Different Prognostic Factors for Early and Late Recurrence After Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Surgery, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A69
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation, Recurrence
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Clinical Science: Liver - Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Recurrence after liver transplantation (LT) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unsatisfactory. However, some patients with HCC recurrence after LT show good long-term survival results. The aim of this study is to investigate prognostic factors affecting survival after recurrence mainly focusing on the period of recurrence. Between January 2000 and December 2015, 532 patients underwent adult living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) for HCC. Among these, 92 patients (17.3%) who experienced recurrence were retrospectively reviewed. 1-,3-, and 5-year survival rates after recurrence were 59.5%, 23.0%, and 11.9%, respectively. 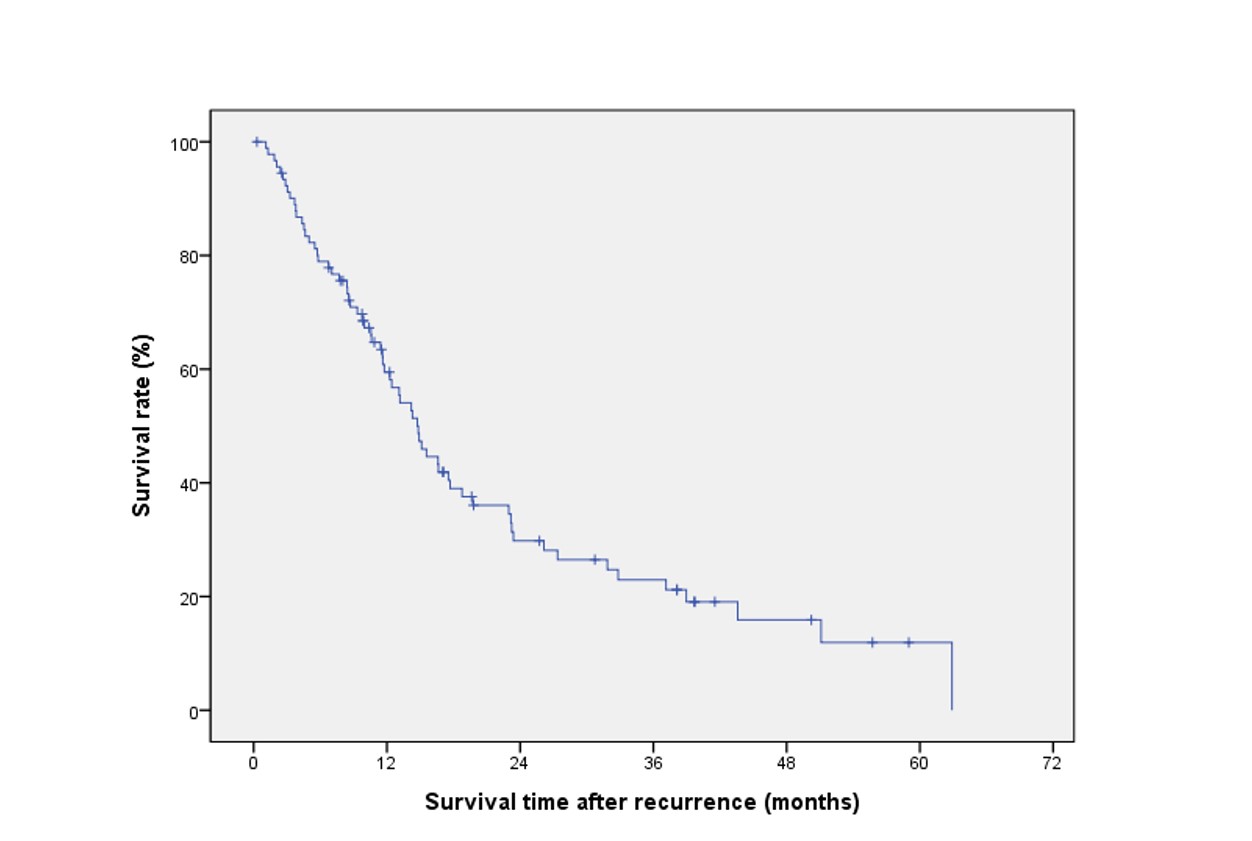 By multivariate analysis, PET positivity [hazard ratio (HR)=0.45] and multi-organ involvement at the time of primary recurrence [hazard ratio (HR)=5.98] were related to poorer survival after recurrence. Time to recurrence >6 months [hazard ratio (HR)=0.45] was related to longer survival after recurrence. We classified the patients into early (≤6 months) and late (>6 months) recurrence group.
By multivariate analysis, PET positivity [hazard ratio (HR)=0.45] and multi-organ involvement at the time of primary recurrence [hazard ratio (HR)=5.98] were related to poorer survival after recurrence. Time to recurrence >6 months [hazard ratio (HR)=0.45] was related to longer survival after recurrence. We classified the patients into early (≤6 months) and late (>6 months) recurrence group. 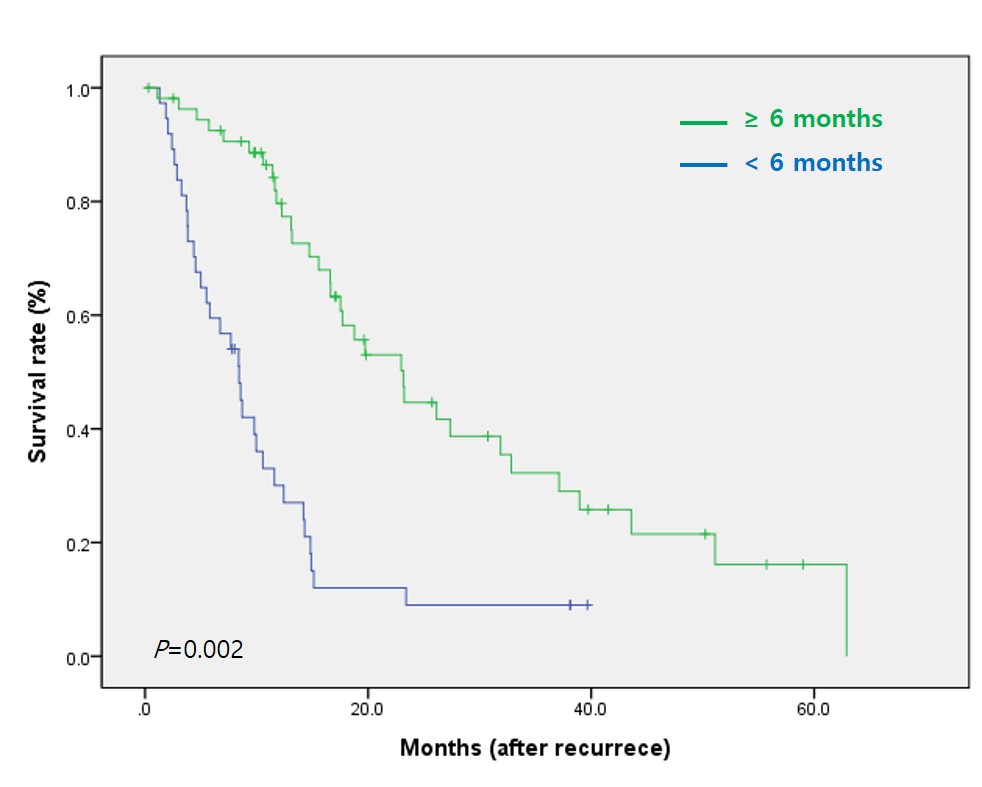 In early recurrence group, only multi-organ involvement at the time of primary recurrence was related to poorer survival on multivariate analysis. In late recurrence group, multi-organ involvement [hazard ratio (HR)=2.76] and mTORi use after recurrence [hazard ratio (HR)=0.42] were significantly associated with prognosis on multivariate analysis. In conclusion, different therapeutic approach is needed according to the period of recurrence after LT. Primary tumor factors should be more considered in early recurrence patients and using mTORi even after recurrence should be considered in late recurrence patients.
In early recurrence group, only multi-organ involvement at the time of primary recurrence was related to poorer survival on multivariate analysis. In late recurrence group, multi-organ involvement [hazard ratio (HR)=2.76] and mTORi use after recurrence [hazard ratio (HR)=0.42] were significantly associated with prognosis on multivariate analysis. In conclusion, different therapeutic approach is needed according to the period of recurrence after LT. Primary tumor factors should be more considered in early recurrence patients and using mTORi even after recurrence should be considered in late recurrence patients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Hong S, Lee K.-W, Kim H.-S, Ahn S.-W, Yoon K, Kim H, Yi N.-J, Suh K.-S. Different Prognostic Factors for Early and Late Recurrence After Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hong S, Lee K-W, Kim H-S, Ahn S-W, Yoon K, Kim H, Yi N-J, Suh K-S. Different Prognostic Factors for Early and Late Recurrence After Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/different-prognostic-factors-for-early-and-late-recurrence-after-adult-living-donor-liver-transplantation-for-hepatocellular-carcinoma/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
