Benefits of Normothermia Regional Perfusion (NRP), Hypothermic Machine Perfusion (HMP) and Short Cold Ischemia Time (CIT) for Kidney Transplants with Controlled Donation after Circulatory Death (cDCD)
1Agence de la Biomedecine, La Plaine Saint Denis, France, 2CHU Nantes, Nantes, France, 3CH Annecy, Annecy, France, 4CHU Pitié Salpetriere, Paris, France, 5CHU Saint Louis, Paris, France, 6CHU Rouen, Rouen, France, 7CHU Tours, Tours, France, 8CHU Kremlin-Bicetre, Kremlin-Bicetre, France, 9CHU Poitiers, Poitiers, France
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 339
Keywords: Donors, non-heart-beating, Graft function, Kidney transplantation, Warm ischemia
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Deceased Donor Selection II
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: cDCD are considered as extended criteria donors with poorer kidney transplant outcomes and high delayed graft function (DGF) rate. We built a French national protocol for cDCD kidney transplants. The donors selection criteria: age ≤65 y, functional warm ischemia time (fWIT) <120 min, nRP and HMP use and CIT <18h. The recipients criteria: 1st transplant and virtual negative crossmatch. We compared outcomes of kidney transplants from cDCD donors to those of similar transplants from donation after brain death (DBD) donors and identified factors explaining differences observed.
*Methods: We included all consecutive cDCD donors from 2015 to 2018 and DBD donors from 2015 to 2017. cDCD and DBD transplants were matched using a propensity score. The primary end point, DGF occurrence was compared using GEE model stratified on pairs.
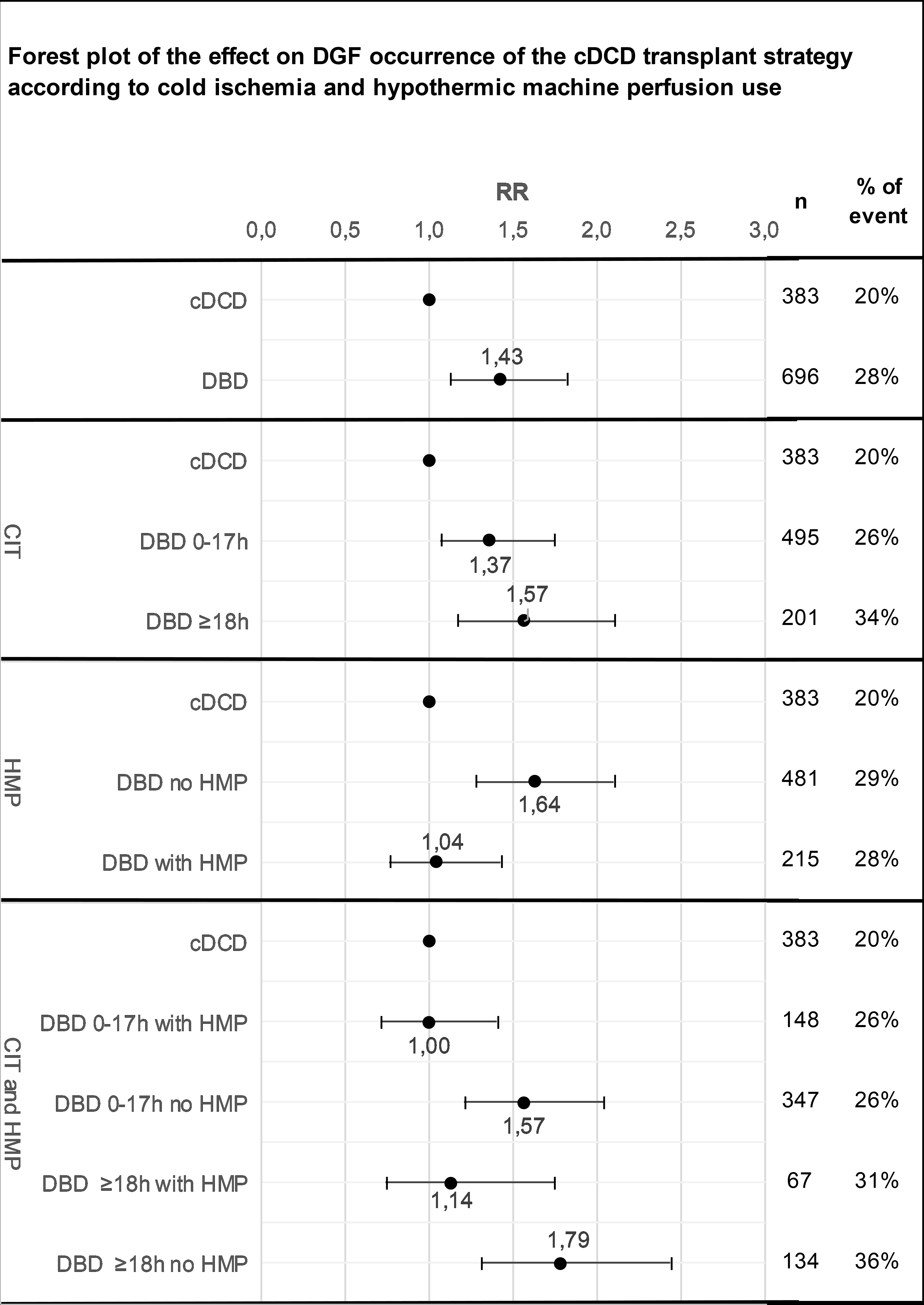
*Results: 504 kidney transplants were performed from 282 donors: 50 years mean age, 52% admitted for hypoxic brain damage with a median delay between admission and death of 7 days. The matching procedure retained 442 cDCD and 810 DBD transplantations. cDCD recipients had a DGF rate of 20% and DBD recipients 28% (adjusted relatif risk, aRR=1.43, 95% CI 1.12-1.82). When DBD transplants were separated according to CIT and HMP and compared to cDCD transplants, we observed a higher aRR for DBD donors without HMP (aRR for DBD donors without HMP with CIT < 18 h =1.57, 95% CI 1.20-2.03, and for DBD donors without HP with CIT ≥ 18 h =1.79, 95% CI 1.31-2.44) and no difference for DBD donors with HMP even CIT ≥ 18 h. The 1-year graft survival was comparable in cDCD (94.4%, 95% CI 91.0%-96.5%), and in DBD patients (93.7%, 95% CI 91.7% - 95.2%).
*Conclusions: Early outcome of kidney transplants from cDCD donors was excellent when compared to DBD transplants and data from literature. Results of this analysis should be confirmed on long term follow-up study. The French cDCD protocol which limits fWIT injuries, allows better initial outcome in cDCD patients as compared to matched DBD patients. Systematic use of nRP with optimal graft preservation might provide optimal cDCD organs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Savoye E, Legeai C, Branchereau J, Gay S, Drouin S, Gaudez F, Veber B, Venhard J, Cheisson G, Kerforne T, Bastien O, Antoine C. Benefits of Normothermia Regional Perfusion (NRP), Hypothermic Machine Perfusion (HMP) and Short Cold Ischemia Time (CIT) for Kidney Transplants with Controlled Donation after Circulatory Death (cDCD) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/benefits-of-normothermia-regional-perfusion-nrp-hypothermic-machine-perfusion-hmp-and-short-cold-ischemia-time-cit-for-kidney-transplants-with-controlled-donation-after-circulatory-death-cdcd/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress