Effect of Everolimus on IgM and IgG Memory B Cell Growth and Survival In Vitro and Applications for Effective Administration in Clinical Practice
Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A243
Keywords: B cells, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Everolimus (EVR), which is converted from CNI, is reported to improve renal function and reduce renal toxicity, DSA production, and rejection development. However, there have been conflicting reports, and hence, the most effective approach for EVR administration, including the time point of CNI to EVR conversion, should be clear.
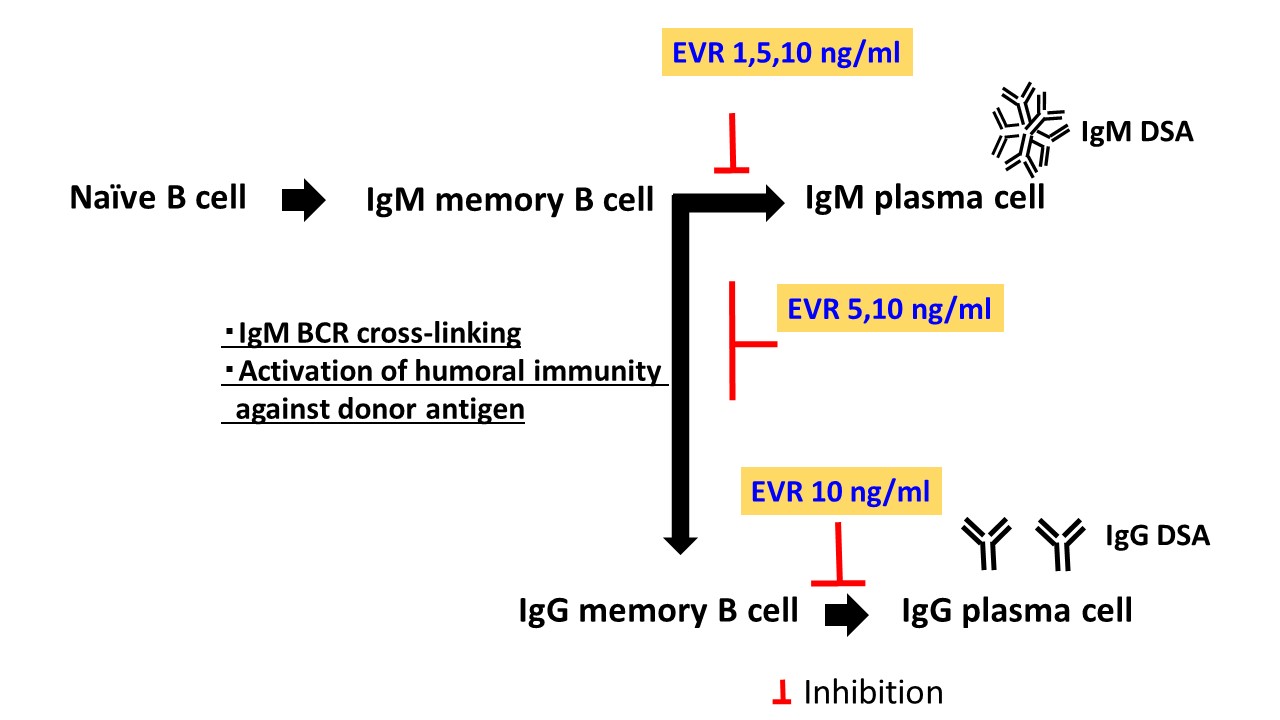
*Methods: IgM and IgG memory B cells (mBCs) were separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) obtained from healthy donors (n = 10). Cells were cultured with IL-21, CPG-ODN, and PBMC supernatant produced by stimulating CD19+ B-cell-depleted PBMCs with PMA and PHA to induce these cells differentiation into plasma cells for 5 days in vitro. Further, to induce IgM mBC class switching, cells were cultured in basal medium containing AffiniPure F(ab′)2 fragment goat anti-human IgM for 3 days in vitro. We examined the direct effects of EVR (1, 5, and 10 ng/mL) on IgM mBC differentiation into IgM-producing plasma cells and class switching into IgG mBC and on IgG mBC differentiation into IgG-producing plasma cells in vitro.
*Results: EVR inhibited IgM mBCs differentiation into IgM-producing plasma cells and suppressed IgM mBCs class switching into IgG mBCs, as demonstrated by in vitro findings. Moreover, EVR suppressed IgG mBCs differentiation into IgG-producing plasma cells.
*Conclusions: EVR was expected to suppress production of both IgM- and IgG-producing plasma cells by administration of IgM mBCs before class switching into IgG mBCs. These findings provide further support for early administration immediately following transplant. However, differences in the EVR susceptibility for IgM and IgG mBC growth and survival under in vitro and in vivo conditions should be further examined in a larger cohort taking into consideration the effect of T cells, inflammatory cell-mediated immunity, and sensitization via donor-specific antigens through BCR-mediated signaling.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matsuda Y. Effect of Everolimus on IgM and IgG Memory B Cell Growth and Survival In Vitro and Applications for Effective Administration in Clinical Practice [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/effect-of-everolimus-on-igm-and-igg-memory-b-cell-growth-and-survival-in-vitro-and-applications-for-effective-administration-in-clinical-practice/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress