Elective Allograft Nephrectomy After Transplant Failure
University Hospitals, Transplant Institute, Cleveland, OH.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B118
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Graft failure, Kidney transplantation, Surgical complications
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Complications: Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background/Methods: Because of high rates of allograft intolerance and alloantibody sensitization after kidney transplant failure, we undertook a pilot study of elective allograft nephrectomy (ENx) prior to weaning immunosuppression in patients targeted for retransplantation. Over a three year period, seven ENxs were performed in patients after failure but still on calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) therapy, and outcomes were compared to 18 patients who presented with fever, pain and/or hematuria, and underwent Nx for symptoms (SNx). Additional patients with Nx for infection, obstruction, tumors, thrombosis, or to provide space for a new transplant were excluded from analysis (n=20).
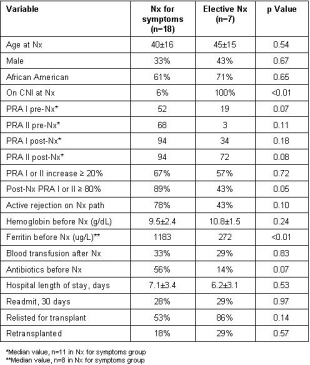
Results: Outcomes are shown in the Table. Demographic data were similar between groups. In the SNx group, all but one patient had weaned off CNI therapy prior to Nx. PRA data within six months pre- and post-Nx were available in 18 patients. SNx patients had a higher median PRA pre- and post-Nx. However, a PRA increase of ≥ 20% after Nx was common in both groups. Three of the 7 ENx patients became highly sensitized after Nx (PRA I or II ≥ 80%). Active rejection was seen on pathology in 78% of SNx patients vs. 43% of ENx patients. In all 25 patients, active rejection on biopsy correlated with a post-Nx PRA I and/or II of ≥ 80% (r=0.59, p=0.02). There was a trend for more anemia and a significantly higher ferritin level prior to surgery in the SNx group, consistent with great inflammation vs. ENx patients. Blood transfusion, length of stay, and readmission rates were similar between groups, although there was a trend for greater antibiotic usage for initial suspected infection in the SNx group.
Conclusions: In this early pilot experience, we noted less inflammation and alloantibody sensitization in patients undergoing ENx on CNI therapy after transplant failure. However, blood transfusions and hospital readmissions were common in both ENx and SNx patients. Future studies are needed to determine whether there is a benefit of ENx in selected patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Augustine J, Woodside K, Noon K, Hricik D, Sanchez E, Schulak J. Elective Allograft Nephrectomy After Transplant Failure [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/elective-allograft-nephrectomy-after-transplant-failure/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
