Cyclosporine Nephrotoxicity Is Associated With Diminished Expression of Heat Shock Protein 27 (HSP27) and Loss of Claudin-2-Dependent Intercellular Adhesion
1Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
2INSERM U1082, Poitiers, France.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 259
Keywords: Calcineurin, Immunosuppression, Renal dysfunction
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Basic Mechanisms of Chronic Injury and Fibrosis
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Location: Room 121-C
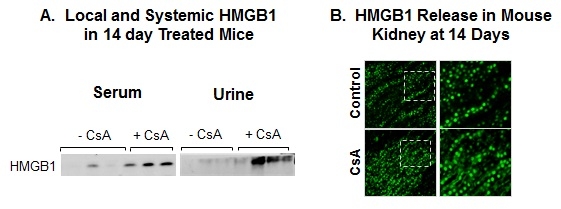
Although Cyclosporine A (CsA), a calcineurin inhibitor (CNI), is an effective immunosuppressant used to prevent kidney allograft rejection, prolonged administration is frequently associated with kidney dysfunction. To further investigate CsA-mediated renal injury, mice were placed on a salt deprived diet for 4 weeks followed by treatment with CsA 30 mg/kg IP daily for 14 days. Morphology and cell-to-cell adhesion were examined in control and CsA-treated human proximal tubular epithelial cells (hPTEC). HSP27, claudin-2 and HMGB1 subcellular localization/extracellular release were measured in culture media, sera, and urine and assessed by immunohistochemistry and Western Blot analysis. Cytokine expression was determined using quantitative RT-PCR. Exposure of hPTEC to CsA for 72h resulted in a marked decreasebin the expression of HSP27 (0.70±0.13-fold, p<0.05), a major heat shock protein involved in thermotolerance and preservation of cellular function during stress conditions. CsA treatment also diminished claudin-2 followed by loss of cell-to-cell adhesion. These changes were further accompanied by HMGB1 translocation from nucleus to cytosol followed by release into the culture media. In vivo, after prolonged treatment with CsA, significant amounts of HMGB1 were detected in the serum and urine (Fig. A). This was associated with diminished expression of HSP27 and increased IL-6 (10.9±3.6-fold, p<0.01), TNFα (5.1±2.1-fold, p<0.01), and TGFβ (33.4±12.3-fold, p<0.01) in CsA toxic kidneys. Notably, the highest extent of HMGB1 translocation and intercellular release was detected in medulla of CsA-treated mice (Fig. B). These results demonstrate an inflammatory milieu mediated by CsA-induced HMGB1 release. The diminished expression of the major cellular chaperon HSP27 and loss of claudin-2 -mediated regulation of tight junctions and intercellular adhesion indicate enhanced tissue remodeling. Interruption of this pathway could mitigate CNI-associated renal injury and could lead to more effective use of these agents.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zmijewska A, Thuillier R, Chen J, Zmijewski J, Mannon R. Cyclosporine Nephrotoxicity Is Associated With Diminished Expression of Heat Shock Protein 27 (HSP27) and Loss of Claudin-2-Dependent Intercellular Adhesion [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cyclosporine-nephrotoxicity-is-associated-with-diminished-expression-of-heat-shock-protein-27-hsp27-and-loss-of-claudin-2-dependent-intercellular-adhesion/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
