Efficacy, Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Once-Daily, MeltDose® Tacrolimus (Envarsus® XR) Versus Twice-Daily Tacrolimus (Prograf®) in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipient Sub-Groups: A 2 Year Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Trial
1David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles
2Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit
3Central Pennsylvania Transplant Foundation, Harrisburg
4University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago
5California Institute of Renal Research, San Diego.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B70
Keywords: African-American, Elderly patients, Immunosuppression
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Clinical Science: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Agents
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Differences in tacrolimus (tac) metabolism are evident in certain populations; in particular, lower tac bioavailability has been shown in females and black kidney transplant recipients (KTR). Poorer clinical outcomes post-transplant are also seen in specific populations, including black and older KTR. Envarsus XR, a novel once-daily, MeltDose formulation of tac, has greater bioavailability, a more consistent concentration profile, noninferior efficacy and similar safety and with lower total daily dose (TDD) vs. traditional twice-daily tac (Prograf). From a Phase 3, double-blind, double-dummy, multicenter, 2 year trial of de novo KTR randomized to once-daily Envarsus XR (n=268) or twice-daily Prograf (n=275), PK, efficacy and safety was examined, stratified by age, race, and sex. The proportion of KTR with treatment failure (biopsy proven acute rejection [BPAR], death, graft loss, or lost to follow-up) tended to be lower for Envarsus XR vs. Prograf among older (6.3% vs. 32.1%, p=0.067), black (30.0% vs. 53.3%, p=0.414), and female KTR (19.2% vs. 30.9%, p=0.092). The proportion of KTR with adverse events (AE) was similar between Envarsus XR and Prograf; the proportion of KTR with serious AE tended to be lower with Envarsus XR vs. Prograf within the black (40.0% vs. 93.3%) and female (63.8% vs. 71.3%) KTR sub-groups. From month 1 on, across subgroups, TDD tended to be lower for Envarsus XR and bioavailability (C0/TDD) higher. These data suggest Envarsus XR may be associated with numerically lower efficacy failure rates within specific challenging KTR subgroups. Future studies with larger samples are warranted to see if these trends persist and reach statistical significance.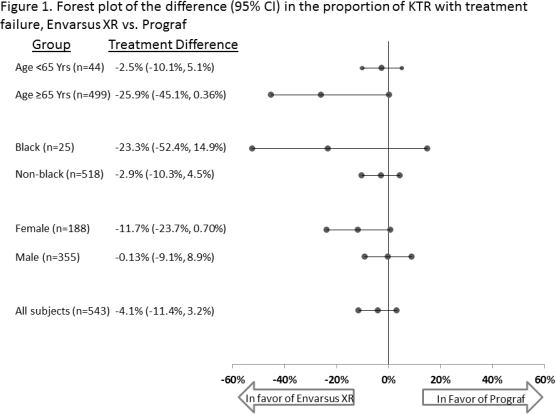
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bunnapradist S, Denny J, Waybill M, West-Thielke P, Steinberg S. Efficacy, Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Once-Daily, MeltDose® Tacrolimus (Envarsus® XR) Versus Twice-Daily Tacrolimus (Prograf®) in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipient Sub-Groups: A 2 Year Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Trial [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/efficacy-safety-and-pharmacokinetics-of-once-daily-meltdose-tacrolimus-envarsus-xr-versus-twice-daily-tacrolimus-prograf-in-de-novo-kidney-transplant-recipient-sub-groups-a-2-yea/. Accessed July 18, 2025.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
