Comprehensive Functional Assessment of the Pathogenic Potential of Immunodominant Donor Specific Antibody Following Treatment of Late Antibody Mediated Rejection or Mixed Acute Rejection.
1U of Cincinnati, Cincinnati
2Christ Hospital, Cincinnati
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 303
Keywords: Antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: B Cells and Antibody in Rejection
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: E350
HLA donor specific antibody (DSA) mediates injury by both complement dependent and independent mechanisms, including direct signaling via HLA antigens and via Fc receptor (FcR) engagement. Functional assessment of DSA has historically been limited to complement-based assays. FcR binding capacity and IgG isotypes provide complementary approaches for assessment of pathogenic potential of DSA. Assessment of the effects of proteasome inhibitor (PI) based treatment on global immunodominant DSA (iDSA) functional capacity has not been seen previously. We present analysis of comprehensive iDSA functional capacity assessment following PI-based treatment.
Methods: Serum samples obtained at the time of AMR diagnosis and following AMR treatment were analyzed by HLA single antigen bead (SAB) microarrays, C1q assay, IgG isotype-specific SAB assays (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4), and FcR binding assays (performed per standard SOPs for the laboratory-developed test). iDSA FcR binding strength and incidence of IgG3 iDSA were compared pre- and post-treatment with a PI-based regimen.
Results: 51 patients with late AMR/MAR were analyzed (Table 1). Patients expressed reduced proportions of strong iDSA FcR binding capacity (75% vs 53%, p=0.003) and IgG3+ iDSA (73.5% vs. 41.2%, p=0.03) post-treatment. Other results listed in Figure 1.
Conclusions:
1)Treatment with a PI-based regimen reduced iDSA FcR binding strength and IgG3 binding strength in patients with late AMR/MAR
2)Patient with high serum creatinine at the time of rejection diagnosis experienced higher DCGS
3)Impact of comprehensive (FcR, C1q, and IgG isotype) functional analysis in the setting of late AMR/MAR warrants further evaluation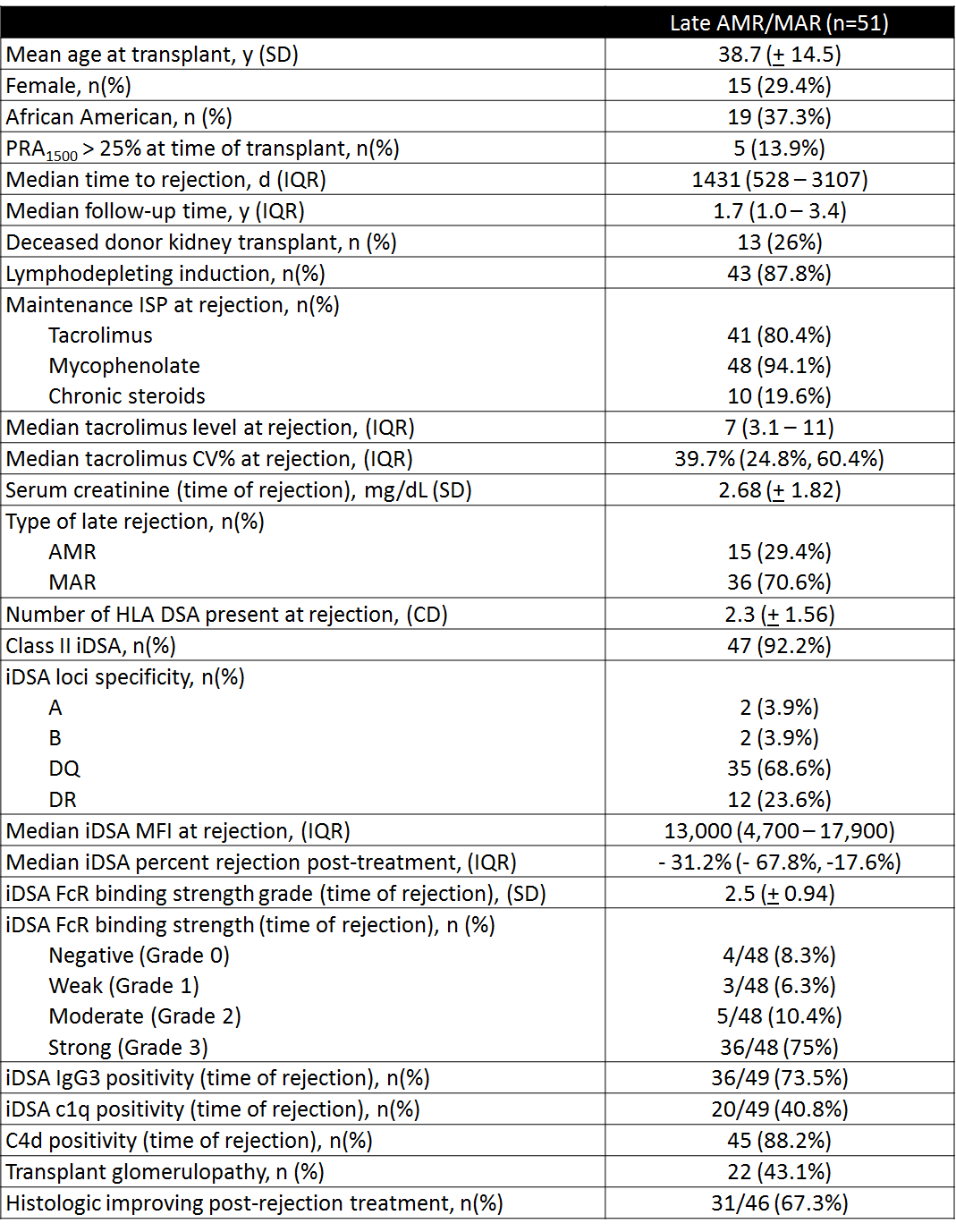
.png)
CITATION INFORMATION: Lichvar A, Portwood E, Brailey P, Tremblay S, Shields A, Abu Jawdeh B, Kremer J, Paterno F, Alloway R, Girnita A, Woodle E. Comprehensive Functional Assessment of the Pathogenic Potential of Immunodominant Donor Specific Antibody Following Treatment of Late Antibody Mediated Rejection or Mixed Acute Rejection. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lichvar A, Portwood E, Brailey P, Tremblay S, Shields A, Jawdeh BAbu, Kremer J, Paterno F, Alloway R, Girnita A, Woodle E. Comprehensive Functional Assessment of the Pathogenic Potential of Immunodominant Donor Specific Antibody Following Treatment of Late Antibody Mediated Rejection or Mixed Acute Rejection. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/comprehensive-functional-assessment-of-the-pathogenic-potential-of-immunodominant-donor-specific-antibody-following-treatment-of-late-antibody-mediated-rejection-or-mixed-acute-rejection/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
