Conversion to Belatacept in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Columbia University MC, New York, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A256
Keywords: Glomerulonephritis, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) results in the need for renal replacement therapy (RRT) in 10-30% of LN pts and 30% receive a kidney transplant (KT). Belatacept (bela) is a second-generation selective T-cell co-stimulator blocker (inhibits CTLA-4) used as an alternative to calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) for maintenance regimens after KT; it has a number of indications in KT: CNI nephrotoxicity, mod/severe IFTA and/or arteriosclerosis. The pathogenic relevance of CTLA-4 inhibition and the favorable cardiovascular profile of bela make it a therapeutic option in SLE.
*Methods: A retrospective single center study of adult LN KT recipients evaluated the use and outcomes of bela from 2006-2018. Bela conversion was performed with 5mg/kg q 2 weeks x 5 doses, followed by monthly doses. CNI weaning among the bela group was not standardized. Immunosuppressive regimen, kidney allograft function, and SLE activity were examined.
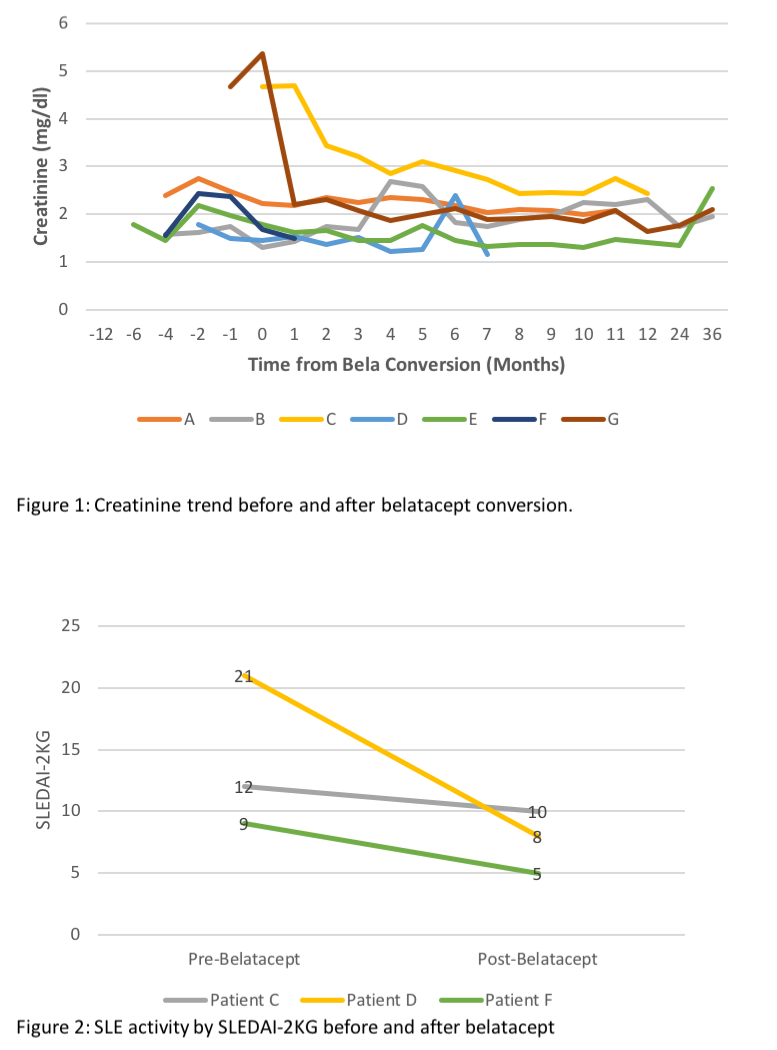
*Results: During the study period 48 pts w/ LN underwent KT, mean follow-up time was 72.2 ± 74.6 mos (Table). 7 pts were converted from CNI to bela maintenance, at 15.5 ± 17.1 mos after KT. All pts were female, age at SLE dx 21.1 ± 4.9 yrs; 5 had undergone RRT prior to KT (4 hemodialysis, 1 peritoneal dialysis) for 38.7 ± 37.8 mos. Time from SLE diagnosis and KT was 13.1 ± 8.3 yrs. At the time of switching from CNI to bela, pts were treated w/ prednisone (7.1 ± 2.7 mg/day), and 6 w/ mycophenolate (1123 ± 625 mg/day), 1 azathioprine (25 mg/day). CNIs were continued in 5/7 patients at 6 mos after bela conversion. In 5 patients, creatinine stabilized 6 mos after conversions to bela, 1 returned to RRT due to CNI-toxicity and pyelonephritis, 1 is relisted for KT due to ACR and cortical necrosis (Figure 1). No allograft failure due to recurrent LN was noted in any of the 7 pts. 5 pts are followed by rheumatology for extrarenal lupus; no extrarenal manifestations are documented in the other 2. Data on SLE Disease Activity pre and post bela was available and scored in 3/5 pts using the SLEDAI-2KG which accounts for clinical and laboratory manifestations, as well as steroid use (Figure 2).
*Conclusions: Bela conversion for LN KT recipients may attenuate CNI toxicity, stabilize allograft function, and decrease extrarenal manifestations for LN KT pts.
| ID | Age at SLE Dx | Race | LN Class | Type KT | Induction | Reason for Bela Conversion | Immunosuppressive Regimen Before Bela Conversion |
| A | 16 | Black | IV, VI | DDKT | Thymo | Non-adherence & Mod IFTA | TAC, MMF |
| B | 30 | Asian | LRKT | Thymo | Mod IFTA & Arteriosclerosis | TAC, MPA, PRED | |
| C | 18 | White | IV, V | DDKT | Thymo | Cortical necrosis | CYC, MMF, PRED |
| D | 19 | Black | V | LUKT | Thymo | CNI side effects | TAC, MPA, PRED |
| E | 22 | Asian | LRKT | Thymo | CNI side effects & Mod IFTA | TAC, MMF, PRED | |
| F | 18 | Black | V | DDKT | Alemtuzumab | CNI side effects | TAC, MMF, PRED |
| G | 25 | White (Hispanic) | III, IV | DDKT | Basiliximab | TMA | TAC, MPA, PRED |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Barberà ICarrión, Fajardo MC, Tsapepas D, Gartshteyn J, Askanase A, Fernandez HE. Conversion to Belatacept in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/conversion-to-belatacept-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress