Burden of Early Antibody-Mediated Rejection (AMR): Complications, Resource Utilization and Cost-Differential in Treatment of AMR
1Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
2Division of Transplantation Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
3Division of Biostatistics, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
4Health Outcomes Research, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Cheshire, CT.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A296
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Kidney transplantation, Rejection, Resource utilization
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Late Breaking
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 2, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Early antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is common in positive crossmatch kidney transplants (+XMKTx). The current study determined the complications, resource utilization and cost associated with early, clinical AMR in +XMKTx.
Methods: We retrospectively studied 48 adult patients with +XMKTx between January 2005 and September 2007. Clinical AMR was defined as an increase in serum creatinine >0.3 mg/dl and a biopsy consistent with AMR (Banff 2013). Complications and resource utilization were assessed from day -14 to 365 days post-transplant for 21 with AMR vs 27 without AMR. Cost was estimated using a a standardized cost-accounting tool corrected for 2014 dollars (OCHEUD database–Transplantation, 2006; 82:155).
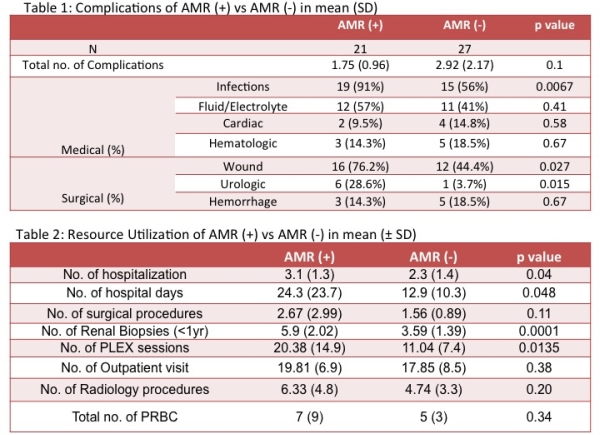
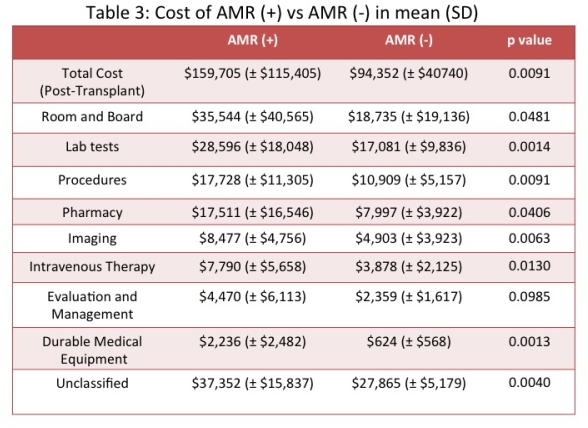
Results: There were no differences in demographics of the two groups or in pretransplant therapies. All episodes of clinical AMR except one occurred within 90 days of Tx. AMR was associated with higher rates of complications (infections, wound and urologic complications, Table 1) and resource utilization (almost double the number of hospital days (24.3 vs 12.9), PLEX sessions (20.38 vs 11.04) and surgical procedures including splenectomy and wound dehiscence, Table 2). Pre-transplant costs were similar between the two groups. However, AMR was associated with much higher post-transplant costs ($159,705 vs $94,352 no AMR; p=0.009).
Conclusion: Early clinical AMR increases complications and resource utilization in the first year after +XMKTx and increases cost by approximately $65,000.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Banga R, Schinstock C, Boscoe A, Hathcock M, Kremers W, Stegall M. Burden of Early Antibody-Mediated Rejection (AMR): Complications, Resource Utilization and Cost-Differential in Treatment of AMR [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/burden-of-early-antibody-mediated-rejection-amr-complications-resource-utilization-and-cost-differential-in-treatment-of-amr/. Accessed July 9, 2025.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
