Early Mortality After Liver Transplant is Associated with Pre-Transplant Alterations in Monocyte Phenotype and Gene Expression
1Department of Surgery, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ, 2Center for Immunity and Inflammation, Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences, Newark, NJ, 3J.C. Walter Jr. Center for Transplantation, Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 479
Keywords: Gene expression, Immune deviation, Liver cirrhosis, Mononuclear leukocytes
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 16 - Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: -omics and Systems Biology
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:40pm-4:50pm
Presentation Time: 4:40pm-4:50pm
Location: Hynes Room 304 / 306
*Purpose: Persistence of pre-liver transplant (LT) immune dysfunction (immune frailty) significantly increases post-LT morbidity and mortality. We have identified a pre-LT biomarker panel, the liver immune frailty index (LIFI) which accurately stratifies patients at low, moderate, or high risk for early (<1yr) post-LT mortality due to immune dysfunction. Herein, we explore the immunologic mechanism by which immune frailty occurs by harnessing the resolution of single-cell RNAseq analysis.
*Methods: LIFI was calculated from pre-LT HCV IgG, Eotaxin, and Fractalkine levels (POD0). Representative LIFI-high, -moderate, -low, and healthy control (NHC) were selected based on immune profiles. Single-cell (sc)RNAseq of POD0 PBMCs was performed through 5’ sequencing(10x Genomics). Pathway analysis was also performed(Qiagen).
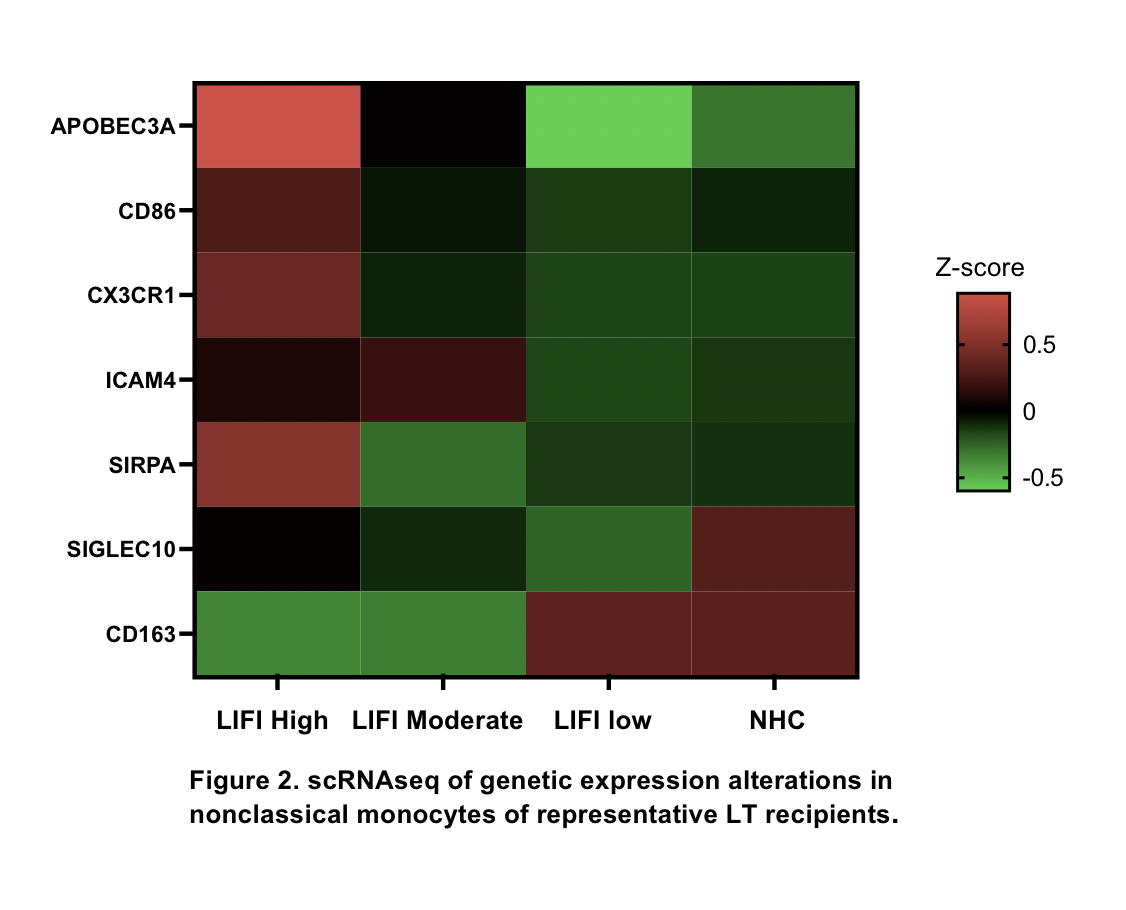
*Results: In 262 LT patients, %monocytes was substantially decreased in LIFI-high compared with LIFI-Moderate, LIFI-Low, and NHC (p<0.01). On scRNAseq, monocytes were similarly depleted in LIFI-high. Clustered monocyte population was analyzed for CD14 (classical) and CD16a (nonclassical, NCM). LIFI-high had decreased CD14 and increased CD16a, suggesting skewing towards NCM (Figure1).NCM gene expression shows upregulation of CX3CR1 (migration), ICAM-4 (adhesion), SIRPA (regulate immunity) for LIFI-high (Figure2). Pathway analysis of all monocytes indicates impaired NO production and MAPK signaling and upregulation of apoptotic pathways.
*Conclusions: LT recipients with immune frailty appear to have both quantitative and phenotypic alterations of monocyte populations. Initial data suggests not only an inappropriate skewing towards NCMs but also genetic alteration which may affect leukocyte function within this population. These alterations may increase recipients’ susceptibility to postLT infection and mortality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jin L, Lemenze A, Panayotova G, Simonishvili S, Qin Y, Ayorinde T, Prakash G, Minze LJ, Paterno F, Brown L, Amin A, Li XC, Ghobrial R, Guarrera JV, Lunsford KE. Early Mortality After Liver Transplant is Associated with Pre-Transplant Alterations in Monocyte Phenotype and Gene Expression [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/early-mortality-after-liver-transplant-is-associated-with-pre-transplant-alterations-in-monocyte-phenotype-and-gene-expression/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress