Does Transplantation of Hepatitis C Infected Kidneys Into Uninfected Recipients Cause Hepatitis C-Associated Kidney Injury?
R. H. Naik, S. Shawar, R. C. Forbes, H. Schaefer, D. Shaffer, M. Rossi, V. Imperio, B. P. Concepcion, M. Kapp
Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-211
Keywords: Biopsy, Hepatitis C, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Non-Organ Specific: Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: With increasing utilization of Hepatitis C infected (HCV+) kidneys for transplantation into uninfected (HCV-) recipients, there is concern for the development of HCV-associated kidney injury in the allograft in the setting of acute HCV infection and immunosuppression. HCV-associated kidney pathologic findings include immune-complex disease with a membranoproliferative pattern, cryoglobulinemia, and thrombotic microangiopathy.
*Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all HCV+/- recipients at our center from 10/2018-11/2019. All recipients were transplanted under a clinical protocol and were treated with direct acting antiviral (DAA) therapy posttransplant. We identified recipients who underwent for-cause kidney transplant biopsies and reviewed their pathology, specifically looking for HCV-associated pathologic findings.
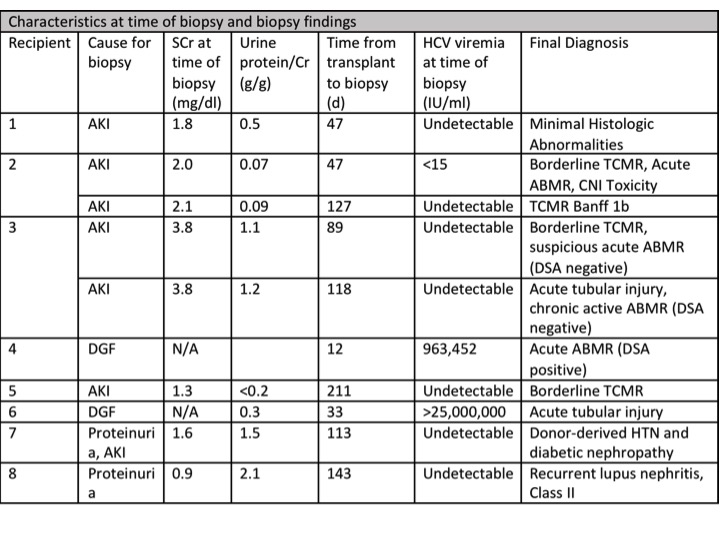
*Results: There were 49 HCV +/- kidney transplants (43 kidney-alone, 6 heart-kidney) performed at our center during the study period. Of these, 8 (7 kidney-alone, 1 heart-kidney) underwent a total of 10 for-cause kidney transplant biopsies. All recipients had unique donors: mean age 43y, 7/8 white, mean KDPI 65%, mean terminal SCr 0.7mg/dl, 4/8 with procurement biopsies (all without HCV-associated pathology). Recipient characteristics include: mean age 52y, 7/8 male, 4/8 white, 7/8 alemtuzumab induction, all FK/MMF based maintenance IS, mean nadir SCr 1.2 mg/dl (excluding 1 recipient with primary non-function). Mean time from transplant to initiation of DAA treatment was 36d. Mean time from transplant to biopsy was 94d. Two recipients were viremic at the time of biopsy. There were no HCV-associated pathologic findings.
Notable biopsy findings include: Recipient 2 had T-cell mediated rejection Banff 1b; Recipient 3 had acute antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) on first biopsy, then chronic active ABMR on second biopsy; Recipient 4 had acute ABMR. Recipient 3 developed graft loss at 133d posttransplant due to refractory non-HLA ABMR. Recipient 6 (heart-kidney) had a tumultuous postoperative course and had the primary non-function of the kidney allograft.
*Conclusions: HCV +/- kidney transplantation leading to acute HCV infection in the setting of immunosuppression does not seem to pose a significant risk of HCV-associated kidney injury. However, in this cohort, 3 recipients developed acute rejection of whom one lost the graft. The association of acute HCV infection from HCV +/- transplantation with acute rejection warrants further study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Naik RH, Shawar S, Forbes RC, Schaefer H, Shaffer D, Rossi M, Imperio V, Concepcion BP, Kapp M. Does Transplantation of Hepatitis C Infected Kidneys Into Uninfected Recipients Cause Hepatitis C-Associated Kidney Injury? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/does-transplantation-of-hepatitis-c-infected-kidneys-into-uninfected-recipients-cause-hepatitis-c-associated-kidney-injury/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress