Dialysis Modality, Inflammation, and Frailty in Kidney Transplant Candidates
JHU, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 536
Keywords: Elderly patients, Inflammation, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Perioperative Considerations
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Room 303
Inflammation is associated with poor physical performance, frailty, disability and death in community-dwelling older adults. Given the elevated inflammation levels among ESRD patients, it is likely that inflammatory markers are associated with adverse outcomes such as frailty or physical limitation among kidney transplantation (KT) candidates, although the strength of these associations is unclear.
Methods: 974 participants were enrolled at the time of evaluation for KT (4/2014 to 5/2017). Inflammatory markers, Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), and frailty were assessed at the time of KT evaluation. Participants with a SPPB score <10 were classified as SPPB impaired. Elevated inflammation markers were defined as >1SD higher level of IL-6, sTNFR1, CRP or an inflammation index in log scale.
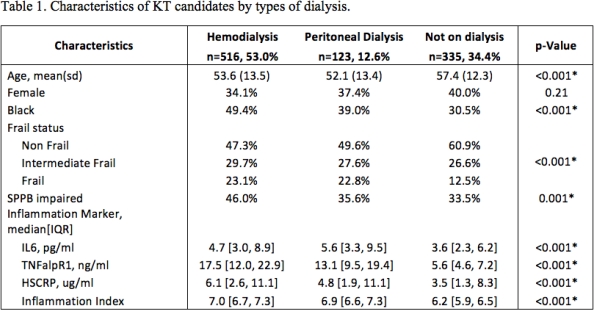
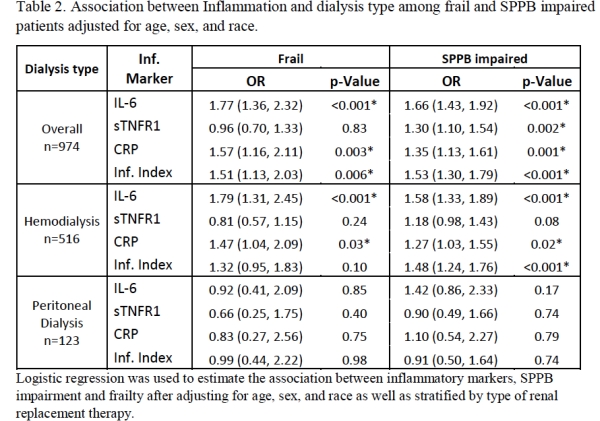
Results: Dialysis groups had higher inflammation; HD patients were most likely to be SPPB impaired and frail (Table 1). Overall, the odds of being frail or SPPB impaired at the time of KT evaluation were higher with increasing IL-6, CRP, and inflammation index, while the odds of being SPPB impaired were also higher with increasing sTNFR1 (Table 2). Among HD patients, the odds of being frail at the time of KT evaluation were higher with increasing IL-6 and CRP and the odds of being SPPB impaired were higher with increasing IL-6, CRP, and inflammation index (Table 2).
Conclusion: Among KT candidates, those undergoing HD have higher odds of being frail and SPPB impaired with elevated levels of inflammatory markers. HD patients with elevated inflammatory markers, especially IL-6, CRP, and inflammation index, may need special care such as closer follow up or prehabilitation to improve lower extremity function and reduce frailty burden while they are on the waitlist.
CITATION INFORMATION: Shrestha P., Ying H., McAdams DeMarco M., Segev D. Dialysis Modality, Inflammation, and Frailty in Kidney Transplant Candidates Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shrestha P, Ying H, DeMarco MMcAdams, Segev D. Dialysis Modality, Inflammation, and Frailty in Kidney Transplant Candidates [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/dialysis-modality-inflammation-and-frailty-in-kidney-transplant-candidates/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress