Blood Type A2/a2b to B Renal Transplantation: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study
NYU Langone Transplant Institute, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 213
Keywords: Allocation, Histocompatibility, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Basic Science » Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics
Session Information
Session Name: B cell/Antibody and Histocompatibility
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 7, 2021
Session Time: 4:30pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:50pm-4:55pm
Presentation Time: 4:50pm-4:55pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Blood type B candidates on the deceased donor kidney waitlist have a lower transplantation rate and longer wait time than candidates of other blood types. The new national kidney allocation system (KAS), implemented in December 2014, prioritizes the allocation of kidneys from blood type A2 and A2B deceased donors to blood type B candidates to mitigate this disparity in access to transplantation. We analyzed our center’s data to determine whether blood type A2/A2B to B transplantation is clinically feasible without the need for additional immunosuppression.
*Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective cohort study to analyze the utilization and outcomes in A2/A2B to B deceased donor renal transplants. Data on adult, kidney-only recipients were extracted with custom reports from the United Network for Organ transplantation (UNOS) portal. We used multivariable Cox-proportional hazards models to compare graft and patient survival in blood type A2/A2B to B deceased donor renal transplants to survival in blood type B to B transplants. We estimated Kaplan-Meier (KM) graft and patient survival functions.
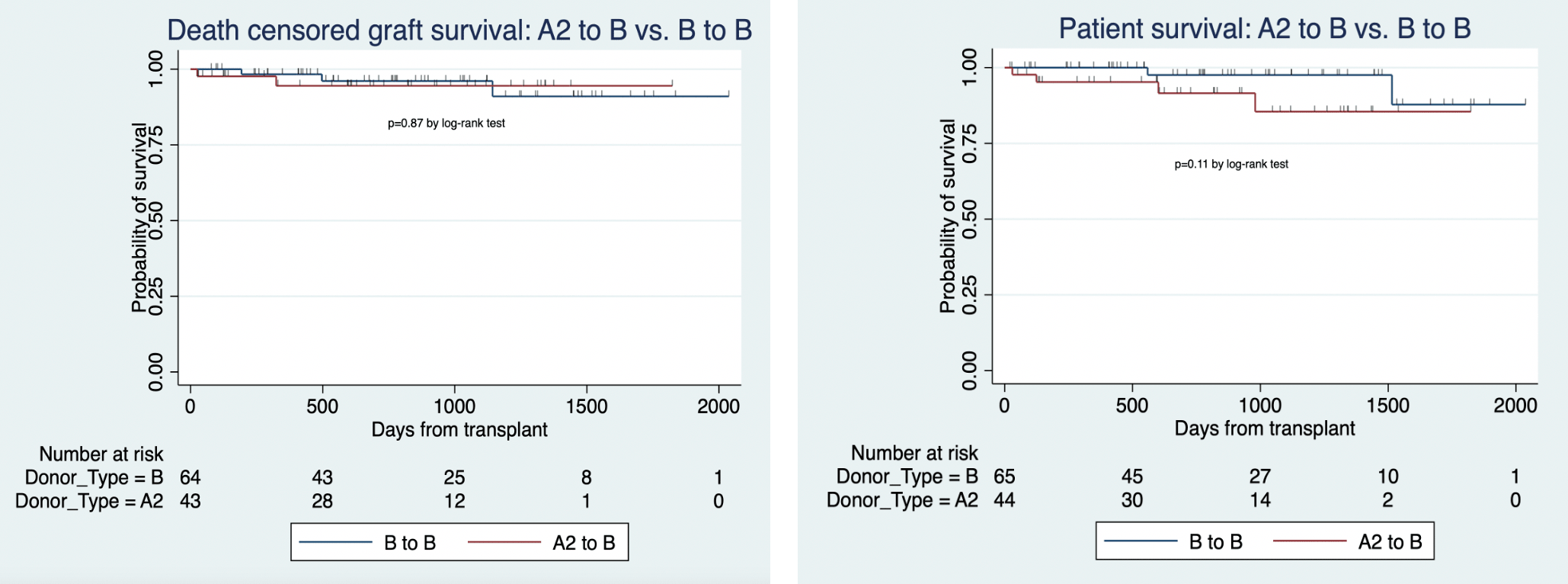
*Results: Since 2015, our center has performed 44 A2/A2B to B and 65 B to B kidney transplants. We followed the patients for a median of 712 days (IQR 343-1143). Recipients of A2/A2B to B and B to B kidney transplants were similar with respect to age, gender, estimated post-transplant survival (EPTS), calculated panel reactive antibody (CPRA), HLA ABDR mismatch, kidney donor profile index (KDPI), and the incidence of delayed graft function (DGF). A higher percentage of A2/A2B to B transplant recipients were Black/African American (22/44, 50%) than B to B transplant recipients (14/65, 21.5%). Blood type A2/A2B to B and B to B transplant recipients had similar 1-year graft (97.7% vs. 93.8%, p=0.34) and 1-year patient survival (97.7% vs. 98.5%, p=0.78) rates. Multivariable models adjusted for race/ethnicity showed that death censored graft survival (adjusted HR=1.45, p=0.70, 95% CI=0.21 to 9.82) and patient survival (4.22, p=0.14, 95% CI=0.64 to 27.92) in A2/A2B to B transplant recipients were similar to the traditionally ABO blood type compatible B to B transplants.
*Conclusions: The NYU Langone blood type A2/A2B to B transplantation adds to the body of evidence suggesting that blood type A2/A2B to B transplantation is clinically feasible. This provision of the KAS appears to be having its intended effect of increasing access to transplantation in blood type B candidates with no attendant compromise in overall patient or death censored graft survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tatapudi VS, Alnazari N, Chand R, Ali NM, Lonze BE, Montgomery RA. Blood Type A2/a2b to B Renal Transplantation: A Single Center Retrospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/blood-type-a2-a2b-to-b-renal-transplantation-a-single-center-retrospective-cohort-study/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress