Clinical Response to Salvage Bortezomib Therapy for Antibody Mediated Rejection and Mixed Acute Rejection in a High Immunologic Risk Renal Transplant Population
University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A107
Keywords: Antibodies, High-risk, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Proteasome inhibitor (PI) containing regimens treat antibody mediated rejection (AMR) and mixed acute rejection (MAR) due to elimination of donor specific antibody (DSA). Commonly, this agent is used in the setting of salvage therapy after traditional treatments (i.e. plasmapheresis and IVIG) fail to achieve desired clinical responses. The long-term impact of this strategy is unknown. The purpose of this evaluation was to assess salvage PI-based therapy in high risk patients with AMR or MAR.
Methods: High immunologic risk renal transplant (RTx) recipients experiencing AMR or MAR from 1/2008–09/2017 treated with a salvage PI-based regimen were assessed. Salvage therapy was introduced when primary therapy (plasmapheresis/IVIG) was deemed ineffective by transplant team. The Banff Criteria was utilized to diagnose AMR and ACR. MAR was defined as having both ACR and AMR concurrently. Bortezomib 1.3mg/m2 was dosed on days 1, 4, 8, and 11 with the option of additional doses. The primary outcome was incidence of patients achieving a >25% reduction in serum creatinine (SCr) 30 days post-bortezomib initiation.
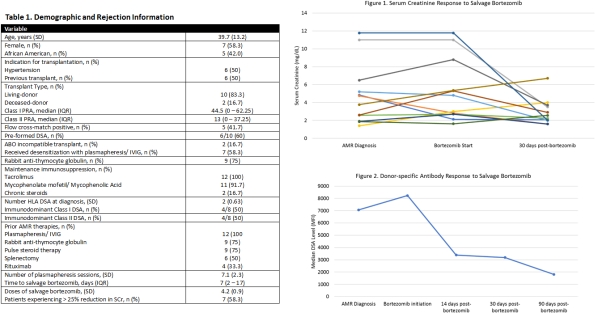
Results: A total of 12 RTx patients were analyzed and followed for a median of 474 (IQR 193 – 1723) days post-salvage bortezomib treatment. A majority of patients were female (58.3%) and African American (42%) with living-donor RTxs (83.3%). Pre-formed DSA occurred in 60% of recipients and 50% had positive flow cross-matches at the time of RTx. Table 1 details cohort demographics. 58.3% of patients experienced a >25% reduction in SCr, and 66.7% of patients experienced a >50% reduction in immunodominant DSA. Figure 1 and 2 detail SCr and DSA trends. Four patients (33.3%) experienced graft loss 471 (IQR 227 – 1285) days post-salvage bortezomib therapy.
Conclusions: After introduction to a PI-based regimen, there was a reduction in both SCr and DSA in a majority of patients. Salvage bortezomib is a viable therapeutic option in refractory AMR and MAR in a high immunologic risk population as a part of a multi-modal treatment regimen. Future studies are needed to determine its individual role within humoral treatment.
CITATION INFORMATION: Lichvar A., Benken J., Benedetti E. Clinical Response to Salvage Bortezomib Therapy for Antibody Mediated Rejection and Mixed Acute Rejection in a High Immunologic Risk Renal Transplant Population Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lichvar A, Benken J, Benedetti E. Clinical Response to Salvage Bortezomib Therapy for Antibody Mediated Rejection and Mixed Acute Rejection in a High Immunologic Risk Renal Transplant Population [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/clinical-response-to-salvage-bortezomib-therapy-for-antibody-mediated-rejection-and-mixed-acute-rejection-in-a-high-immunologic-risk-renal-transplant-population/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress