Defatting Steatotic Rat Livers during Ex Situ Normothermic Perfusion Improves Lactate Clearance and Bile Quality
1Transplant Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Center for Engineering in Medicine, Shriners Childrens Hospital, Boston, MA, 3Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 279
Keywords: Donors, marginal, Machine preservation, Obesity, Perfusion solutions
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilition II
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: Room 313
*Purpose: Donor livers with moderate-to-severe steatosis are not generally used for transplantation because of poor post-transplant function. Ex situ normothermic machine perfusion (ENMP) provides an opportunity to decrease fat content and assess functional improvement. We evaluated the ability of a 7-component defatting cocktail to decrease macrosteatosis (MaS) and improve perfusion parameters in rat fatty livers.
*Methods: 6 each of lean Zucker rat livers (NL) and steatotic livers (SL) from obese Zucker rats underwent 6 hours of ENMP with standard perfusion medium; an additional 6 SL were perfused with the addition of a defatting cocktail (SLD) containing visfatin, hypericin, forskolin, scoparone, L-carnitine, GW7647, and GW501516. Perfusion dynamics were recorded and perfusate samples collected hourly; macrosteatosis at the end of perfusion was determined in blinded fashion by a pathologist by H & E.
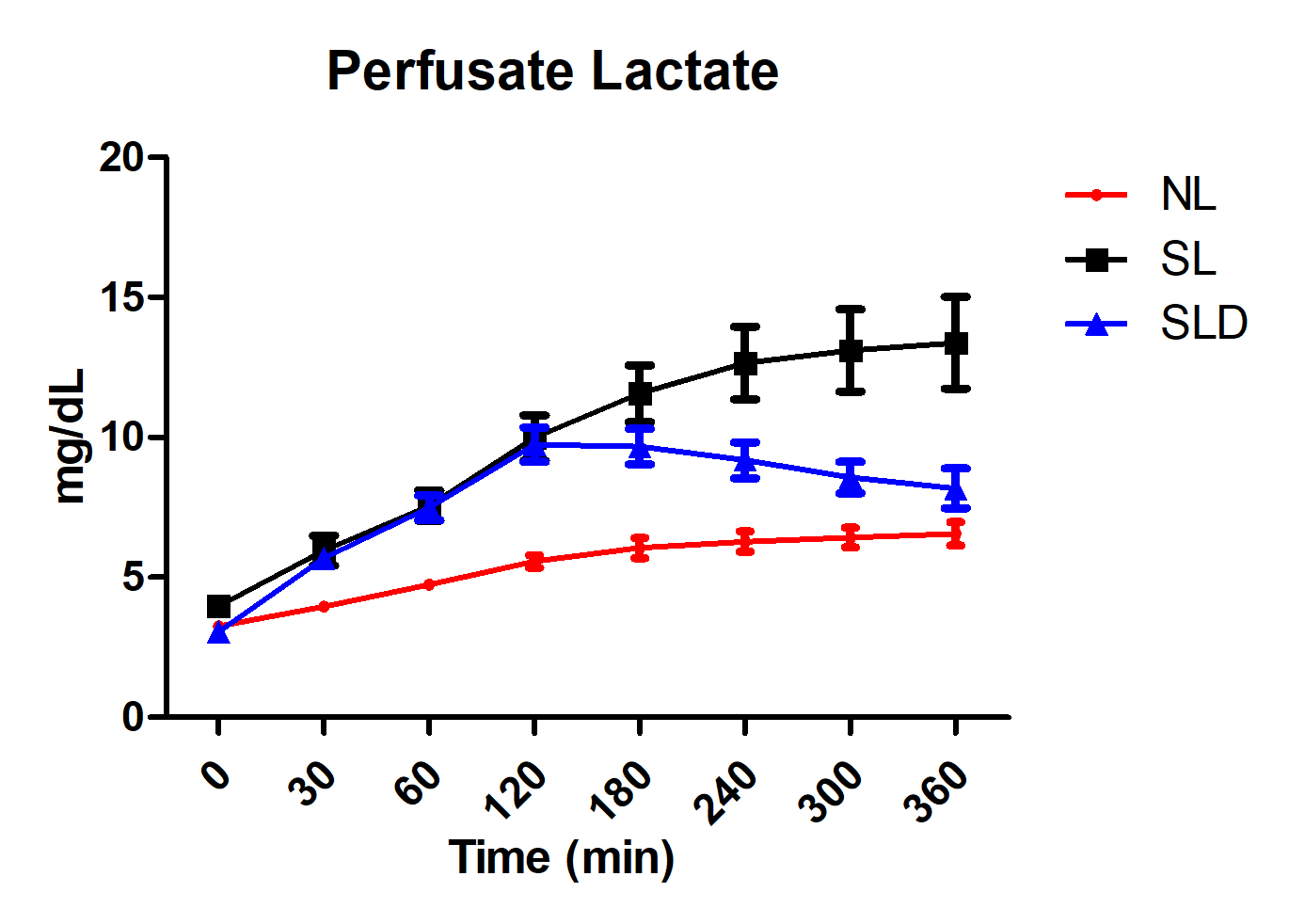
*Results: After 6 hours ENMP, SL livers retained 41.5% MaS (range 25-58%) while SLD had only 8.5% MaS (range 1-18%); NL were <2% MaS, as expected. At 6 hours, perfusate lactate content was significantly higher in SL (13.4 ±4.0 mg/dL) compared to LL (6.6 ±1.0 mg/dL, p=0.001) and SLD (8.2 ±1.7 mg/dL, p=0.01). Perfusate ketone content (as a proxy for fatty acid beta-oxidation) was significantly higher at 4 and 6 hours in SLD compared to SL (p<0.05 for both). Interestingly, perfusate triglyceride levels increased significantly more over 6 hours in SL (140 ng/uL) than SLD (43 ng/uL, p<0.001). Bicarbonate content in produced bile was significantly higher in SLD (42 mmol/L) than SL (26 mmol/L), and even NL (31 mmol/L, p<0.001), although cumulative bile volume remained higher in NL.
*Conclusions: Moderate-to-severe macrosteatosis can be reversed in rat fatty livers using a 7-component defatting cocktail during 6 hours of ENMP, resulting in significantly improved lactate clearance and bile quality. Further studies to test liver viability in a transplant model are planned.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raigani S, Carroll C, Cronin S, Pendexter C, Rosales I, Yarmush M, Uygun K, Yeh H. Defatting Steatotic Rat Livers during Ex Situ Normothermic Perfusion Improves Lactate Clearance and Bile Quality [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/defatting-steatotic-rat-livers-during-ex-situ-normothermic-perfusion-improves-lactate-clearance-and-bile-quality/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress