Changes in Health-Related Quality of Life During the First Year in Lung Transplantation Recipients
Lung Transplant Center, Wuxi People’s Hospital, Wuxi, China
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 191
Keywords: Lung transplantation, Quality of life
Session Information
Session Name: Living in the Real World: Decision Making and Outcomes After Lung Transplant
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: This longitudinal study was conducted to recognize the tracks of HRQOL during the first year after transplantation and the main factors associated with HRQOL of lung transplantation recipients.
*Methods: A total of 118 patients were investigated before and 3, 6, 9, and 12 months post-transplantation. The Medical Outcomes SF-36 (Chinese version) was used to measure the HRQOL. The recipients’ demographic characteristics and clinical data were evaluated to determine the relative contributions to HRQOL outcomes.
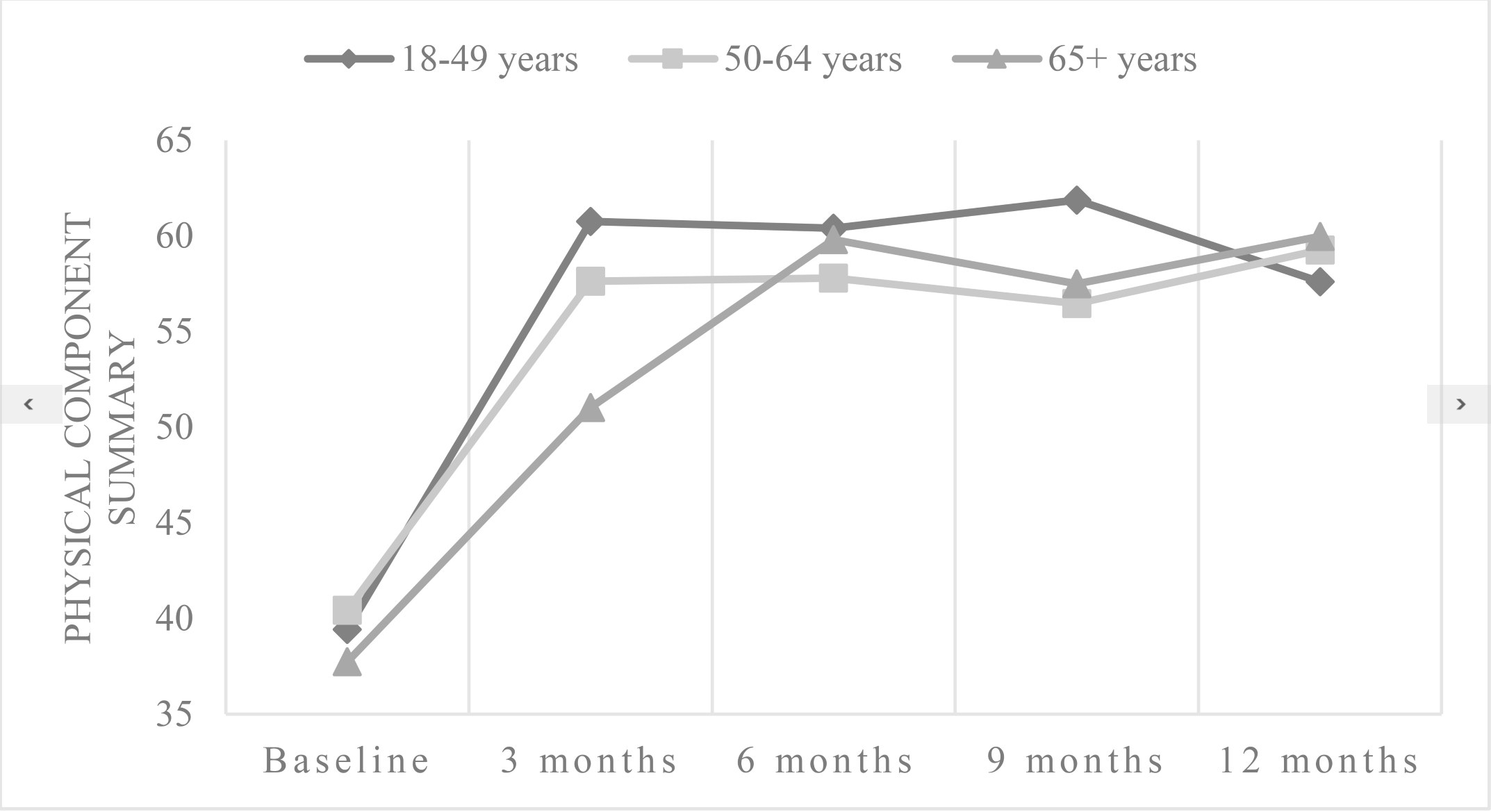
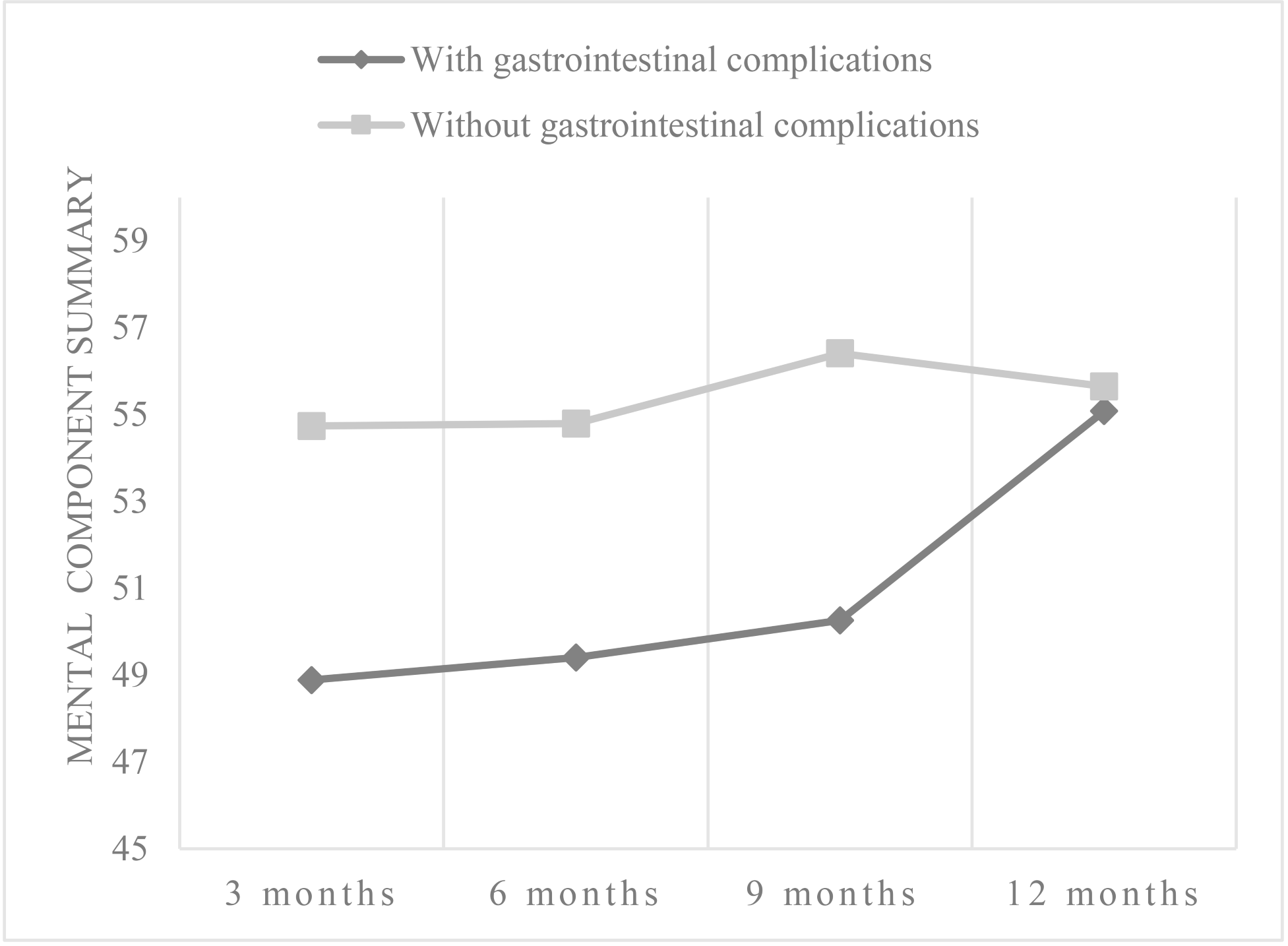
*Results: Recipients reported a mean physical component summary of 39.62 ± 6.57, 57.90 ± 9.99, 59.15 ± 8.73, 58.79 ± 8.52, and 58.72 ± 8.99 before transplantation and at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after transplantation (F = 64.960, P < 0.001). By 3 months after transplant, patients experienced significant improvement in physical component summary (MD = 18.27, SE = 1.52, P < 0.001), but between 3 and 12 months, no significant improvement was observed (MD = 0.82, SE = 1.77, P = 0.645). Patients reported a continuous rise with means of 44.63 ± 5.35, 51.13 ± 10.25, 51.92 ± 9.72, 53.23 ± 10.34, 55.40 ± 8.83 for the mental component summary before transplantation and at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after transplant (F = 13.059, P < 0.001). By 3 months after transplant, patients experienced significant improvement in mental component summary (MD = 6.50, SE = 1.50, P < 0.001). Between 3 and 12 months, a continuous significant improvement was observed (MD = 4.27, SE = 1.92, P = 0.030). The generalized estimated equation showed that age (β = -2.187, P = 0.002), BODE index (β = -5.381, P = 0.002), and gastrointestinal complications (β = 3.937, P = 0.007) were associated with HRQOL.
*Conclusions: The HRQOL of lung transplant patients improved significantly at 3 months after transplantation, but between 3 and 12 months after transplantation, the changes were not obvious. Health practitioners should pay more attention to elderly patients, patients with high BODE indexes and patients with gastrointestinal complications.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhou H, Chen J. Changes in Health-Related Quality of Life During the First Year in Lung Transplantation Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/changes-in-health-related-quality-of-life-during-the-first-year-in-lung-transplantation-recipients/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress