Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Based Virtual Biopsy System in Kidney Transplant Patients
D. Yoo1, G. Divard1, M. Raynaud1, A. Bentall2, M. Stegall3, M. Naesens4, I. Batal5, S. Coley6, J. Gill7, M. Mengel8, L. Cornell3, M. P. Alexander2, T. Coates9, C. Legendre10, P. Reese11, c. lefaucheur12, O. Aubert1, A. Loupy1
1Paris Transplant Group, Paris, France, 2-, -, AL, 3Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, 4Microbiology, Immunology and Transplantation, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 5Columbia University Medical Center, Scarsdale, NY, 6Columbia University, New York, NY, 7University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 9University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 10Hopital Necker, Paris, France, 11University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 12Hôpital Saint-Louis, Paris, France
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 536
Keywords: Non-invasive diagnosis
Topic: Clinical Science » Organ Inclusive » 72 - Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Social Media in Transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Social Media in Transplantation
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:40pm-5:50pm
Presentation Time: 5:40pm-5:50pm
Location: Hynes Room 210
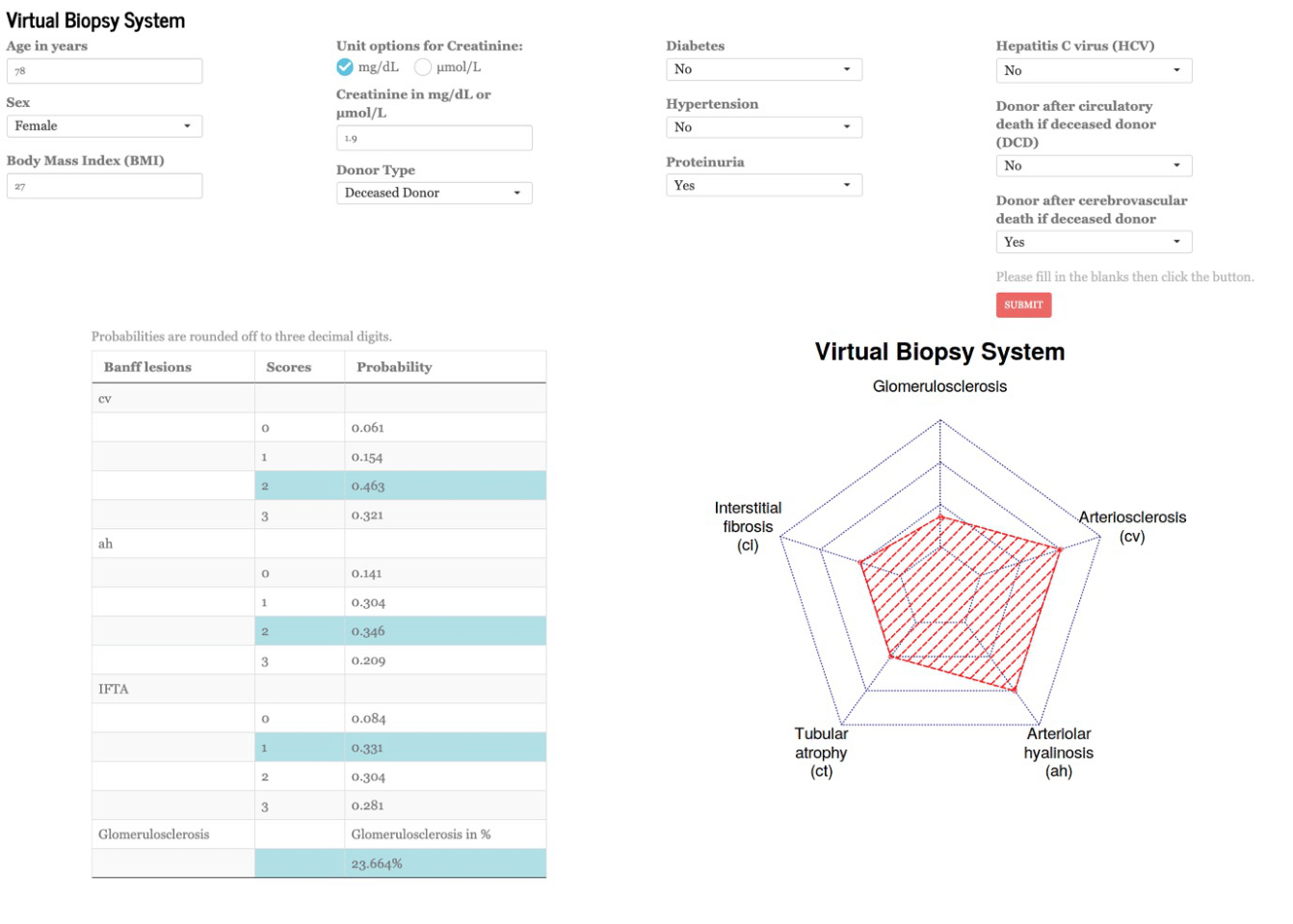
*Purpose: In kidney TX, day-zero biopsies are used to assess organ quality and discriminate lesions inherited from the donor or acquired after transplantation. However, many centers worldwide do not perform those biopsies which remain invasive, costly and may delay the transplant procedure. We aimed to develop and validate a non-invasive virtual biopsy system.
*Methods: 17 centers were included from Europe, North America, and Australia from 2000 to 2019. Candidate predictors were assessed following a pre-specified protocol. Outcome measures were the day-zero biopsy lesions (Banff classification) including cv, ah, IFTA scores and % of sclerotic glomeruli. 6 machine learning models were developed and their performances were assessed.
*Results: A total of 12,992 day-zero biopsies were included. 11 parameters were used to build the classifiers including donor age, kidney function, hypertension, BMI, proteinuria, diabetes, sex, donor type, cause of death, and Hep-C status. The ensemble models (random forests, neural networks, gradient boosting, extreme gradient boosting tree, linear discriminant analysis, and naive Bayes) showed multi-AUC of 0.738, 0.817, and 0.788 for prediction of cv, ah, and IFTA scores, and a good performance for predicting glomerulosclerosis (mean absolute error, MAE=4.766). We confirmed the robustness and generalizability in multiple clinical scenarios and subpopulations and built an online, interface for clinicians https://transplant-prediction-system.shinyapps.io/Virtual_Biopsy_System/.
*Conclusions: We developed and validated the first virtual biopsy system that enables the prediction of DAY-0 biopsy, based on routinely collected parameters. This can assist clinicians in assessing allograft quality, discrimination of donor derived vs acquired lesions after transplantation and prevent overdiagnosis of calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) toxicity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoo D, Divard G, Raynaud M, Bentall A, Stegall M, Naesens M, Batal I, Coley S, Gill J, Mengel M, Cornell L, Alexander MP, Coates T, Legendre C, Reese P, lefaucheur c, Aubert O, Loupy A. Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Based Virtual Biopsy System in Kidney Transplant Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/development-and-validation-of-a-machine-learning-based-virtual-biopsy-system-in-kidney-transplant-patients/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress