Cardiovascular Risk and Subclinical Vascular Damage in Patients after Pediatric Liver Transplantation
1Pediatric Kidney, Liver and Metabolic Diseases, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
2Nephrology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B288
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Pediatric, Post-transplant hypertension, Vascular disease
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Liver: Pediatrics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Cardiovascular (CV) disease causes a high level of morbidity and mortality in adults undergoing solid organ transplantation. Pediatric liver transplant (Li-Tx) recipients were reported to suffer from arterial hypertension (HTN) and display metabolic syndrome, but no data is available on the prevalence of arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis as indicators of subclinical CV damage.
A total of 95 children after Li-Tx (age 11.8±3.7 yrs; 6.9±4.2 yrs after Li-Tx) were analyzed for CV risk factors including hypertension, chronic kidney disease (CKD), dyslipidemia, diabetes, microinflammation (measured by high-sensitive C-reactive protein), and anemia. Furthermore, parameters for subclinical CV damage (pulse wave velocity, PWV, for arterial stiffness; carotid intima media thickness, IMT, for atherosclerosis) were evaluated. 74 patients already passed 1yr. and 43 patients passed 2yr. follow-up examinations (F/U), respectively.
A remarkable number of patients displayed CV risk factors at first examination. About a third of them suffered from dyslipidemia (Hypertriglyceridemia in 31%, low HDL in 26%) or microinflammation (33%); a fifth from either HTN (22%) or reduced renal function (20%). Anemia was present in 15%. Only one patient had diabetes.
Increased PWV or IMT values were found in 19% and 58% of the pediatric Li-Tx recipients. Increased systolic blood pressure was significantly associated with higher BMI (r=0.237, p=0.031). Triglyceride values correlated with lower glomerular filtration rate (r=-0.514, p=0.003). For those patients, in which follow-up data were available, no significant changes in markers of subclinical CV damage were detectable over time.
Our results show a high prevalence of CV risk factors and subclinical CV damage in liver transplanted children. Our first F/U analyses also indicate that subclinical CV damage remains stable. 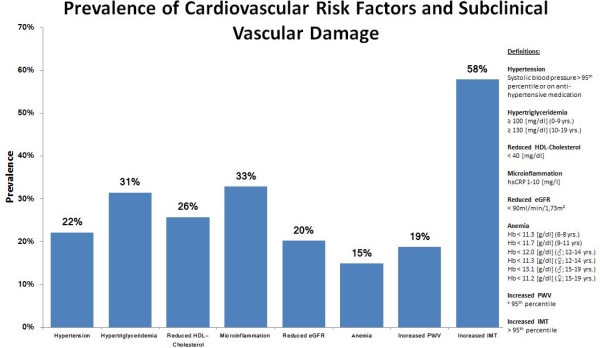
CITATION INFORMATION: Wilke H., Memaran N., Goldschmidt I., Borchert-Mörlins B., von Wick A., Bauer E., Blöte R., Schmidt B., Melk A. Cardiovascular Risk and Subclinical Vascular Damage in Patients after Pediatric Liver Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wilke H, Memaran N, Goldschmidt I, Borchert-Mörlins B, Wick Avon, Bauer E, Blöte R, Schmidt B, Melk A. Cardiovascular Risk and Subclinical Vascular Damage in Patients after Pediatric Liver Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cardiovascular-risk-and-subclinical-vascular-damage-in-patients-after-pediatric-liver-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
