Can Immunosuppression Maintenance after Renal Allograft Failure Prevent Further Sensitization?
University of Florida, Gainesville.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 320
Keywords: Graft failure, Kidney transplantation, Panel reactive antibodies, Retransplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Complications: Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Location: Room 6E
After renal graft failure, retransplantation(ReTx) becomes more difficult due to sensitization to alloantigens. In 2013, our center opened a specialty clinic to maintain immunosuppression(IS) after graft failure in an attempt to minimize sensitization in ReTx candidates. We present our 1-year post graft failure cohort data.
Methods: We retrospectively examined patients at a single center with renal graft failure 7/2011-10/2016 who were referred to our specialty clinic. Maintenance IS usually consisted of FK506(trough 3-6ng/mL), mycophenolate 250-500mg BID, prednisone 5mg/day. Outcomes were CPRA at graft failure and 1-year later. Also, we compared our cohort with a historical cohort of relisted patients prior to the advent of our specialty clinic.
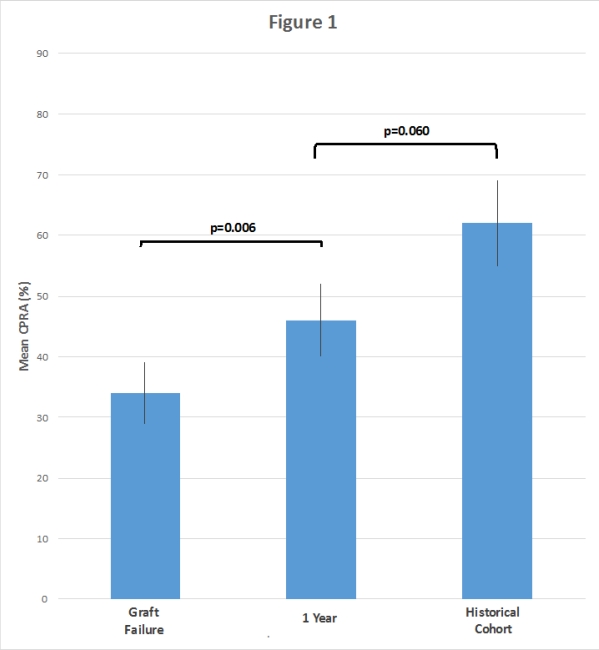
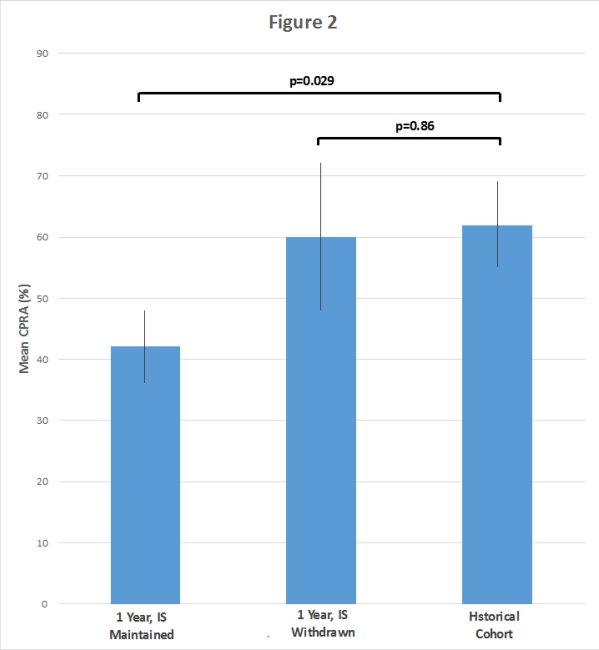
Results: Our cohort had 56 ReTx candidates. 5 patients were excluded due to noncompliance/lost to followup. 11 patients had IS withdrawn<365 days after graft failure due to complications(median 165 days, IQR 118-211). At 1 year, mean CPRA 46% was significantly higher than at graft failure, but not significantly lower than the historical cohort(Fig 1). However, a subgroup analysis of patients on IS ≥365 days after graft failure had a mean CPRA 42% that was significantly lower than the historical cohort. Patients with IS <365 days had a mean CPRA 60% which was similar to the historical cohort(Fig 2). 14 patients on dual agent IS had a significant rise in mean CPRA 38% to 57%, p=0.038, which was not seen with triple IS. Post graft failure infection(n=17), blood transfusion(n=15), and graft nephrectomy(n=3) were not associated with higher CPRA.
Conclusion: In ReTx candidates, maintaining IS after renal graft failure may mitigate the risk of sensitization and may be a reasonable strategy if the waitlist time is short. 4 out of 5 patients tolerated at least 1-year of IS after graft failure.
CITATION INFORMATION: Mena-Gutierrez A., Alquadan K., Santos A., Womer K., Casey M. Can Immunosuppression Maintenance after Renal Allograft Failure Prevent Further Sensitization? Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mena-Gutierrez A, Alquadan K, Santos A, Womer K, Casey M. Can Immunosuppression Maintenance after Renal Allograft Failure Prevent Further Sensitization? [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/can-immunosuppression-maintenance-after-renal-allograft-failure-prevent-further-sensitization/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress