Circulating Tissue Specific Exosomes Enable Noninvasive Diagnosis of Acute Cellular Rejection in Clinical Heart Transplantation
1Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 2Surgery, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, 3Surgery, Yale University, New Haven, CT, 4University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-353
Keywords: Antibodies, Autoimmunity, CD4, Heart transplant patients
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Acute Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
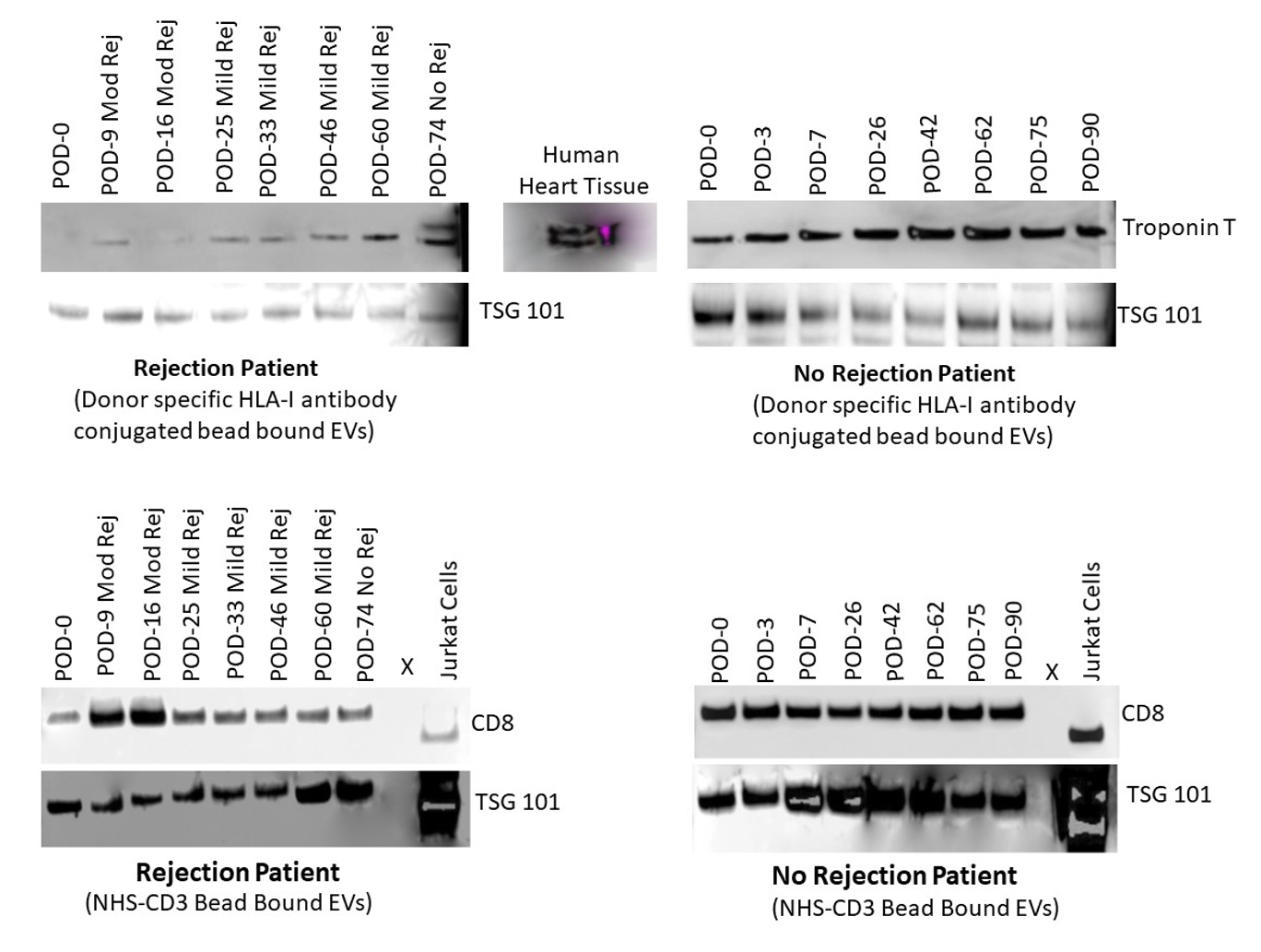
*Purpose: There is a critical need for development of noninvasive biomarkers for allograft surveillance and diagnosis of rejection in heart transplant patients, as endomyocardial biopsy (EMB). In animal models of transplant acute cellular rejection (ACR), we previously demonstrated that tissue specific exosome profiling of circulating donor and recipient T cell specific exosomes enabled noninvasive, time sensitive diagnosis of acute cellular rejection before histologic signs of transplant tissue injury. We investigated the translational potential of this novel, noninvasive platform in the setting of clinical heart transplantation.
*Methods: In 10 subjects undergoing heart transplantation, plasma samples were collected over a follow-up of >100 days per patient, along with collection of clinical and EMB data. 5 subjects had grade 2R ACR, and 5 had no ACR episodes. Plasma exosomes were isolated by column chromatography and ultracentrifugation. Transplant heart exosomes were characterized using anti-donor human leukocyte antigen (HLA) I antibody beads, and T cell exosomes were profiled using anti-CD3 antibody beads.
*Results: Donor heart specific exosome analysis showed time specific decrease in signal for cardiac troponin protein and mRNA in the 5 subjects with EMB proven grade 2R ACR, with subsequent increase upon treatment. In the 5 matched subjects without ACR, donor heart exosome cargo analysis showed stable troponin signal over follow-up of >100 days. Circulating T cell exosome analysis in 5 subjects with ACR showed specific upregulation of CD4, CD8 and T cell receptor signal by Western blot and RT-PCR at time points of grade 2R rejection, with signals returning to baseline upon treatment of ACR. Cargo analysis showed ACR specific upregulation of alloreactive markers such as IL-2 and IFNγ in T cell exosomes. In the matched controls, steady state levels of T cell markers were seen.
*Conclusions: Circulating tissue specific exosome characterization enables noninvasive diagnosis of ACR and allograft surveillance in clinical heart transplantation. This biomarker may also provide a noninvasive window into the effect of ACR treatment, which may reduce the need for post-treatment EMB. Further investigation of this novel platform will help understand its translational potential in transplantation diagnostics.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Korutla L, Hu R, Romano C, Molina M, Sciortino C, Mullan C, McGargle R, Kagawa H, Kilic A, Naji A, Vallabhajosyula P. Circulating Tissue Specific Exosomes Enable Noninvasive Diagnosis of Acute Cellular Rejection in Clinical Heart Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/circulating-tissue-specific-exosomes-enable-noninvasive-diagnosis-of-acute-cellular-rejection-in-clinical-heart-transplantation/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress