Association of De Novo Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Increased Hospital Costs Following Kidney Transplant in Immunologically Low-Risk Patients
1Section of Organ Transplantation & Immunology, Yale University, New Haven, CT
2Section of Nephrology, Yale University, New Haven, CT.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A127
Keywords: Economics, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 2, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
While antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is likely the primary cause of kidney transplant (KTx) failure, and its treatment can be considered expensive, incremental center costs for AMR have not been described. Our objective was to compare direct transplant center costs in low-risk KTx recipients who develop de novo AMR to that of matched controls.
Methods: This is a study of adult patients at Yale-New Haven Hospital transplanted from 2005–2013 and diagnosed with AMR (Banff 2007 criteria) compared to controls who did not develop AMR. We matched up to 2 controls for each case based on donor type (deceased vs. living) and the following recipient variables: dialysis vintage (dialysis time before KTx ≤2 years apart), age (≤10 years apart), sex, race (black vs. non-black), and diabetes. Cumulative individual direct costs (in- and out-patient; excluding staffing and organ allocation costs) were compared between cases and controls via t-test.
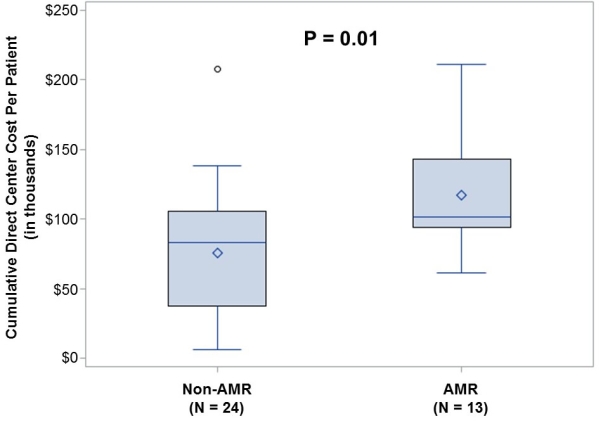
Results: 13 cases were matched to 24 controls (2 cases had 1 control each). Matching variables resulted in a mean age of 35±13 years, 59% male, 24% black and 38% with diabetes. Ten controls were transplanted before their respective cases; 14 were after (<1 year after, 5 controls; 1-2 years, 5; 2-3 years, 2; 3-4 years, 2). Mean total per-patient direct cost was significantly higher with AMR ($116,988 ± $40,969 vs. $75,909 ± $48,042 for non-AMR; P=0.01). Sensitivity analyses after removing 4 recipients (those only matched 1:1, which were also the patients transplanted 3-4 years apart) did not significantly alter these results (AMR cost $123,448 ± $40,422; non-AMR cost $75,988 ± $47,706; P=0.008).
Conclusions: Transplant center costs were significantly higher for immunologically low-risk kidney recipients with de novo AMR compared with matched controls. Besides the known risk of graft failure and the potential treatment-related risks associated with AMR, these increased costs highlight the need for more cost-effective prevention strategies and treatments for recipients that develop de novo AMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kulkarni S, Hall I. Association of De Novo Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Increased Hospital Costs Following Kidney Transplant in Immunologically Low-Risk Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/association-of-de-novo-antibody-mediated-rejection-and-increased-hospital-costs-following-kidney-transplant-in-immunologically-low-risk-patients/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
