CCR2 Antagonism Blocks Microbiota Pro-Inflammatory Effects on Lymph Node Architecture
1University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, 2University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1233
Keywords: Graft survival, Mice, Rejection
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 08 - Innate Immunity; Chemokines, Cytokines, Complement
Session Information
Session Name: Innate Immunity; Chemokines, Cytokines, Complement
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Fecal microbiota transfer (FMT) of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (Desulfo) triggers a pro-inflammatory immune state, causing decreased laminin α4:α5 ratios in the lymph node (LN), increased effector T cells, decreased Tregs, and increased transplant allograft inflammation and fibrosis. In contrast, Bifidobacterium pseudolongum (Bifido) is anti-inflammatory, causing increased laminin α4:α5 ratios, increased Treg, decreased T effectors, and decreased graft inflammation. CCR2-mediated myeloid cell homing from gut to LN may contribute to the transmission of microbiota-specific effects on the immune system. We investigated whether inhibition of CCR2 would alter or eliminate the immunomodulatory effects of FMT.
*Methods: C57BL/6 mice were treated with antibiotics followed by FMT with either Bifido, Desulfo, or PBS followed by daily CCR2 antagonist (RS504393) for 7 days. LNs were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for laminin expression and by flow cytometry for immune cell distribution. Mice also received BALB/c cardiac allografts, and tissues were harvested at the time of rejection.
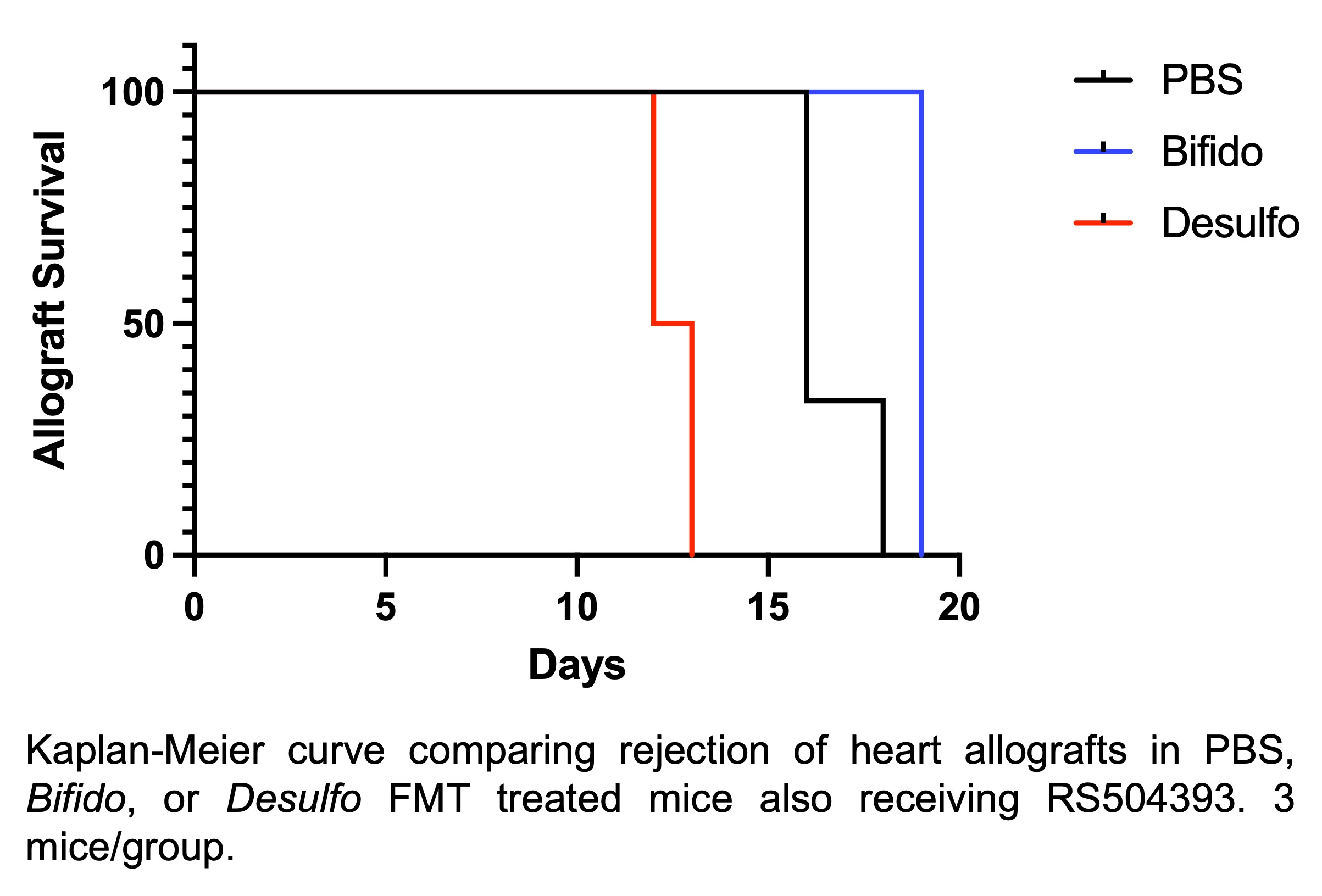
*Results: RS504393 abrogated the pro-inflammatory effect of Desulfo on LN architecture, so that the laminin α4:α5 ratio increased. Bifido treated mice receiving RS504393 had fewer CD11c+ dendritic cells in mesenteric LN (mLN) compared to Desulfo or control (p<0.02). Desulfo treated mice still rejected allografts earlier than PBS and Bifido treated mice (median survival times 12.5, 16, and 19 days, respectively, p<0.004) (Figure).
*Conclusions: These findings implicate CCR2 as mediating homing of pro-inflammatory myeloid cells to LN and causing architectural changes after Desulfo FMT, as well as for tolerogenic myeloid cell homing from gut to mLN after Bifido FMT. However, Bifido and Desulfo remain capable of exerting additional immunomodulatory effects, even in the absence of CCR2 function, since differences in allograft survival remained. These observations suggest multiple mechanisms of immune modulation induced by microbiota.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gavzy SJ, Lakhan R, Iyyathurai J, Saxena V, Lee ZL, Ma B, Mongodin E, Bromberg JS. CCR2 Antagonism Blocks Microbiota Pro-Inflammatory Effects on Lymph Node Architecture [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ccr2-antagonism-blocks-microbiota-pro-inflammatory-effects-on-lymph-node-architecture/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress