Comparison between Urine and Blood NGAL for Early Prediction of Delayed Graft Function in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Department of Laboratory Medicine, West China Hospital, Chengdu, China
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B63
Keywords: Area-under-curve (AUC), Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Neutrophil gelatinase-assoicated lipocalin (NGAL) appears to be a promising proximal tubular injury biomarker for early prediction of delayed graft function (DGF) in kidney transplant recipients. However, its predictive values in urine and blood are varied in different studies. Here, we performed a meta-analysis to compare the predictive values of urine NGAL (uNGAL) and blood NGAL (bNGAL) for DGF in adult kidney transplant recipients.
*Methods: We systematically searched Medline, Cochrane library and Embase for relevant studies from inception to May 2018. The summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves, the pooled sensitivity and specificity as well as diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) were used to evaluate the prognostic performance of post-transplant 24h uNGAL and bNGAL for early identification of DGF.
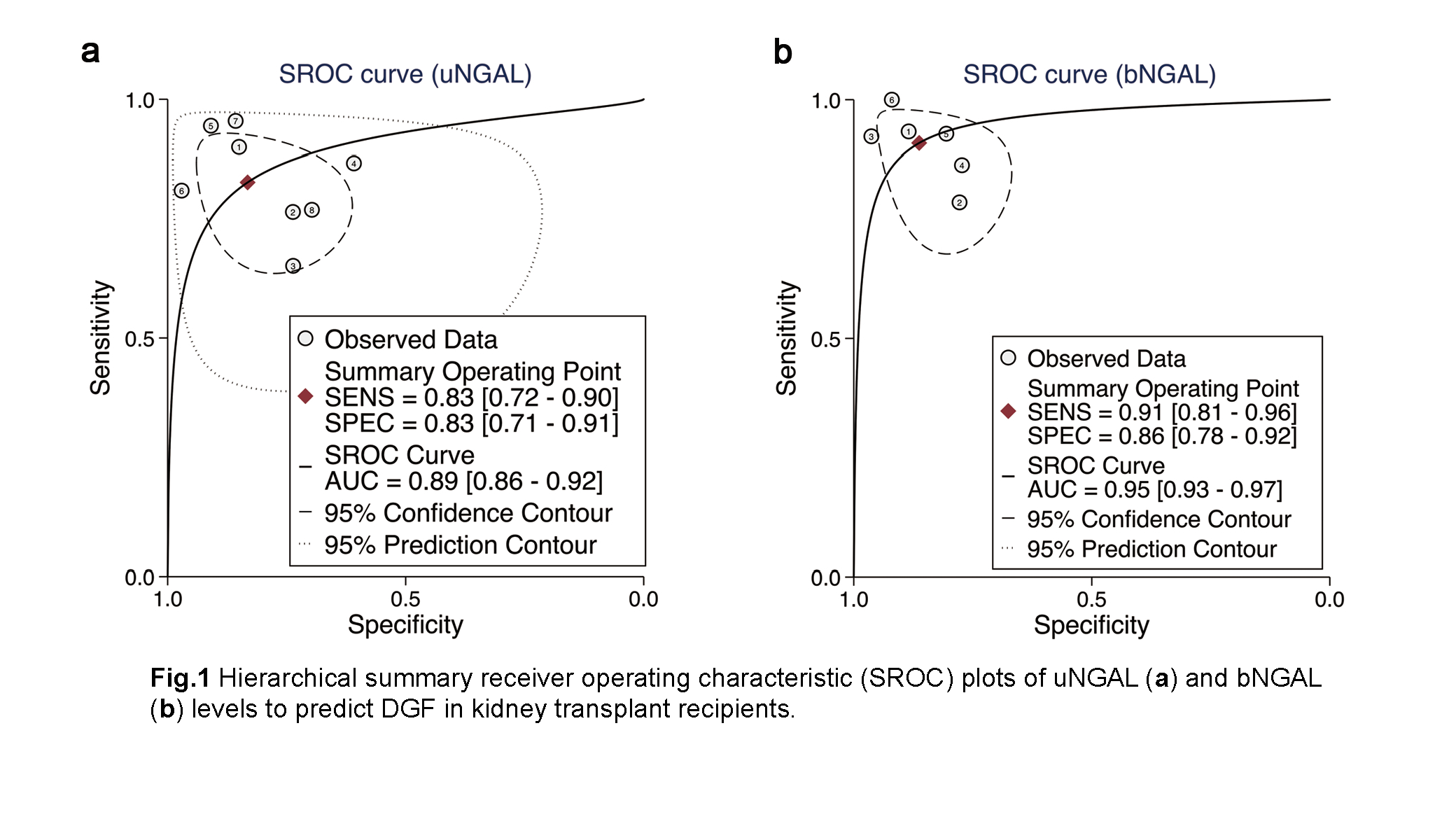
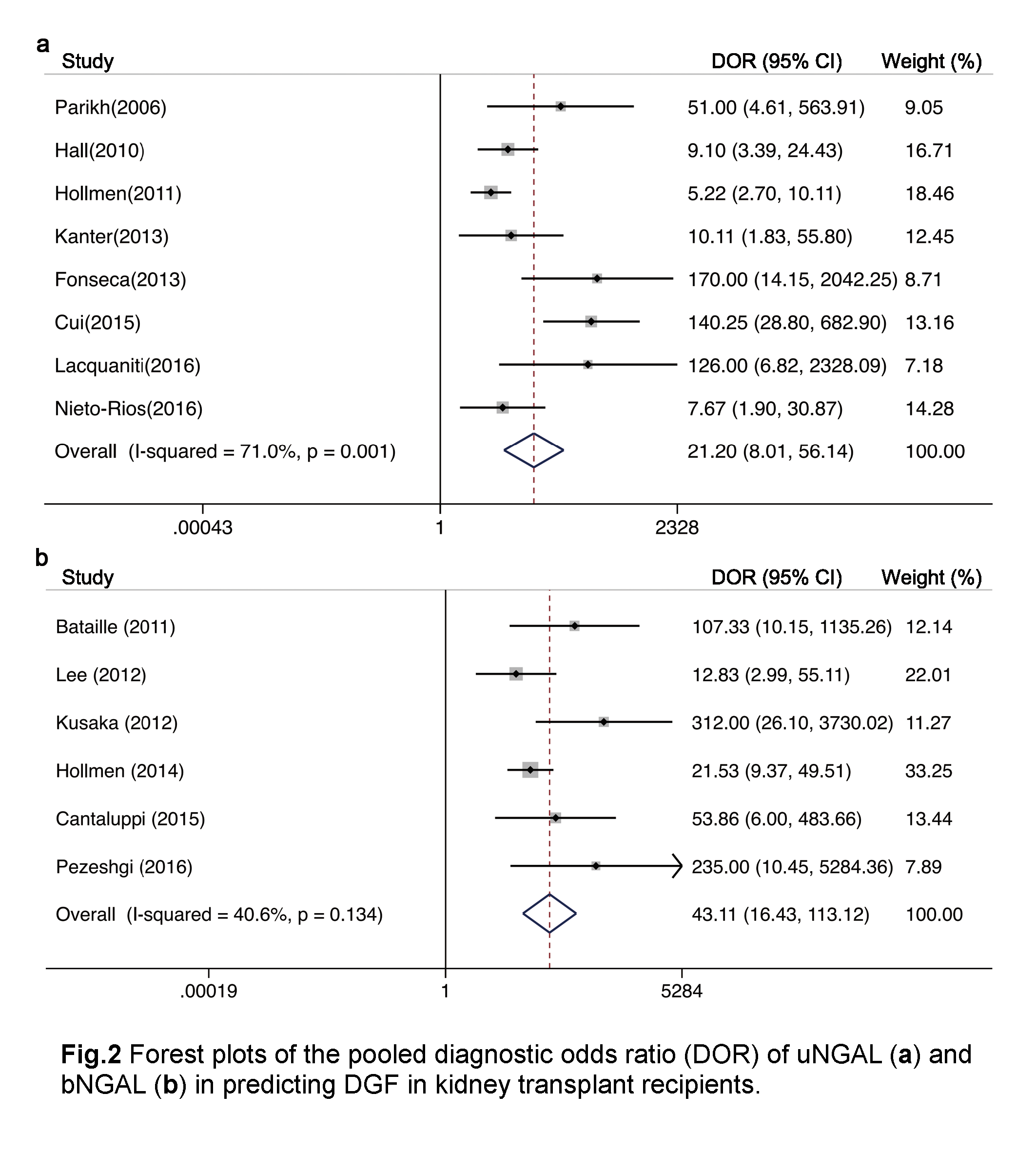
*Results: A total of 1036 patients from 14 eligible studies were included in the analysis. 8 studies focused on NGAL in urine and 6 reported NGAL in serum or plasma. The composite area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) for uNGAL was 0.89 (95%CI, 0.86-0.92) and the overall DOR for uNGAL was 21.20 (95%CI, 8.01-56.14) with sensitivity of 0.83 (95%CI, 0.72-0.90) and specificity of 0.83 (95%CI, 0.71-0.91). The composite AUROC for bNGAL was 0.95 (95%CI, 0.93-0.97) and the overall DOR for bNGAL was 43.11 (95%CI, 16.43-113.12) with sensitivity of 0.91 (95%CI, 0.81-0.96) and specificity of 0.86 (95%CI, 0.78-0.92).
*Conclusions: Urine and serum/plasma NGAL are valuable biomarkers for early identification of DGF in kidney transplantation. Moreover, the blood NGAL was superior to urine NGAL in early prediction of DGF.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li Y, Li Y, Yan L, Wang H, Wu X, Tang J, Wang L, Shi Y. Comparison between Urine and Blood NGAL for Early Prediction of Delayed Graft Function in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/comparison-between-urine-and-blood-ngal-for-early-prediction-of-delayed-graft-function-in-adult-kidney-transplant-recipients-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress