Belatacept and Carfilzomib-based Treatment of Active Antibody-mediated Rejection in a Sensitized Nonhuman Primate Model
1Surgery, Duke University, Durham, NC, 2Pathology & Laboratory Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 345
Keywords: Alloantibodies, B cells, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Basic Science » Immunosuppression Preclinical Studies
Session Information
Session Name: Xenotranplantation and Preclinical Studies
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 8, 2021
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:15pm-6:20pm
Presentation Time: 6:15pm-6:20pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: One third of sensitized, HLA-incompatible transplant recipients experience antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) with limited effective treatment options. We tested a novel treatment strategy for AMR consisting of complement inhibition, proteasome inhibition and costimulation blockade in a nonhuman primate model.
*Methods: Thirteen rhesus macaques were sensitized to maximally MHC mismatched donors by two sequential skin transplants. Primates subsequently received kidney allografts from their skin donors. All primates received induction therapy with rhesus-specific ATG (rhATG) and were maintained on different immunosuppressive regimens. Primates were monitored postoperatively for signs of AMR, which was defined as worsening kidney function resistant to high dose steroid rescue therapy, a rise in serum donor-specific antibody (DSA) levels, and biopsy evidence of active AMR. AMR treatment consisted of carfilzomib and belatacept for a maximum of 4 weeks.
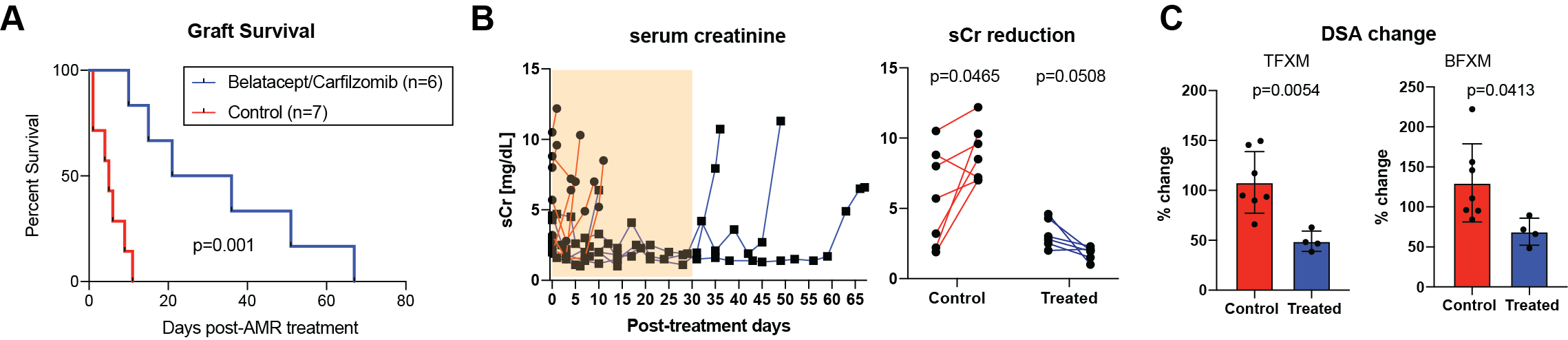
*Results: Treatment with carfilzomib and belatacept was well tolerated and we did not observe any treatment-specific side effects. Once AMR developed, animals without further treatment rejected their graft rapidly. However, animals treated with carfilzomib and belatacept showed prolonged graft survival after the AMR treatment compared to control animals (5d vs. 28.5d, p < 0.01; Figure 1A). As shown in figure 1B, animals without treatment showed significant elevation of serum creatinine (sCr) while profound reduction of sCr was observed in treated animals. After initiation of treatment, we observed a significant reduction of both class I and class II DSA (Figure 1C). However, all animals showed rebound of DSA when the treatment was discontinued.
*Conclusions: Carfilzomib and belatacept were able to control on-going humoral immune response seen during AMR in a nonhuman primate model. This was associated with improved graft function and prolongation of graft survival. Further studies in optimizing maintenance immunosuppression after carfilzomib and belatacept treatment is warranted to continuously control post-transplant humoral response in the sensitized recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kwun J, Schmitz R, Manook M, Fitch Z, Olaso D, Choi A, Yoon J, Bae Y, Lambris J, Knechtle S. Belatacept and Carfilzomib-based Treatment of Active Antibody-mediated Rejection in a Sensitized Nonhuman Primate Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/belatacept-and-carfilzomib-based-treatment-of-active-antibody-mediated-rejection-in-a-sensitized-nonhuman-primate-model/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress