Blood Transcriptomes of Covid-19 Infected Kidney Recipients Demonstrate Frequent and Persistent Sars-cov-2 Virome Gene Expression
Z. Sun1, M. M. Rana2, A. C. Reghuvaran3, Y. A. Azzi4, G. Carrara5, S. Hartzell6, S. Kulkarni3, W. Zhang6, K. Banu3, P. Heeger6, E. Akalin4, P. Cravedi6, Z. Zhang7, M. C. Menon3
1Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 2Infectious Disease Director, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 3Nephrology, Yale University, New Haven, CT, 4Nephrology, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY, 5Clinical Research Coordinator, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 6Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 7Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 544
Keywords: COVID-19, Genomics, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 25 - Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Transplant Infections
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:40pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:40pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom B
*Purpose: Kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) have poor outcomes vs non-KTRs with acute COVID-19. To provide insight into management of immunosuppression during acute COVID-19, we studied peripheral blood transcriptomes during and after COVID-19 from a multicenter KTR cohort.
*Methods: Clinical data were collected by chart review. Paxgene blood RNA was polyA-selected and sequenced at enrollment.
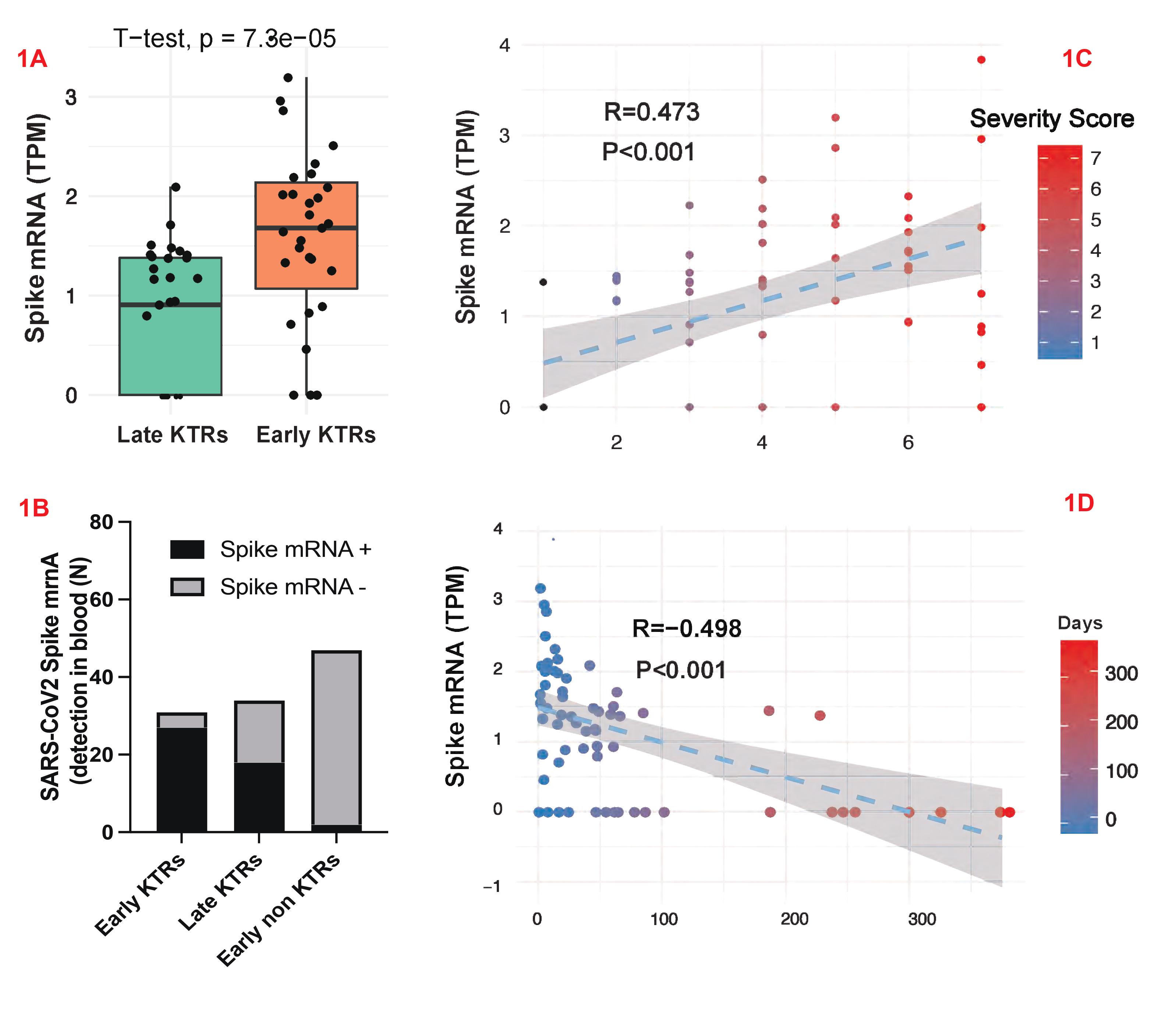
*Results: A total of 64 KTRs with COVID-19 were enrolled (31 Early cases (<4weeks from a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test) and 33 late cases). Out of the 64 patients, eight died and three encountered graft losses during follow-up. Due to presence of mRNA reads in the blood transcriptome unmapped to the human genome, we aligned the mRNA short reads to the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Surprisingly, our strategy detected the SARS-Cov2 mRNA, especially Spike mRNA in 27 (87%) early cases, and 18 (54%) of late cases (Fig 1A and B). We then analyzed the raw reads from a public dataset of non-KTRs with Paxgene RNA (GSE172114). The SARS-CoV-2 Spike mRNA was detected in 2/47 (4.2%) critically ill COVID-19 cases and 0/25 non-critically ill cases in this non-KTR dataset (compared to KTRs, Chi-square P<0.001; Fig 1B). Among our KTRs, the amount of Spike mRNA was associated positively with the COVID-19 severity score (scale of 1 to 7 of increasing severity; Fig 1C) and inversely with time from initial positive PCR (Fig 1D). More interestingly, 7/64 patients had detectable Spike RNA-emia beyond 60 days after COVID-19 diagnosis. Of the 3 graft losses in our cohort, 2 occurred among these 7 patients.
*Conclusions: Blood transcriptome of KTRs with COVID-19 demonstrated a risk for persistent viremia with implications for pathogenesis of COVID-19 disease. This finding also supports using passive immune strategies in COVID-KTRs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sun Z, Rana MM, Reghuvaran AC, Azzi YA, Carrara G, Hartzell S, Kulkarni S, Zhang W, Banu K, Heeger P, Akalin E, Cravedi P, Zhang Z, Menon MC. Blood Transcriptomes of Covid-19 Infected Kidney Recipients Demonstrate Frequent and Persistent Sars-cov-2 Virome Gene Expression [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/blood-transcriptomes-of-covid-19-infected-kidney-recipients-demonstrate-frequent-and-persistent-sars-cov-2-virome-gene-expression/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress