Disparate Risk Factors for Early and Late Death Impact Survival after Lung Transplant
Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C260
Keywords: Lung transplantation, Mortality, Risk factors, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Lung: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Purpose:
After implementation of the lung allocation score, there has been improvement in one- and three-year survival but not in five-year survival after lung transplant (LT). The purpose of this study was to assess risk factors for early and late recipient survival following LT.
Methods:
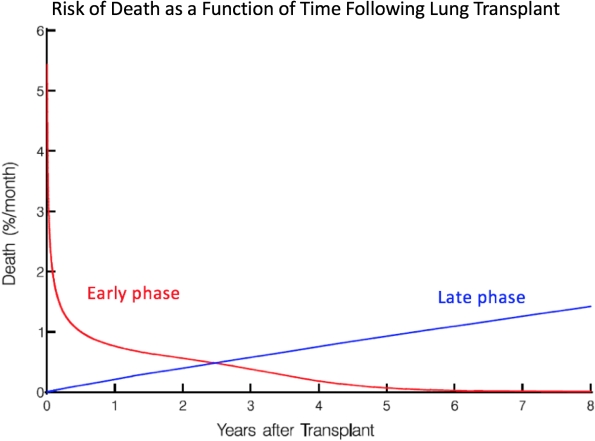
14,253 adults (aged ≥ 18 years) underwent primary LT in the U.S. from 1/1/2006 – 2/19/2015 and were followed to end of the study period or death. Patient data was collected from the OPTN/SRTR national transplant registry, including donor, recipient, and matched donor and recipient variables. A non-proportional hazard parametric model was used to identify risk factors for early deaths (death within the first 3 months) and late deaths (death after 3 years) based on resolution of two distinct phases for risk of death (Figure). Variables were selected by multivariable analysis and reported if the reliability was over 80% via 1000 bootstrap iterations with a p-value of < 0.05.
Results:
There were 5,891 deaths, with 921 deaths occurring in the first 3 months. Recipient risk factors for early death included age, pulmonary vascular disease, hypertension, dialysis, lower albumin, higher creatinine, higher bilirubin, lower total lung capacity, pCO2, shorter walk distance, disabled functional status, hospitalization, longer waitlist time, longer ischemic time, and earlier year of transplant. Donor risk factors for early death included anti-CMV antibodies, greater ratio of recipient to donor weight. Recipient risk factors for late death included age, public insurance (Medicare/Medicaid), lower education level, longer waitlist time, and single lung transplant.
Conclusion:
Our analysis identifies the importance of traditional medical risk factors but also highlights the role of socioeconomic factors in survival after LT. We show that measures of pre-transplant severity of illness contribute to early death while social and economic factors influence late death. While clinicians traditionally identify medical risk factors, this study highlights the importance of social and economic factors as a target for early intervention to improve late survival.
CITATION INFORMATION: Lehr C., Blackstone E., McCurry K., Thuita L., Tsuang W., Valapour M. Disparate Risk Factors for Early and Late Death Impact Survival after Lung Transplant Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lehr C, Blackstone E, McCurry K, Thuita L, Tsuang W, Valapour M. Disparate Risk Factors for Early and Late Death Impact Survival after Lung Transplant [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/disparate-risk-factors-for-early-and-late-death-impact-survival-after-lung-transplant/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress