Deep Learning for Living Donor Surgery: AI Recognition of Surgical Video to Develop Navigation Systems for Laparoscopic Nephrectomy
1Transplant Surgery, International University of Health and Welfare, Mita Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 2Kidney Surgery, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-034
Keywords: Image analysis, Kidney, Laparoscopy, Living donor
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Living Donor: Other
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Laparoscopic surgery for living donors requires high safety, thus establishing of navigation system for surgical operation is urged. The purpose of this study was assessing an ability of Artificial Intelligence to learn and recognize surgical scenes obtained from videos of laparoscopic donor nephrectomy.
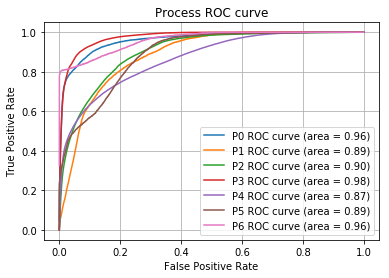
*Methods: Eight videos of hand-assisted transperitoneal laparoscopic left nephrectomies were analyzed by Inception ResNet V2. The scenes in each video were divided into seven processes (P0-6) and manually annotated for surgical transition: (P0) retroperitoneal dissection, (P1) exposing lateral and lower pole of the kidney, (P2) periureteral dissection, (P3) exposing anterior and posterior of the kidney, (P4) hilar dissection, (P5) cut of ureter and (P6) stapling and cut of renal artery and vein. The frame rate of each video was 30. The videos were converted into frame images and each image was annotated, following the movie annotation label. Inception ResNet V2 was used as AI, and modified for binary classification. The hold-out method was chosen for verification of the model, with 4 videos used for training dataset, 2 videos for validation data and 2 for test data. The accuracy was assessed with AUC (area under the ROC curves). This training was conducted for each of the seven process.
*Results: Label AUCs (Area Under the Curves) of the ROC curve of P0 to P6 were 0.962, 0.885, 0.902, 0.975, 0.867, 0.891, 0.962, respectively. The average of AUC was 0.920.
*Conclusions: Interestingly, training for only 4 videos produced such high AUCs. The results implied high possibilities of the deep learning to establish a navigation system ensuring safety of living kidney donor surgery.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nishihara M, Iwadoh K, Noriyuki M, Koyama I, Nakajima I, Tonsho M. Deep Learning for Living Donor Surgery: AI Recognition of Surgical Video to Develop Navigation Systems for Laparoscopic Nephrectomy [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/deep-learning-for-living-donor-surgery-ai-recognition-of-surgical-video-to-develop-navigation-systems-for-laparoscopic-nephrectomy/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress