CD19+ Cell Behavior in the 12 Months Following a Single Dose of Rituximab in Patients with Humoral Rejection: Clinical and Histological Outcomes
Nephrology, INCMNSZ, Mexico City, Mexico
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 115
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Lymphocytes
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Location: Ballroom B
*Purpose: Treatment of antibody mediated rejection (ABMR) commonly includes rituximab, but the dose needed is not yet well defined. It has been suggested that a single dose of rituximab is enough to deplete CD19+ cells. Aim: to analyze CD19+ cell behavior during the 12 months following a 500 mg dose of rituximab and its correlation with clinical and histological outcomes.
*Methods: This is a prospective cohort study of 122 kidney transplant recipients with biopsy proven ABMR who received a single dose of rituximab 500 mg as part of standard ABMR treatment between 2012 and 2018. Peripheral CD19+ cells were measured at baseline, 15, 30, 90, 180, 270, and 360 days after rituximab infusion, and correlated this data with clinical and histological outcomes.
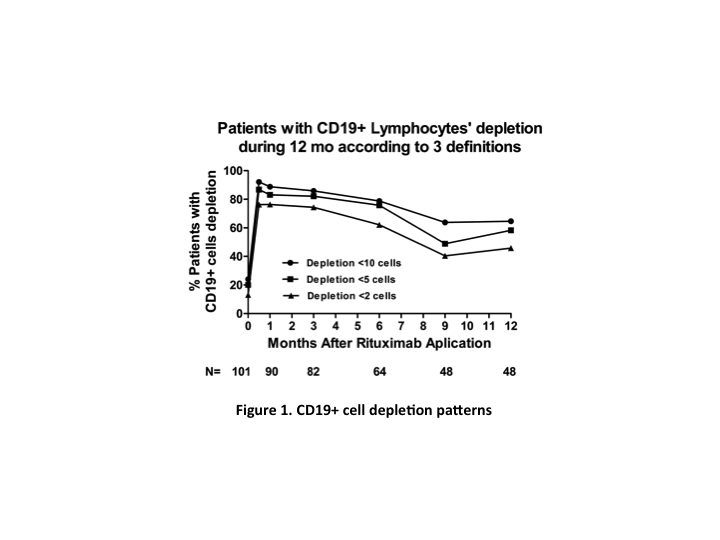
*Results: 122 patients were included. Mean age was 27 y, 56.6% were female, in 93.4% of patients this was their first transplant, 71% were from living donors, and the median time to rejection was 6 y post-transplant. Treatment included plasmapheresis and IVIG in 75% of patients, 21% also received Bortezomib. All patients received 500 mg of rituximab, except for 7.3% of patients that received 375 mg/m2 BSA. Patients were followed for a median of 21 mo (0.1-83). Median allograft survival after ABMR was 5.5 years. CD19+ cell depletion patterns are shown in Figure 1. CD19+ cell depletion (<10 cells) at 1 month was associated with less IFTA at follow-up biopsy and improvement of proteinuria at last follow-up. Early CD19+ cell repopulation was associated with higher graft loss and dead. Persistent CD19+ cell depletion (<10 cells) at 12mo was associated with better graft and patient survival.
*Conclusions: A single dose of Rituximab achieved CD19+ cell depletion in more than 80% of patients, which lasted at least 6 months. CD19+ cell depletion is associated with improvement of proteinuria and less IFTA; and the persistence of CD19+ cell depletion at 12 months improves graft and patient survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marino L, Martínez-Juárez IA, Marino-Sánchez JR, Santander-Velez JI, Zamora F, Juarez H, Vazquez R, Llorente L, Lima G, Cohen-Bucay A, Morales-Buenrostro LE. CD19+ Cell Behavior in the 12 Months Following a Single Dose of Rituximab in Patients with Humoral Rejection: Clinical and Histological Outcomes [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cd19-cell-behavior-in-the-12-months-following-a-single-dose-of-rituximab-in-patients-with-humoral-rejection-clinical-and-histological-outcomes/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress