Basiliximab Induction in Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Transplant
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B148
Keywords: Induction therapy, Kidney/liver transplantation, Simulect
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (rATG) is the most common induction agent in renal transplant recipients; however, induction agent selection for SLK recipients is not well described. SLK recipients may require less overall immunosuppression to achieve expected graft and patient survival. Basiliximab (BAS) may provide adequate induction therapy while avoiding toxicities associated with lymphocyte-depleting induction agents in this population. The aim of this study was to evaluate the utilization and outcomes of BAS induction in SLK recipients.
Methods: We analyzed SRTR data for 6186 adult SLK recipients from 2002-2017. Patients were excluded if they had previous transplants or received multiple non-steroidal induction agents. Multivariate logistic regression, Kaplan-Meier Survival Analysis, and Cox-Regression models were used to determine DGF odds ratio and patient and renal graft survival hazard ratios at one year.
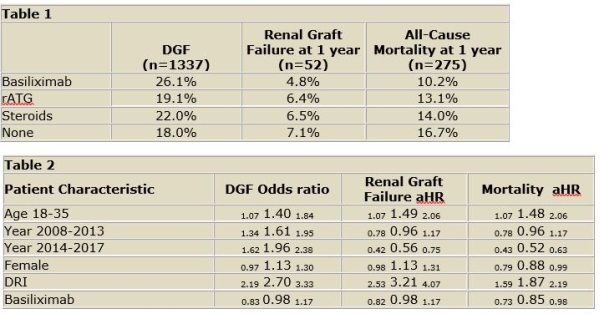
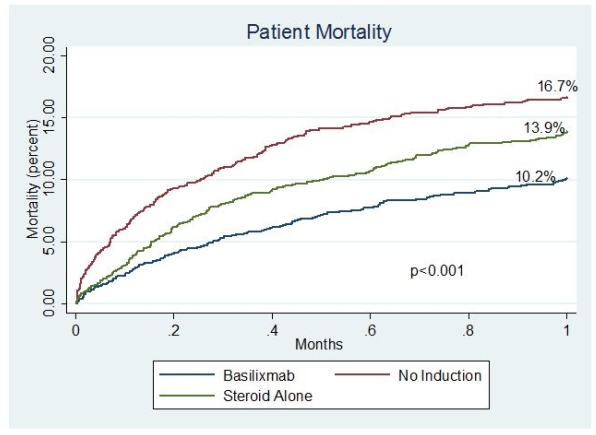
Results: BAS is the most commonly used induction agent for SLK recipients in the United States followed by steroids alone and rATG at 28%, 27%, and 18%, respectively. DGF occurred more commonly in those who received BAS comparedto rATG, steroids, or no induction (26.1%, 19.1%, 22%, 18%, respectively; p<0.001 [table1]). Patient mortality was lower among recipients who received BAS, in comparison to steroid induction or no induction (10.2%, v 13.9%, v 16.7%, p<0.001 [figure 1]). After adjusting for donor and recipient characteristics, BAS induction did not significantly impact risk for DGF (OR 0.98, p=0.85) or renal graft failure at one year (HR 0.98, p=0.98). However, BAS induction was associated with a reduction in one year mortality (HR 0.85, p=0.03 [table2]).
Conclusions: SLK recipients who received BAS had lower mortality with similar DGF and one year graft failure rates.
CITATION INFORMATION: Song C., Luo X., Pote L., Strout S., Segev D., Desai N., Gurakar A., Navqi F., Garonzik Wang J. Basiliximab Induction in Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Transplant Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Song C, Luo X, Pote L, Strout S, Segev D, Desai N, Gurakar A, Navqi F, Wang JGaronzik. Basiliximab Induction in Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Transplant [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/basiliximab-induction-in-simultaneous-liver-kidney-transplant/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress