Combined Liver and Delayed Kidney Transplantation (CLKT) Enables Similar Patient Survival as Liver Transplantation Alone (LTA): Propensity Score-Based Comparison
1Transplant Division - Department of Surgery - Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN, 2Gastroenterology, Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A287
Keywords: Kidney/liver transplantation, Liver transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Liver - Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: We previously showed the positive impact of delayed KT in CLKT on patient survival compared to simultaneous KT. It is well known from the literature that patient survival in CLKT is much lower compared to LTA. The purpose of this study is to identify whether CLKT using delayed approach KT (Indiana Approach) offers similar patient survival as LTA.
*Methods: 83 CLKT were performed using Indiana Approach between 2007-2017 (Group 1). The rationale behind performing delayed KT was to offer less hostile environment with hemodynamically more stable LT recipient at the time of KT. All kidneys underwent continuous hypothermic pulsatile perfusion until KT, which was performed at a later time as a second operation with mean CIT of 53±14h (range 20-83h). Propensity score matching with replacement of the control group was performed from the pool of ~1300 LTAs (performed at the same period) (Group 2, n=265). >25 variables were compared using univariate and multivariate analysis. Kaplan-Meier patient survival curves were calculated up-to 7-years.
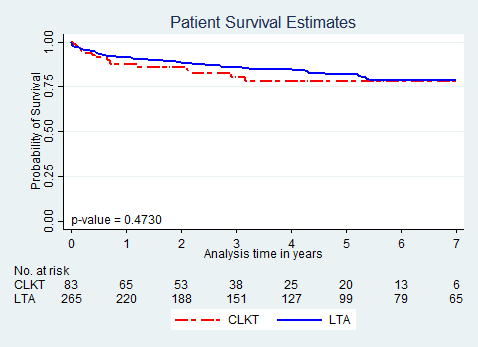
*Results: Recipient and donor characteristics were comparable between Groups 1 and 2, except MELD and D-MELD scores, which were significantly higher in Group 1 (p=0.01), as expected. Liver CIT was shorter in Group 1 (5.7h vs. 6.1h, p=0.035). Liver WIT was also shorter in Group 1 (19 vs. 21min, p=0.007). Median ICU stays were comparable (5 days), whereas median hospital stay was longer in Group 1 (34 vs. 18days, p=0.0003). Kaplan-Meier patient survival curves were similar in both CLKT with Indiana Approach (Group 1) and LTA (Group 2) up to 7-years post-transplant (~77%) (Figure1).
*Conclusions: We here show that the CLKT, if performed using the Indiana Approach despite the sicker patient population, could offer similar patient survival as LTA up to 7 years.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ekser B, Kubal CA, Mangus RS, Mihaylov P, Fridell JA, Timsina LR, Lacerda M, Ghabril M, Powelson JA, Goggins WC. Combined Liver and Delayed Kidney Transplantation (CLKT) Enables Similar Patient Survival as Liver Transplantation Alone (LTA): Propensity Score-Based Comparison [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/combined-liver-and-delayed-kidney-transplantation-clkt-enables-similar-patient-survival-as-liver-transplantation-alone-lta-propensity-score-based-comparison/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress