Does Length of Hospital Stay and Hospital-Wide Incidence Have an Impact on Clostridium Difficile Infection (CDI) in Organ Transplant Recipients?
University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B1050
Several risk factors contributing to CDI have been identified in organ transplant recipients (Txs)(Transplantation 2012; 93:1051-57). Among these factors is hospital length of stay (LOS). Hospital-wide incidence may also be important. We examined whether reduced LOS and hospital incidence would have an impact on the incidence of CDI in Txs. Methods. Data on kidney (K), liver (Lv), lungs (Lg) and heart (H) Txs were collected from 2005 to 2011 from a single center. UNC hospital database was analyzed for incidence of CDI for all non-Tx and Tx patients. All Txs received induction with SoluMedrol. Some H and L received induction with Basiliximab. K Txs were induced with Campath or Thymoglobulin. Maintenance therapy consisted of tacrolimus & MMF. Maintenance with prednisone was given to patients when T-cell depletion therapy was not administered. Results are reported as mean (standard error). Student’s T-test was used to determine significance (GraphPad V5.0d). Results. From 2005 to 2011, 872 Tx were performed, 414 K, 297 Lv, 79 Lg and 82 H. Incidence of Hospital-wide CDI was stable in 2005-9, at rate of 0.31 to 0.28 per 1000 pts days (d). In 2010 to 2011, it increased from 0.56 to 0.83, respectively (Fig. 1). Incidence of CDI in Txs was: total 4.2%, K 2.4%, Lv 5.4%, Lg 3.8% and H 4.8% (respective n= 10, 16, 3 & 4). Annual CDI distribution was as in Fig. 1. LOS after Tx was different for each organ group. After 2009 there was a shorter LOS in K and Lv but not in Lg or H groups. K LOS was reduced from 10.3±0.7 to 5±0.3 d in 2005-8 when compared to 2009-11. In Lv, LOS was reduced from 28.9± 2.5 to 15.9±1.8 d (K & Lv p<0.001). Lg and H LOS was 35.7±5.1 and 35.5±5.9 d (ns) respectively. LOS for all Txs in 2005-8 was 21.4 vs. 14.7 d in 2009-11 (p<0.001). None of the Txs required colectomy.
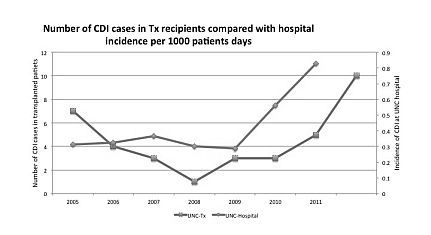
Conclusion. Despite a reduction in LOS in the majority of organ Txs, the number of CDI cases in the Tx population has increased similar to the institution’s trend in non-Tx cases (Fig. 1). Minimization of CDI incidence among the transplant population appears to depend also on local institutional control of CDI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deyo J, Huang J, Wheeler M, Lee R, Zeynep T, Dupuis R, Kozlowski T. Does Length of Hospital Stay and Hospital-Wide Incidence Have an Impact on Clostridium Difficile Infection (CDI) in Organ Transplant Recipients? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/does-length-of-hospital-stay-and-hospital-wide-incidence-have-an-impact-on-clostridium-difficile-infection-cdi-in-organ-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
