Clinical Outcome of Pancreas Transplantation in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus.
1Nursing, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
2Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C224
Keywords: Age factors, Pancreas transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Pancreas and Islet (Auto and Allo) Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Introduction: The age of the recipient is an important factor affecting the outcome of pancreas transplantation. In elderly people, it was a taboo due to the accompanying complications and increased mortality, but the number of transplant has been increasing as accumulating experience and developing of immunosuppressive agents. We aimed to analyze the clinical outcome of pancreas transplantation in elderly patients with diabetes.
Methods: A total of 345 recipients underwent transplantation between July 1992 and Nov 2016 in single center. 18 recipients (elderly group) were 55 years or older, whereas 327 patients (younger group) were younger than 55 years old. Anti-thymocyte globulin was used as induction, tacrolimus and mycophenolate was used as maintenance therapy with steroid early withdrawal protocols.
Results: Median follow-up after transplantation was 40 months (1~282 months). Both groups of recipients had similar donor characteristics. Mean age was 57.4 ± 3.1 years old in elderly group and 35.2 ± 9.2 years old in younger group. In elderly group, type 2 diabetes was more frequent (73.3% vs. 27.6%), and recipient body mass index was higher (22.5±2.3 vs. 20.9±2.6) comparing with younger group. Surgical complication and infectious complications were similar in both groups but rejection was less in elderly group (0 % vs. 10.3%). In elderly group, there were no rejection or death censored graft failure after transplantation. However, one patient died from traumatic cerebral hemorrhage followed by pneumonia. In elderly group, the patient survival rate and death censored graft survival rate was not inferior than younger group; the 1, 5, and 10 year pancreas graft and patient survival rates were 100%, 83.3%, 83.3% respectively. 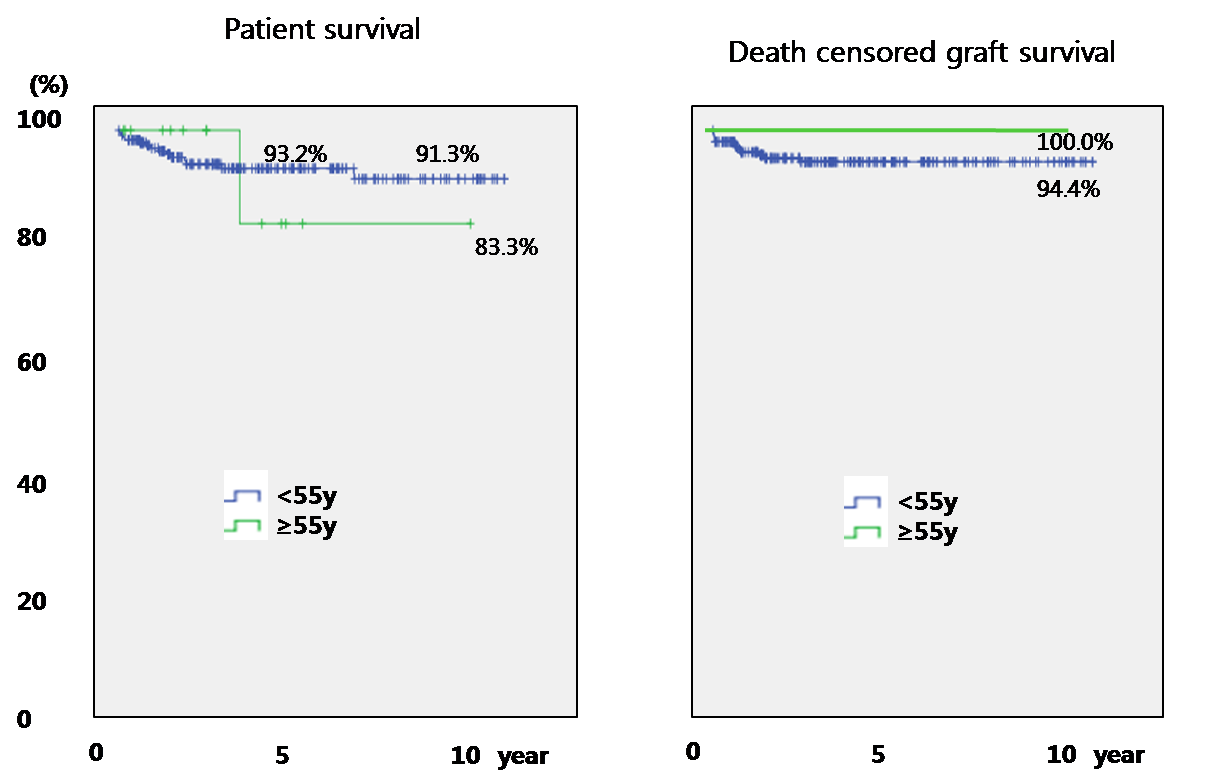 Discussion: Pancreas transplantation can be performed safely in recipients older than 55 years age. Chronological age alone should not be used to determine transplant candidacy. Therefore, it is necessary to select the appropriate recipient through pre-examination before transplantation and to observe continuously after transplantation.
Discussion: Pancreas transplantation can be performed safely in recipients older than 55 years age. Chronological age alone should not be used to determine transplant candidacy. Therefore, it is necessary to select the appropriate recipient through pre-examination before transplantation and to observe continuously after transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Jung J, Choi J, Shin S, Kim Y, Han D. Clinical Outcome of Pancreas Transplantation in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jung J, Choi J, Shin S, Kim Y, Han D. Clinical Outcome of Pancreas Transplantation in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/clinical-outcome-of-pancreas-transplantation-in-elderly-patients-with-diabetes-mellitus/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
