Characterization of Chronic Renal Allograft Dysfunction at Single Cell Resolution
1Surgery, James D Eason Transplant Institute, UTHSC, Memphis, TN, 2Surgery, James D Eason Transplant Institute, Memphis, TN, 3Institute for Genome Sciences, School of Medicine, University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, 4Nephrology, James D Eason Transplant Institute, Memphis, TN, 5Surgery, Program in Transplantation - University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, 6Surgery, Division of Surgical Science - University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1065
Keywords: Graft function, Kidney, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Complications: Immune Mediated Late Graft Failure
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Complications: Immune Mediated Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Chronic allograft dysfunction (CAD) is one of the major complications after kidney transplantation. Hereby, we aim to assess the molecular and cellular mechanism of Chronic Allograft Dysfunction at a single cell resolution to identify potential interventions. Single-cell genomics has played unprecedented role for diagnosis and finding novel treatment methods.
*Methods: We performed single nuclei sequencing from 8 kidney allograft biopsies (3 normal allografts (normal histology and normal creatinine at 24 months post-transplant), 2 Chronic Allograft Dysfunction (CAD) with inflammation, and 3 CAD without inflammation) using droplet based 10X Genomics Chromium platform. Data is analyzed on “Cell-Ranger” pipeline and “Seurat” package was used for cell clustering and cell identification. CAD classifications were done using Banff criteria.
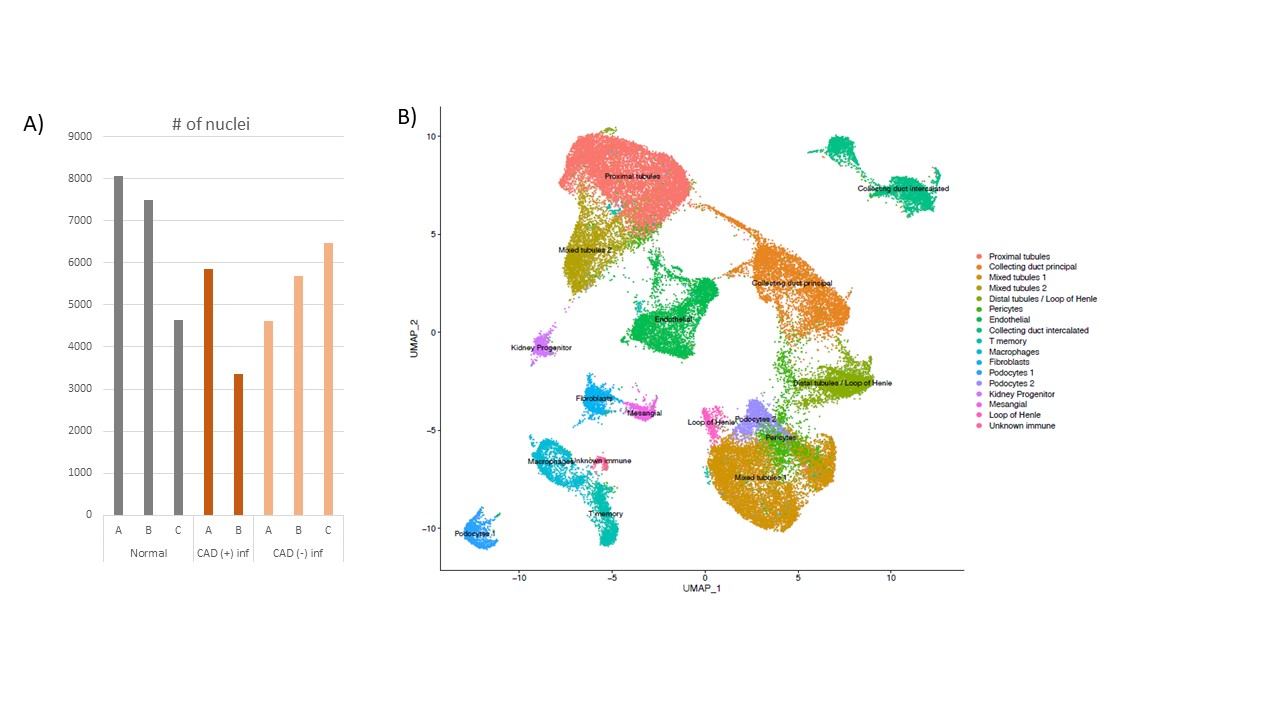
*Results: We obtained >40,000 cells in our analysis with an average of 1400 genes per cell (Fig 1a). We identified 17 different clusters in aggregated analysis. Our single-nuclei RNA-seq allow us to identify rare pericytes and kidney progenitor cells in addition to the main cell types of kidney such as tubular cells and endothelial cells (Fig 1 A-B). Interestingly, we identified significant number podocytes which cannot be detected by ordinary single-cell RNA sequencing. ARL17B and FKBP5 genes are found to be differentially expressed in several cell types including tubular cells, podocytes when CAD(- inflammation) compared to CAD(+ inflammation).
*Conclusions: Our results identified pericytes and kidney progenitor cells (in addition to the main cell types of kidney such as tubular cells and endothelial cells) in patients with chronic allograft dysfunction
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kuscu C, Kuscu C, Shetty A, Talwar M, Eason J, Maluf DG, Mas V. Characterization of Chronic Renal Allograft Dysfunction at Single Cell Resolution [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/characterization-of-chronic-renal-allograft-dysfunction-at-single-cell-resolution/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress