Basiliximab Induction in HIV-Positive Renal Transplant Recipients Compared to an HIV-Negative Cohort
1Pharmacy, Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago
2Infectious Diseases and Organ Transplantation, Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B147
Keywords: HIV virus, Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Purpose: There is an elevated risk of acute rejection in HIV+ renal transplant recipients and continued evaluation of the most appropriate induction therapy remains. Use of an IL-2 inhibitor may avoid the potential risks of lymphocyte depletion on accelerated HIV disease progression and infection in the HIV+ recipient. The objective of this study is to assess the role of basiliximab on acute rejection, patient, and allograft survival in HIV+ recipients compared to a matched cohort of HIV- recipients.
Methods: This is a single center, retrospective study of adult HIV+ renal transplant recipients, matched 1:2 to an HIV- cohort, transplanted from 2006 to 2016 who received basiliximab induction. Matching was based on date of transplant within 1 year and race. BPAR, patient and allograft survival were evaluated at 1 and 3 years post-transplant.
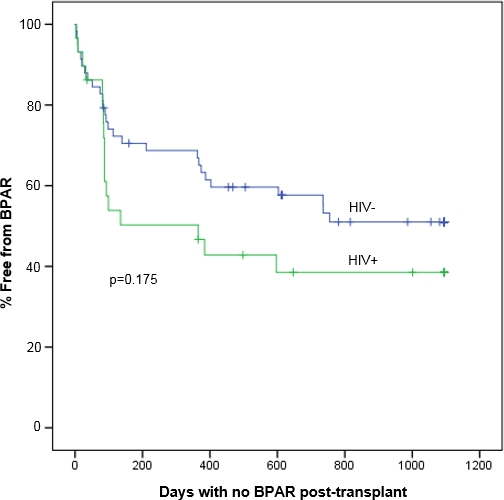
Results: A total of 87 patients were included. A trend towards increased biopsy proven acute rejection at 3 years was observed in the HIV+ group (Figure 1). Measured GFR at 1 year was significantly higher in HIV- patients. There was no difference between patient or graft survival at 1 year.
Conclusions: Similar rejection, graft, and survival outcomes were observed when non-lymphocyte depleting induction and CNI-based maintenance therapy was used in an HIV+ and HIV- matched renal transplant cohort.
| HIV-Positive
(n=29) |
HIV-Negative
(n=58) |
p-value | |
| Age (year±SD) | 47 ± 9 | 57 ± 9 | <0.01 |
| Male gender | 27 (93%) | 34 (59%) | <0.01 |
| Black | 22 (76%) | 40 (69%) | 0.67 |
| Dialysis prior to transplant | 28 (96%) | 41 (71%) | <0.01 |
| HCV+ | 9 (7%) | 23 (38%) | <0.01 |
| Deceased donor | 21 (72%) | 35 (60%) | 0.35 |
| DGF | 7 (24%) | 19 (33%) | 0.62 |
| GFR at 1 year | 37 ± 14 | 44 ± 14 | <0.01 |
| Patient survival at 1 year | 28 (96%) | 57 (98%) | 0.61 |
| Graft survival at 1 year | 27 (93%) | 55 (95%) | 0.75 |
CITATION INFORMATION: Schulte J., Richardson C., Stosor V., Cunningham K., D'Agostino C., Kane C. Basiliximab Induction in HIV-Positive Renal Transplant Recipients Compared to an HIV-Negative Cohort Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schulte J, Richardson C, Stosor V, Cunningham K, D'Agostino C, Kane C. Basiliximab Induction in HIV-Positive Renal Transplant Recipients Compared to an HIV-Negative Cohort [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/basiliximab-induction-in-hiv-positive-renal-transplant-recipients-compared-to-an-hiv-negative-cohort/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress