De Novo Once-Daily Tacrolimus in Liver Transplantation: Long-Term Outcomes of a Single Center Cohort of 150 Patients
Liver Transplantation Unit, Cruces University Hospital. University of the Basque Country, Bilbao, Vizcaya, Spain.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A214
Keywords: Adverse effects, FK506, Immunosuppression, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Liver: Immunosuppression and Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 2, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Purpose: To describe the long-term safety and efficacy profile of de novo once-daily tacrolimus (Tac QD) in orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT)
Patients and methods: A retrospective study was conducted including 150 consecutive adult OLTs treated with de novo Tac QD at our institution between April 2008 and March 2011. First oral dose of Tac QD was 0.15 mg/kg/day or 0.1 mg/kg/day when Tac QD was combined with MMF. Renal function was evaluated using estimated glomerular filtration rate based on MDRD-4 formula.
Results: Median age of recipients was 55.5 years (range 20-67). Primary disease leading to OLT was alcoholic cirrhosis in 47.3% of the patients, hepatitis C in 30.6%, hepatitis B in 5%, cholestatic disease in 5% and a miscellaneous in 12%. Median MELD score was 15 (r 8-40). Fifty-nine patients had hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Antibody induction was used in 17.3% of the patients, steroids in 81.3% and MMF in 36%.
Median follow-up was 45.6 months (r 1-76). Median tacrolimus trough levels during the first week and at 1, 3 and 5 years after OLT were 7.85 (r 1.9-32.5), 6.5, 4.8 and 4.5 ng/mL , respectively. Acute cellular rejection was diagnosed in 17 patients (11.3%). During follow-up, chronic renal dysfunction was observed in 23 patients (15%) arterial hypertension in 29 (19.3%) and diabetes mellitus in 21 (14%). Infection rates during hospitalization and after discharge were 17.3% and 22.2%, respectively. Cytomegalovirus infection accounted for 44.8% of all infections. Seven patients developed de novo tumors (4.7%). Retransplantation rate was 5.3%.
Pretransplant, 1-, 3- and 5-years mean creatinine clearance was 98.7, 77.7, 79.3 and 74.8 ml/min/1.73m2, respectively. Patient survival at 1, 3 and 5 years was 96.6%, 92.5% and 87.8%, respectively.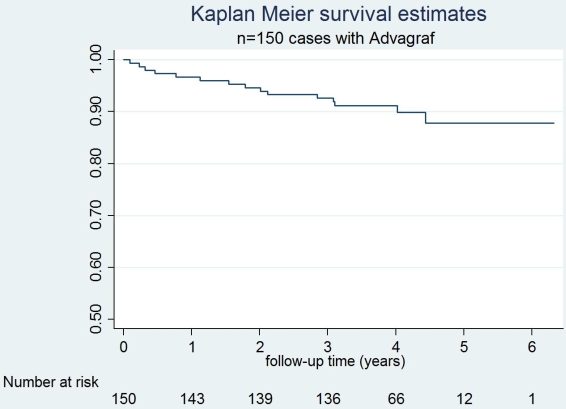 Conclusion: Immunosuppression based on de novo once-daily tacrolimus in adult OLT is effective and safe at the long-term with outstanding patient survival.
Conclusion: Immunosuppression based on de novo once-daily tacrolimus in adult OLT is effective and safe at the long-term with outstanding patient survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gastaca M, Valdivieso A, Bustamante J, Ruiz P, Fernandez J, Ventoso A, Testillano M, Palomares I, Salvador P, Prieto M, Matarranz A, Suarez M, Urbina JOrtizde. De Novo Once-Daily Tacrolimus in Liver Transplantation: Long-Term Outcomes of a Single Center Cohort of 150 Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/de-novo-once-daily-tacrolimus-in-liver-transplantation-long-term-outcomes-of-a-single-center-cohort-of-150-patients/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
