B Cell Deficiency Inhibits Both Antibody Mediated Rejection and T Cell Mediated Acute Rejection in a Rat Kidney Transplant Model.
S. Panzer, S. Reese, N. Wilson Schlei, B. Verhoven, D. Xiang, W. Zhong, A. Djamali.
University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 306
Keywords: B cells, Graft-infiltrating lymphocytes
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: B Cells and Antibody in Rejection
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Location: E350
Purpose: The specific role of B cells in the pathogenesis of acute rejection remains unclear.
Methods: To address this question, we generated B cell deficient Lewis rats (B-/-) via CRISPR technology with a targeted deletion of the Igh6 gene for IgM. Full mismatch kidney transplants were performed with Brown Norway (BN) donor to B-/- recipients (N=7) and a control group of BN donors to wild type Lewis recipients (WT, N=6). All animals were given cyclosporine until harvest at 7 days.
Results: Cellular rejection was significantly reduced in B-/- compared to WT based on Banff scores for tubulitis and interstitial inflammation (P=0.02 and 0.001, respectively, Figure 1A-B). The amount of graft infiltrating macrophages was reduced in B-/- compared to WT (P=0.0001 by quantitative densitometry, Fig 1C-D). 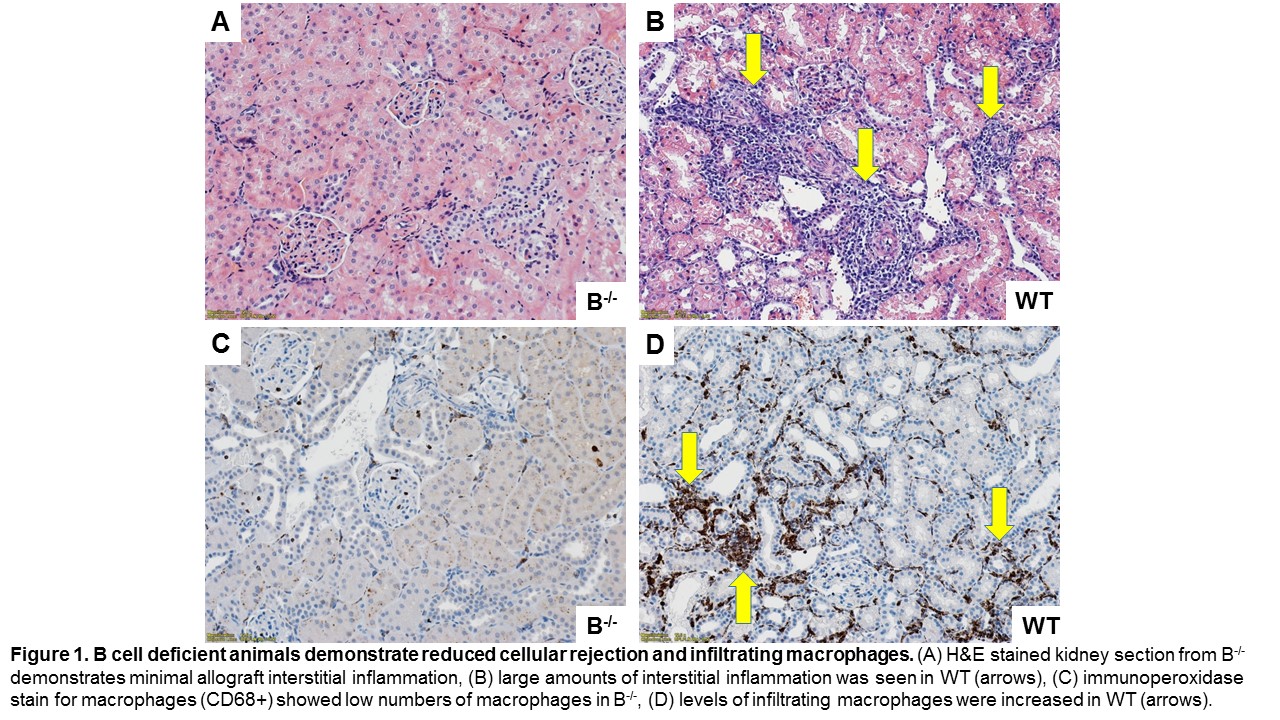 Measures of antibody mediated rejection showed reduced IgM DSA (P=0.03) and a trend towards reduced peritubular capillaritis (P=0.07) in B-/- compared to WT. Serum BAFF levels were lower in B-/- compared to WT (P=0.08). Flow cytometry confirmed absence of B cells in spleen, bone marrow, lymph node, and peripheral blood of the B-/-. ELISPOT analysis demonstrated no antibody production in B-/-. Assessment of splenic tissue in B-/- demonstrated loss of architecture and frequent macrophages (Fig 2A). Typical germinal center formation was seen in WT (Fig 2B). Splenic T cells were seen in B-/- and WT (Fig 2C and D, respectively). B-/- lacked splenic B cells (Fig 2C), B cells were present in WT (Fig 2D).
Measures of antibody mediated rejection showed reduced IgM DSA (P=0.03) and a trend towards reduced peritubular capillaritis (P=0.07) in B-/- compared to WT. Serum BAFF levels were lower in B-/- compared to WT (P=0.08). Flow cytometry confirmed absence of B cells in spleen, bone marrow, lymph node, and peripheral blood of the B-/-. ELISPOT analysis demonstrated no antibody production in B-/-. Assessment of splenic tissue in B-/- demonstrated loss of architecture and frequent macrophages (Fig 2A). Typical germinal center formation was seen in WT (Fig 2B). Splenic T cells were seen in B-/- and WT (Fig 2C and D, respectively). B-/- lacked splenic B cells (Fig 2C), B cells were present in WT (Fig 2D).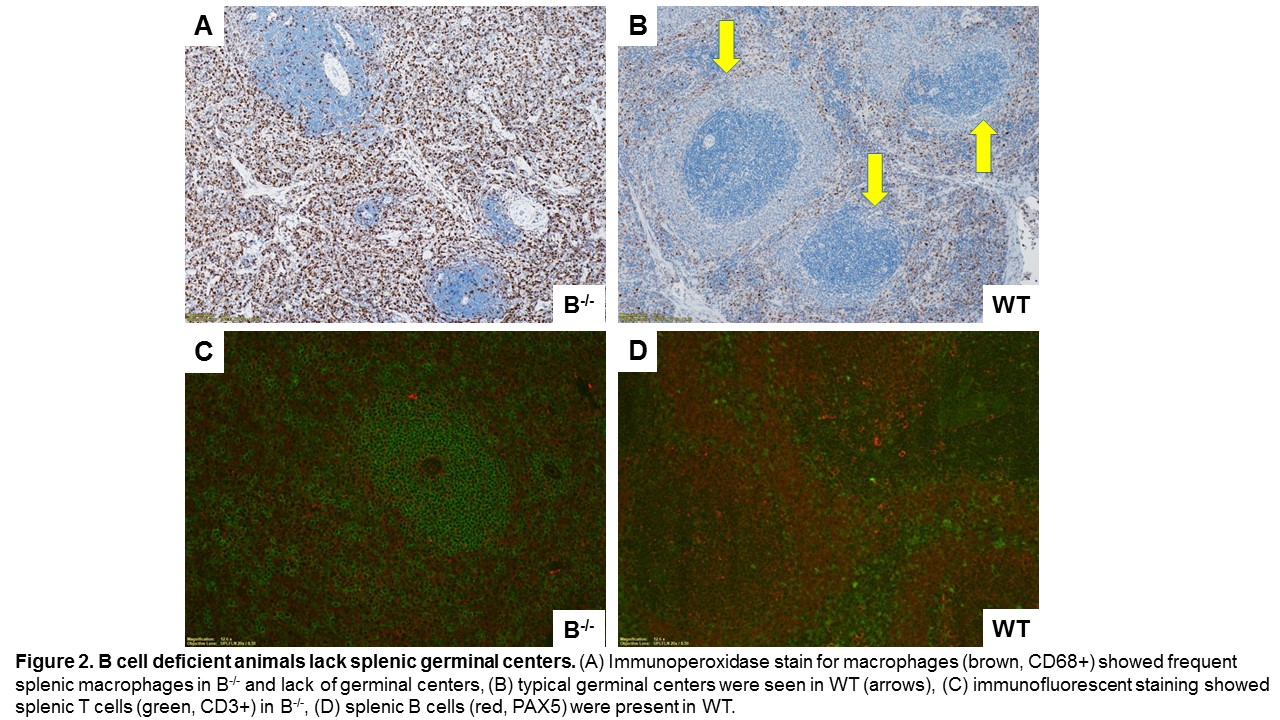 Conclusions: Our studies demonstrate B cell deficiency inhibits both antibody and T cell mediated rejection while also downregulating graft-infiltrating macrophages. The cellular mechanisms and alterations in lymphoid architecture that are involved in this cross-talk are under investigation.
Conclusions: Our studies demonstrate B cell deficiency inhibits both antibody and T cell mediated rejection while also downregulating graft-infiltrating macrophages. The cellular mechanisms and alterations in lymphoid architecture that are involved in this cross-talk are under investigation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Panzer S, Reese S, Wilson Schlei N, Verhoven B, Xiang D, Zhong W, Djamali A. B Cell Deficiency Inhibits Both Antibody Mediated Rejection and T Cell Mediated Acute Rejection in a Rat Kidney Transplant Model. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Panzer S, Reese S, Schlei NWilson, Verhoven B, Xiang D, Zhong W, Djamali A. B Cell Deficiency Inhibits Both Antibody Mediated Rejection and T Cell Mediated Acute Rejection in a Rat Kidney Transplant Model. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/b-cell-deficiency-inhibits-both-antibody-mediated-rejection-and-t-cell-mediated-acute-rejection-in-a-rat-kidney-transplant-model/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
