Efficacy and Safety of Everolimus with Reduced-Exposure Tacrolimus and Corticosteroid Withdrawal in De Novo Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients: 12-Month Results from the CRADLE Study.
1A2314 Study Group, Los Angeles
2Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
3Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, East Hanove
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 569
Keywords: Efficacy, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Pediatric
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Late Breaking
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Location: E353C
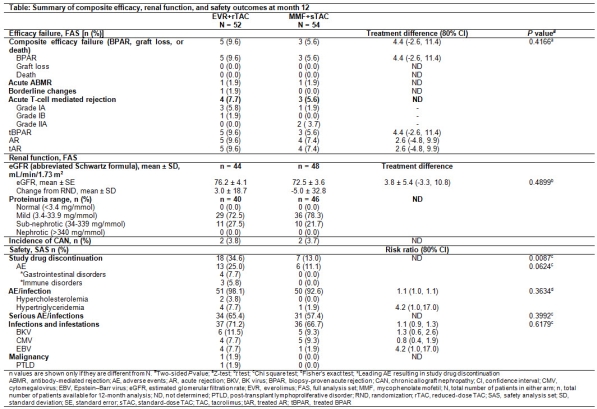
PURPOSE: We present 12-month (M) results from the CRADLE study (NCT01544491) that assessed efficacy and safety of everolimus (EVR) with reduced-exposure tacrolimus (rTAC) and early corticosteroid (CS) withdrawal in pediatric renal transplant recipients (pRTR).
METHODS: In this 12M core+24M follow-up, phase III, multicenter, open-label, parallel-group study, pRTR (≥1-<18 yr) on mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)+standard-exposure TAC (sTAC)+CS±basiliximab were randomized (1:1) at 4-6 weeks posttransplantation to EVR+rTAC with CS withdrawal at 6M (EVR C0: 3-8ng/mL; TAC C0: randomization [RND]-M3, 4-6ng/mL; >3M, 2-4ng/mL) or sTAC+MMF+CS (TAC C0: RND-M3, 7-10ng/mL; >3M, 5-8ng/mL). Coprimary objectives were incidence of composite efficacy failure of biopsy-proven acute rejection (BPAR), graft loss, or death and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR; abbreviated Schwartz). Safety and growth parameters were also assessed.
RESULTS: Of 106 randomized patients, 76.4% completed study treatment up to M12. Composite efficacy failure events were not significantly different between arms and were driven by BPAR (Table). No death or graft loss occurred. Mean eGFR and change from RND to M12 were comparable between arms; no patient experienced nephrotic proteinuria. From RND to M12, incidence of steroid use decreased from 94.2% to 8.3% in EVR+rTAC arm, compared to 98.1% to 100% in MMF+sTAC arm. Between-arm differences in adverse event (AE)/infections were small. Study drug discontinuation rate was significantly higher in EVR+rTAC vs MMF+sTAC arm, mainly due to gastrointestinal and rejection events. Mean height (25.3% vs 21.2%) and weight (37.1% vs 39.6%) percentiles and frequencies of hormone levels outside normal ranges were comparable between arms.
CONCLUSION: EVR+rTAC allowed CS discontinuation while maintaining efficacy and safety, thereby representing a viable treatment regimen in pRTR. Long-term follow-up will help validate these findings.
CITATION INFORMATION: Ettenger R, Tönshoff B, Tedesco H, Dello Strologo L, Marks S, Pape L, Martzloff E, Rauer B, Ng J, Lopez P. Efficacy and Safety of Everolimus with Reduced-Exposure Tacrolimus and Corticosteroid Withdrawal in De Novo Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients: 12-Month Results from the CRADLE Study. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ettenger R, Tönshoff B, Tedesco H, Strologo LDello, Marks S, Pape L, Martzloff E, Rauer B, Ng J, Lopez P. Efficacy and Safety of Everolimus with Reduced-Exposure Tacrolimus and Corticosteroid Withdrawal in De Novo Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients: 12-Month Results from the CRADLE Study. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-everolimus-with-reduced-exposure-tacrolimus-and-corticosteroid-withdrawal-in-de-novo-pediatric-renal-transplant-recipients-12-month-results-from-the-cradle-study/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress