Belatacept and Rapamycin Maintenance Immunosuppression in a Sensitized Nonhuman Primate Kidney Allotransplantation Model
1Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, 2Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 507
Keywords: Alloantibodies, B cells, Kidney transplantation, Rapamycin
Topic: Basic Science » Acute Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Acute Rejection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Desensitization with costimulation blockade and proteasome inhibition prior to kidney transplantation prevents early antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) and prolongs graft survival in highly sensitized nonhuman primates (NHP). However, recipients develop late AMR accompanied by elevation of Tfh and plasma cells. Therefore, we hypothesized that belatacept as a maintenance immunosuppression would control the post-transplant humoral immune response in conjunction with rapamycin.
*Methods: Nine (9) rhesus macaques were sensitized to maximally MHC mismatched donors by two sequential skin transplants. Primates were desensitized with belatacept and carfilzomib. Following desensitization, primates received kidney allografts from their skin donors. Five primates received induction therapy with rhesus specific anti-thymocyte globulin (rhATG) and four primates received induction therapy with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies. Maintenance immunosuppression of all primates consisted of belatacept, rapamycin and prednisone.
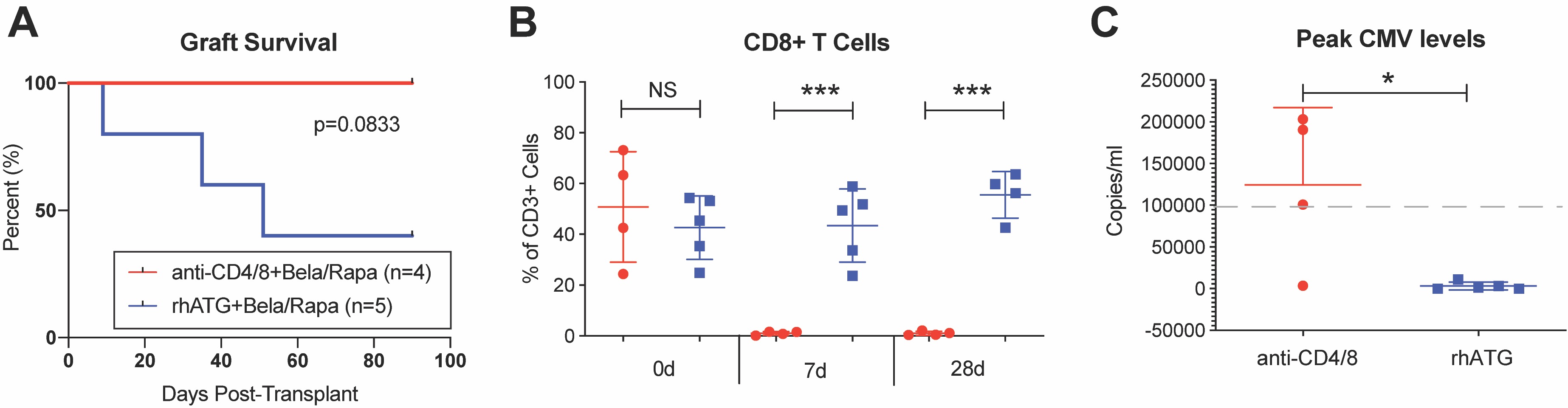
*Results: All primates tolerated the treatment well. In the rhATG group (n=5), we observed 3 cases of early graft rejection without DSA elevation, while we had no rejection 3 months post-transplant in the anti-CD4/8 group (p=0.08; Figure 1A). As expected, more significant depletion of CD8+ T cells was induced with the monoclonal antibodies compared to rhATG (Figure 1B). While preventing early graft rejection, the use of anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 mAbs increased the frequency of CMV reactivation requiring treatment (Figure 1C). Interestingly, all six animals that survived long-term showed no AMR under belatacept and rapamycin maintenance immunosuppression. We were furthermore able to wean immunosuppression to belatacept monotherapy in one primate and wean all immunosuppression in a second primate without observing graft dysfunction for at least 3 months.
*Conclusions: Maintenance immunosuppression with belatacept and rapamycin prevents post-transplant AMR and allows for weaning of immunosuppression in highly sensitized nonhuman primate kidney transplant recipients. Induction therapy with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies prevents early ACR, which was observed with rhATG.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schmitz R, Fitch ZW, Manook M, Yoon J, Farris AB, Kwun J, Knechtle SJ. Belatacept and Rapamycin Maintenance Immunosuppression in a Sensitized Nonhuman Primate Kidney Allotransplantation Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/belatacept-and-rapamycin-maintenance-immunosuppression-in-a-sensitized-nonhuman-primate-kidney-allotransplantation-model/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress