CD4+IFN-γ+IL-10+ Regulatory Type 1 Cells Facilitate Prolongation of Graft Survival in Old Recipient Mice Treated with Rapamycin.
Transplant Surgery Research Laboratory and Division of Transplant Surgery, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C282
Keywords: Age factors, Immunosuppression, Rapamycin
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Tolerance/Immune Regulation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Although the elderly represent a rapidly growing population among transplant recipients, age-specific aspects have not been considered sufficiently in clinical trials. Moreover, age-specific effects of immunosuppressive therapies remain poorly understood.
Here, we assessed the impact of Rapamycin on alloimmune responses in aging using a fully MHC-mismatched (DBA/2 on B57BL/6) murine transplantation model.
Old untreated recipients displayed a prolonged skin graft survival compared to their young counterparts (median survival time 9 vs. 7 days, p=0.006). Rapamycin led to a marked and significant prolongation of graft survival specifically in old but not young recipients (19 days vs. 12 days, p=0.004).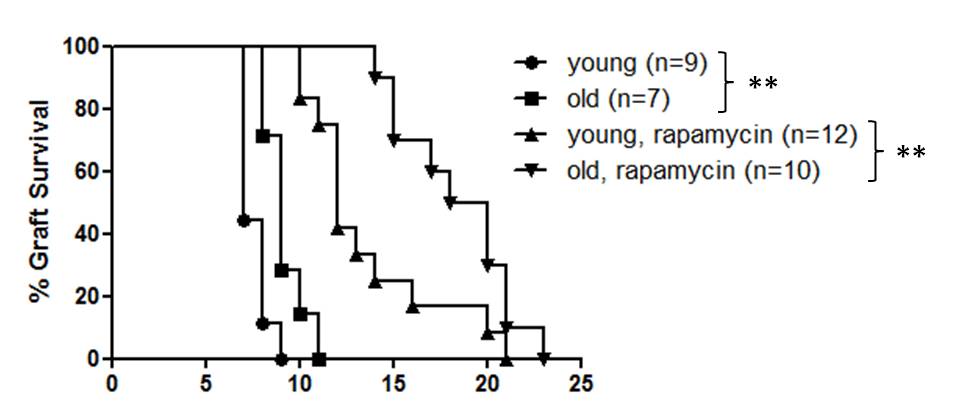 This age-specific effect was not linked to changes in frequencies or subset composition of either CD8+ or CD4+ T cells. Moreover, anti-proliferative effects of Rapamycin on CD8+ and CD4+ T cells as assessed by in-vivo BrdU-incorporation were comparable and age-independent. In contrast, the systemic production of IL-10 was markedly elevated in old recipients treated with Rapamycin. This shift in cytokine balance was linked to an emergence of IFN-g/IL-10 double-positive regulatory type 1 cells during Th1-differentiation of old T helper cells in presence of Rapamycin, a process that was independent of regulatory T cells.
This age-specific effect was not linked to changes in frequencies or subset composition of either CD8+ or CD4+ T cells. Moreover, anti-proliferative effects of Rapamycin on CD8+ and CD4+ T cells as assessed by in-vivo BrdU-incorporation were comparable and age-independent. In contrast, the systemic production of IL-10 was markedly elevated in old recipients treated with Rapamycin. This shift in cytokine balance was linked to an emergence of IFN-g/IL-10 double-positive regulatory type 1 cells during Th1-differentiation of old T helper cells in presence of Rapamycin, a process that was independent of regulatory T cells.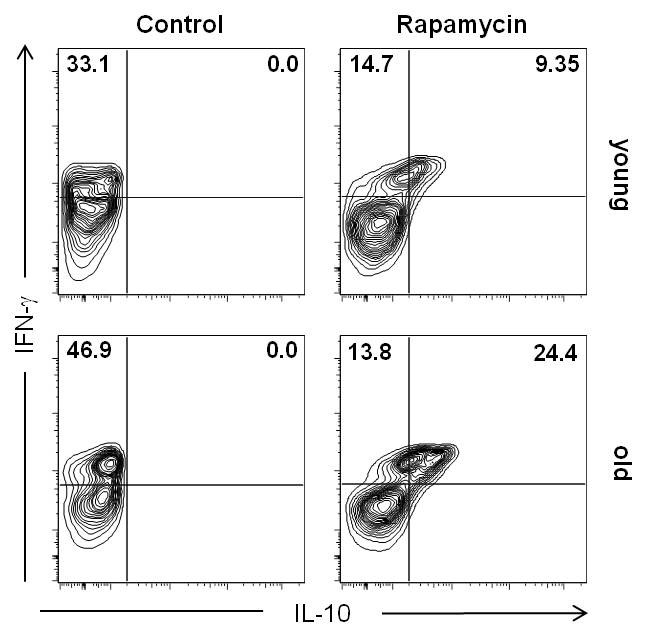 These results demonstrate a novel pathway of age-dependent alloimmunity for an immunosuppressive drug currently in widespread clinical use and with relevance for an age-specific immunosuppression.
These results demonstrate a novel pathway of age-dependent alloimmunity for an immunosuppressive drug currently in widespread clinical use and with relevance for an age-specific immunosuppression.
CITATION INFORMATION: Heinbokel T, Quante M, Minami K, Elkhal A, Tullius S. CD4+IFN-γ+IL-10+ Regulatory Type 1 Cells Facilitate Prolongation of Graft Survival in Old Recipient Mice Treated with Rapamycin. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Heinbokel T, Quante M, Minami K, Elkhal A, Tullius S. CD4+IFN-γ+IL-10+ Regulatory Type 1 Cells Facilitate Prolongation of Graft Survival in Old Recipient Mice Treated with Rapamycin. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cd4ifn-il-10-regulatory-type-1-cells-facilitate-prolongation-of-graft-survival-in-old-recipient-mice-treated-with-rapamycin/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
