CMV Specific T Cell Immune Response in Hepatitis C Negative Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving Transplant from Hepatitis C Viremic Donors and Hepatitis C Negative Donors
M. Z. Molnar1, M. Tsujita2, M. Talwar2, V. Balaraman2, A. Bhalla2, J. D. Eason2, S. S. Nouer2, K. Sumida2, A. Remport3, I. E. Hall1, R. Griffin2, G. George Rofaiel4, A. Azhar5
1Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Nephrology & Hypertension, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, 2University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN, 3Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary, 4Department of Surgery, Division of Transplantation and Advanced Hepatobiliary Surgery, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, 5Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, Richmond, VA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 55
Keywords: Cytomeglovirus, Hepatitis C
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 25 - Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Name: Cytomegalovirus and other Herpes Viruses
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:20pm-4:30pm
Presentation Time: 4:20pm-4:30pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom B
*Purpose: Kidney transplants (KT) from hepatitis C (HCV) viremic donors to HCV negative recipients has shown promising short-term and long-term outcomes. However, high incidence of cytomegalovirus (CMV) viremia has been shown in the HCV negative recipients receiving kidneys from HCV viremic donors.
*Methods: We performed a prospective cohort study of 52 HCV negative KT recipients including 41 receiving transplants from HCV negative donors and 11 from HCV viremic donors. The primary outcome was the development of positive CMV specific T cell immune response post-transplant, measured by intracellular flow cytometry assay. The association between donor HCV status and CMV specific T cell immune response was analyzed by Cox proportional hazard models.
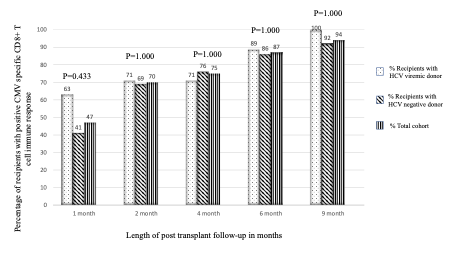
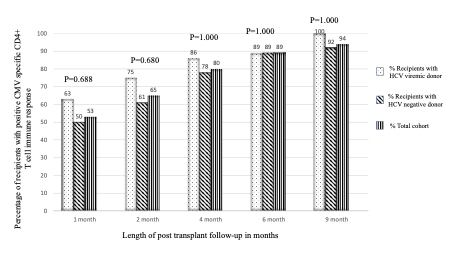
*Results: Mean recipient age was 48±13 years, 73% were male and 82% were African American. Positive CMV specific CD4+ and CD8+T cell immune response was found in 53% and 47% of the cohort at 1 month, 65% and 70% at 2 months, 80% and 75% at 4 months, 89% and 87% at 6 months, and 94% and 94% at 9 months post-transplant, respectively. There was no significant difference in the incidence of positive CMV specific T cell immune response between recipients of transplants from HCV negative donors compared to HCV viremic donors in unadjusted (for CD8+: HR=1.169, 95%CI: 0.521-2.623; for CD4+: HR=1.208, 95%CI: 0.543-2.689) and adjusted (for CD8+: HR=1.072, 95%CI: 0.458-2.507; for CD4+: HR=1.210, 95%CI: 0.526-2.784) Cox regression analyses.
*Conclusions: HCV viremia in donors was not associated with impaired development of positive CD4+ and CD8+T cell immunity against CMV in recipients in this cohort.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molnar MZ, Tsujita M, Talwar M, Balaraman V, Bhalla A, Eason JD, Nouer SS, Sumida K, Remport A, Hall IE, Griffin R, Rofaiel GGeorge, Azhar A. CMV Specific T Cell Immune Response in Hepatitis C Negative Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving Transplant from Hepatitis C Viremic Donors and Hepatitis C Negative Donors [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cmv-specific-t-cell-immune-response-in-hepatitis-c-negative-kidney-transplant-recipients-receiving-transplant-from-hepatitis-c-viremic-donors-and-hepatitis-c-negative-donors/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress