft survival, Kidney, marginal
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Optimizing Donor/Recipient Selection and Matching
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: E450a
Introduction: Donor diabetes mellitus (DM) is a risk factor for impaired outcomes following renal transplant. Donor DM is factored into the Kidney Donor Risk Index (KDRI) to prognosticate performance of a potential allograft. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) reflects glycemic control over preceding 90 days. We tested the hypothesis that donor HbA1C confers discriminatory power with respect to post-transplant outcomes in assessment of an organ from a DM donor.
Methods: OPTN/UNOS STAR file was queried for adult recipients undergoing primary isolated renal transplant. A1C data were available between 09-2010 and 06-2015. 24,648 recipients were identified. The cohort was partitioned by donor DM, yielding a study cohort of 1,491 recipients. Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank test compared survival between recipients of allografts from DM donors with elevated and non-elevated HbA1C.
Results: 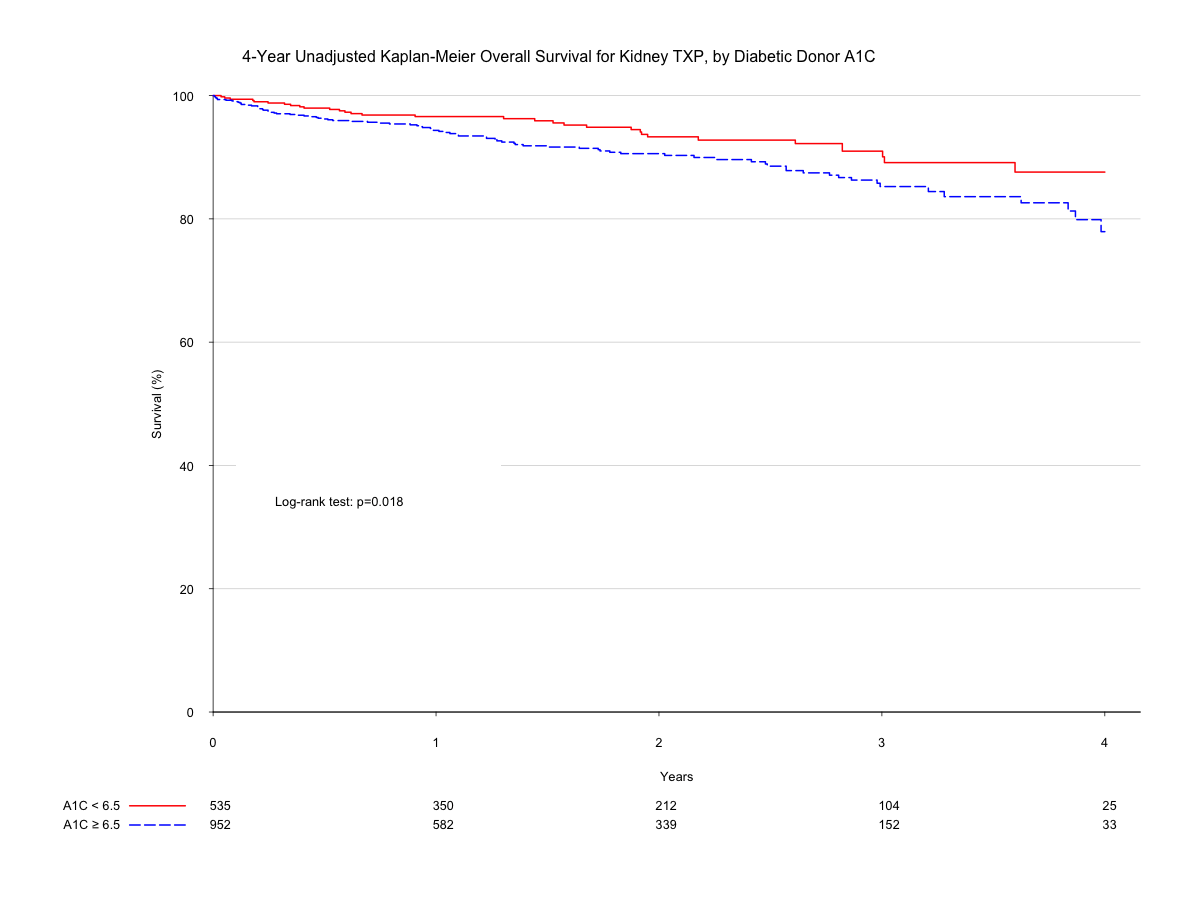 Mean HbA1C for the cohort was 5.61 (IQR 5.2, 5.8). 1,491 donors had a history of DM. DM donors had mean HbA1C of 7.84 (IQR 6.0, 9.3). Recipients from DM donors with normal and elevated A1C were similar with respect to age (58 v 59yrs, p=0.015), gender (61.8 v 64.7% male, p=0.279), number of HLA mismatches (5 v 4, p=0.38), and waitlist days (849 v 905 days, p=0.79). DM donors with normal vs. elevated HbA1C were similar with respect to KDPI (0.7 v. 0.8, p=0.03), age (48 v. 49, p=0.12), serum creatinine (1 v. 1, p=0.05), and history of hypertension (63.1 v. 67%, p=0.14). DM donors with elevated HbA1C were more likely to be male (55.9 v. 47.4%, p=0.002). Median follow up time was 21.1 months. Unadjusted 4-year survival for recipients of allografts from euglycemic and hyperglycemic donors was 87.6 and 77.9%, respectively (p=0.018). 4-year allograft survival was 77.4 vs. 60.0%, respectively (p < 0.001).
Mean HbA1C for the cohort was 5.61 (IQR 5.2, 5.8). 1,491 donors had a history of DM. DM donors had mean HbA1C of 7.84 (IQR 6.0, 9.3). Recipients from DM donors with normal and elevated A1C were similar with respect to age (58 v 59yrs, p=0.015), gender (61.8 v 64.7% male, p=0.279), number of HLA mismatches (5 v 4, p=0.38), and waitlist days (849 v 905 days, p=0.79). DM donors with normal vs. elevated HbA1C were similar with respect to KDPI (0.7 v. 0.8, p=0.03), age (48 v. 49, p=0.12), serum creatinine (1 v. 1, p=0.05), and history of hypertension (63.1 v. 67%, p=0.14). DM donors with elevated HbA1C were more likely to be male (55.9 v. 47.4%, p=0.002). Median follow up time was 21.1 months. Unadjusted 4-year survival for recipients of allografts from euglycemic and hyperglycemic donors was 87.6 and 77.9%, respectively (p=0.018). 4-year allograft survival was 77.4 vs. 60.0%, respectively (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: In recipients receiving an allograft from DM donor, long term outcomes are impaired when HbA1C is elevated. HbA1C may provide additional discriminatory power in risk stratification of potential allografts. Further studies should elucidate the optimal role of HbA1C in KDRI.
CITATION INFORMATION: Mulvihill M, Yerokun B, Davis R, Barbas A, Hartwig M. Elevated Donor HbA1C Confers Impaired Overall Survival Following Renal Allotransplantation in Recipients of Allografts from Donors with Diabetes Mellitus: A National Analysis. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mulvihill M, Yerokun B, Davis R, Barbas A, Hartwig M. Elevated Donor HbA1C Confers Impaired Overall Survival Following Renal Allotransplantation in Recipients of Allografts from Donors with Diabetes Mellitus: A National Analysis. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/elevated-donor-hba1c-confers-impaired-overall-survival-following-renal-allotransplantation-in-recipients-of-allografts-from-donors-with-diabetes-mellitus-a-national-analysis/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
