Can Cxcr3+Cd62l–Cd4+ T Cells Serve as Early Warning Sentinels for Subclinical Rejections after Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation (vca)?
1Surgical Oncology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY, 2Immunology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 511
Keywords: CD4, Rejection, T cell activation
Session Information
Session Name: Vascularized Composite Allograft
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: New microsurgical techniques and powerful immunosuppressive drugs have made it possible for severely injured patients to receive VCA to replace limbs, hands, or faces, vastly improving quality of life. However, rejection rates of these types of composite grafts remain high with over 80% for acute graft rejection, and there are also major hurdles to overcome chronic rejection. So, it is crucial to establish early biomarkers to detect subclinical rejection. At present, there is not a reliable non-invasive, cost-effective diagnostic tool. Graft skin biopsy is the primary method to monitor the dynamic changes of graft rejection; however, this technique is invasive and risks graft damage. Transplanted allograft rejection is associated with intense production of IFNγ. CXCR3 is a chemokine receptor which is activated by three IFNγ-inducible ligands CXCL9, 10 and11. This CXCR3 chemokine axis is a key regulator of T cell peripheralization, delivering activated T cells to sites of inflammation. CD62L on the other hand is a trafficking protein that delivers naïve T cells to lymph nodes and is lost upon activation. We hypothesize that detection of CXCR3+CD62L–CD4+ T cells in the blood can serve as a reliable diagnostic for subclinical VCA rejection
*Methods: Heterotopic hind limb transplantation mouse model was used with C57BL/6 (H-2b) as recipients and BALB/c (H-2d) mice as donors. Gross and pathologic rejection grades of transplanted grafts were analyzed along with the prevalence of CXCR3+CD62L–CD4+ T cells in the blood.
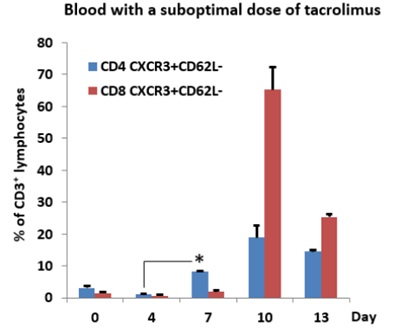
*Results: CD4+/8+ central (CD44+CD62L+) and effector (CD44+CD62L–) memory cells were significantly increased in the blood and the transplanted graft after VCA. In addition, an increase in circulating IFNγ secreting CD4 T cells was found prior to clinical changes in the graft such as skin dryness or color changes, swelling, or formation of granulation tissue. Interestingly, the composition of CXCR3+CD62L–CD4+ T cell population was greater than the CXCR3+CD62L–CD8+ T cell population in early rejection response, and was a better predictor of rejection than CD8 cells (Figure, *; p<0.05). Importantly, grafts identified by this method with subclinical rejection could be salvaged with tacrolimus.
*Conclusions: The CXCR3+CD62L–CD4+ T cell population is a strong candidate to be applied clinically to monitor VCA patients for subclinical graft rejection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim M, Fisher D, Loo J, Skitzki J, Repasky E. Can Cxcr3+Cd62l–Cd4+ T Cells Serve as Early Warning Sentinels for Subclinical Rejections after Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation (vca)? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/can-cxcr3cd62l-cd4-t-cells-serve-as-early-warning-sentinels-for-subclinical-rejections-after-vascularized-composite-allotransplantation-vca/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress