Early Hospital Readmission After Kidney Transplantation: Seasonality, Causes and Prognosis.
Nephrology Division, Hospital do Rim Foundation, Universidade Federal de Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C260
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Mortality, Prognosis
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Poster Session 1: Kidney Complications-Other
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background: In the general population, 30-day hospital readmission rate is a well-accepted quality metric and a predictor of mortality. A growing body of data suggests that this is also true among kidney transplant recipients.
Objective: The aim of this study is to investigate the prevalence of early readmission (ER) within 30 days after initial kidney transplant hospitalization and whether ER is an independent risk factor for mortality.
Methods: We analyzed all renal transplant recipients performed between January and December of 2012 in a single center and determined ER rate, characteristics, risk factors and impact on mortality during the first 12 months post-transplantation.
Results: Of 917 kidneys only transplants performed in the study period, 555 with complete data were included in this analysis. The mean age was 49.1 years, 63% male, 10% diabetic, 1.3% HCV positive, mean time on dialysis 3.7 years, 9% Luminex-PRA Class I >50%, 74% deceased-donors transplants (37% expanded criteria donors, ECD), and 27% received anti-thymocyte globulin induction. The rate of ER was 25%, ranging from 38 % in April to 16 % in November [figure 1]. Of 555 kidney recipients, 6.3 % had at least one readmission within 7 days of discharge, 8.1 % within 14 days and 10.8% within 30 days. The median time was 14 days .The main reasons for ER were infection (62.9%), metabolic disturbances (12.1%), surgical complications (11.4%), acute rejection (7.9%) and cardiovascular events (4.3%). Independent risk factors for ER were recipient age, time on dialysis, DR-mismatch and anti-thymocyte globulin induction. Mortality was 4% with ER [OR 5.17(95%CI1.87-14.26)] and ECD transplants the only independent risk factors identified upon multivariable Cox regression analyses.
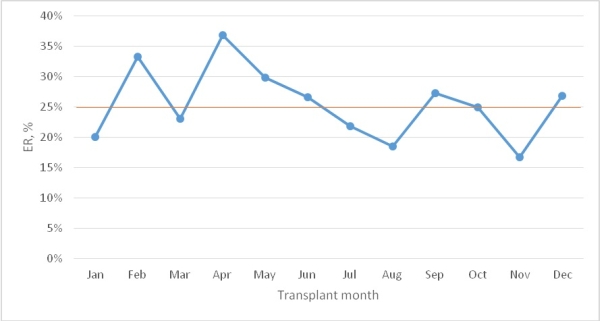 Early Readmission Seasonality
Early Readmission Seasonality
Conclusions: Mean ER was 25%, showed a seasonal distribution and was an independent risk factor for mortality in the first year of kidney transplant. Better identification of patients at risk may guide discharge planning and early post transplant outpatient monitoring.
CITATION INFORMATION: Tavares M, Cristelli M, Viana L, de Paula M, Silva Junior H, Medina Pestana J. Early Hospital Readmission After Kidney Transplantation: Seasonality, Causes and Prognosis. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tavares M, Cristelli M, Viana L, Paula Mde, Junior HSilva, Pestana JMedina. Early Hospital Readmission After Kidney Transplantation: Seasonality, Causes and Prognosis. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/early-hospital-readmission-after-kidney-transplantation-seasonality-causes-and-prognosis/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
