Association of Pre-Transplant Anti A1 IgM Antibody Titers with Survival Outcomes in A2/A2B to B Kidney Transplantation
Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1558
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Rejection, Survival
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Clinical Science » 17 - Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The new kidney allocation system implemented in 2014 has allowed blood type B recipients to receive kidneys from A2/A2B donors. Although many centers use pre-transplant anti-A1 IgG titers of <1:8 to determine eligibility for A2/A2B kidney transplant, the relevance of pre-transplant IgM titers is unclear. Our aim was to evaluate the association between pretransplant anti-A1 IgM titers in A2/A2B kidney transplant recipients and graft survival.
*Methods: In this retrospective, single-center analysis, we included all adults who received A2/A2B to B deceased donor kidney transplants from December 2014 to June 2021. Anti-A1 titers were measured in dithiothreitol (DTT) treated serum (containing IgG only) and untreated serum (containing both IgG and IgM). Our protocol defined eligible recipients as having pre-transplant anti-A1 IgG titer <1:8 and IgM/IgG titer ≤1:64. All recipients had an induction with alemtuzumab, methylprednisolone, and maintenance with tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and prednisone. Patients with IgM/IgG >1:16 but ≤ 1:64 received plasmapheresis for 5 days, followed by a single dose of IVIG 2g/kg and rituximab 375 mg/m2. The effects of pre-transplant IgM/IgG titers, stratified as ≤1:8 and ≥1:16, on death-censored, rejection-free, and overall graft survival were tested using the Kaplan-Meier method.
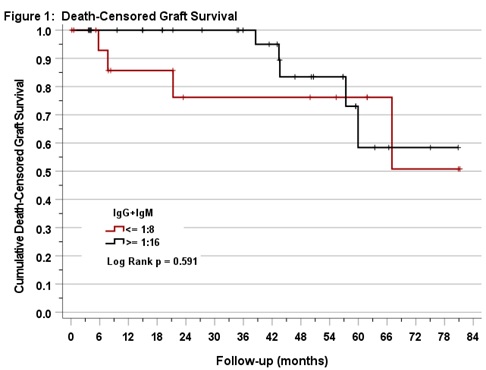
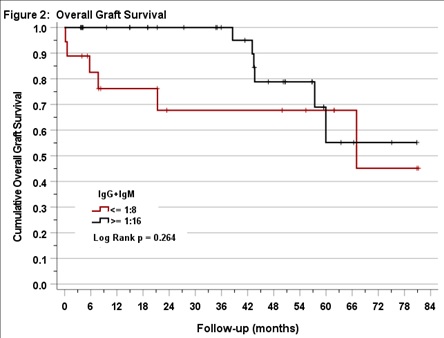
*Results: 53 adults with A2/A2B deceased donor kidney transplants were included. Pre-transplant IgM/IgG titers ranged from 1:4 to 1:64 (in 8% and 15% of persons). 18 persons (34%) had titers ≤1:8 and 35 (66%) had IgM/IgG titers ≥1:16. In this sample, we did not detect an effect of pre-transplant titer group on death-censored (p=0.59, figure 1), rejection-free (p=0.61), or overall graft survival (p=0.26, figure 2).
*Conclusions: In our study, allograft survival outcomes were not significantly different between patients with low and high pre-transplant anti-A1 IgM/IgG titers. We found it was safe to transplant recipients with pre-transplant IgM/IgG titers up to 1:64. Further studies with a larger samples and longer follow-up are needed to determine the clinical relevance of IgM titers as measured in untreated serum in A2/A2B kidney transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fallahzadeh M, Shaffer D, Chediak AEl, Feurer I, Rega S, Triozzi JL, Shawar S. Association of Pre-Transplant Anti A1 IgM Antibody Titers with Survival Outcomes in A2/A2B to B Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/association-of-pre-transplant-anti-a1-igm-antibody-titers-with-survival-outcomes-in-a2-a2b-to-b-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress