Assessment of Physical Frailty is Positively Correlated with LAS Score in Lung Transplant Candidates
1Department of Cardiac Surgery, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 2Division of Infectious Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 4Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care, UCSF School of Medicine, San Francisco, CA, 5Division of Geriatrics, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 192
Keywords: Lung transplantation, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Setting the Table for Success after Lung Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Location: Room 206
*Purpose: We proposed to evaluate physical frailty in lung transplant candidates to determine whether physical frailty correlated with LAS score and added to ability to predict patient outcomes including death on the waiting list.
*Methods: In this single-center prospective study, frailty was assessed in lung transplant candidates ≥ 60 years of age using Fried’s Frailty Phenotype (FFP) and the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB). The FFP score is based on self-reported weight loss, fatigue, and physical activity, and measures of gait speed and grip strength. The SPPB score consists of measures of gait speed, balance, and lower extremity strength. Using previously established cutoffs, an FFP score of 0 = non-frail; 1-2 = pre-frail; and 3-5 = frail, while an SPPB score of 0-6 = frail; 7-9 = pre-frail; and 10-12 = non-frail.
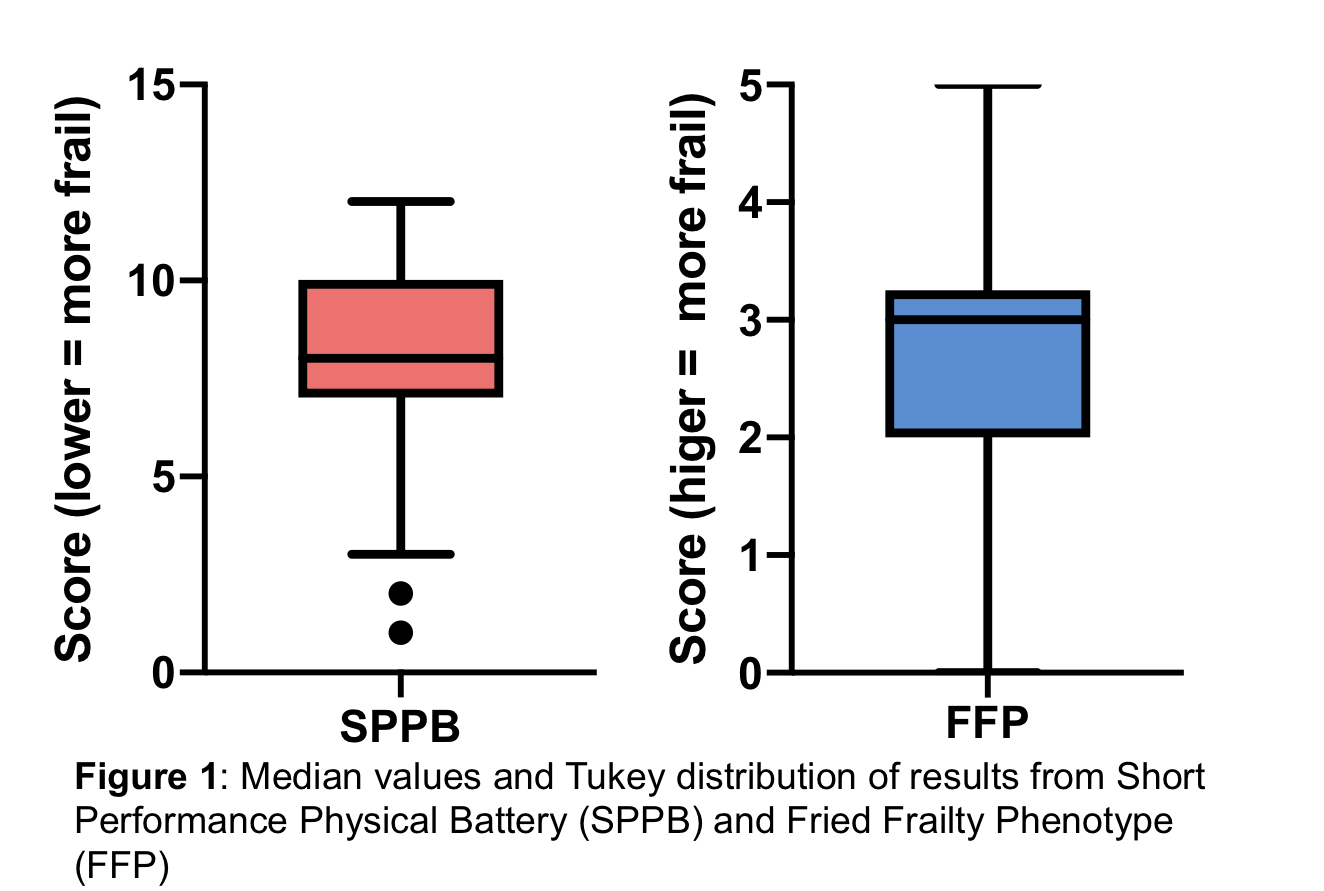
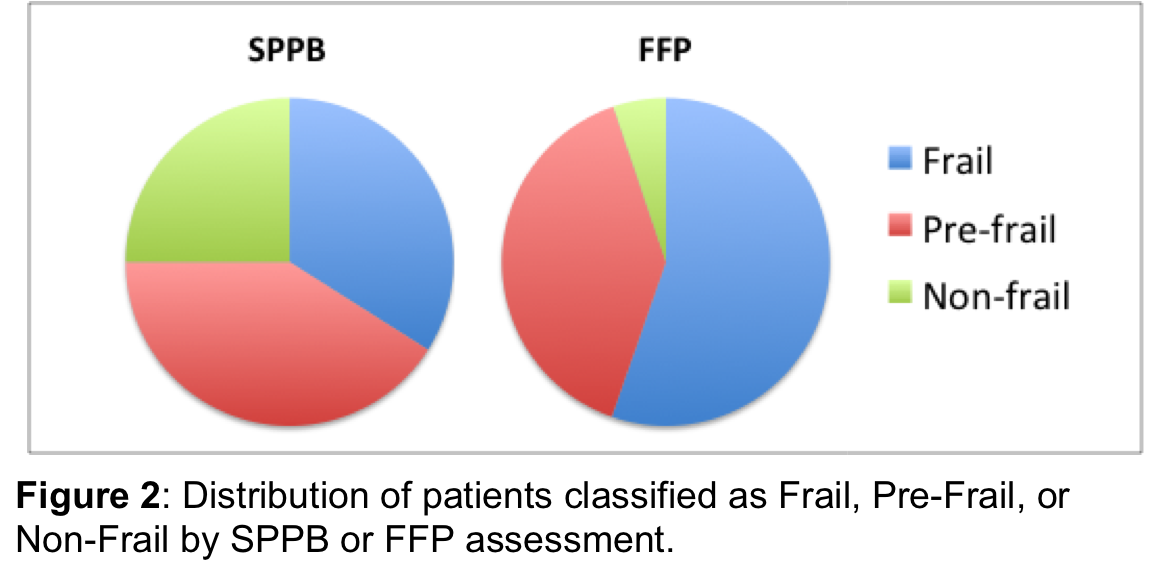
*Results: Out of 44 subjects, 38 completed both SPPB and FFP assessments, while 6 completed only SPPB assessments. The median SPPB and FFP scores were 8 and 3 respectively (Figure 1). By SPPB criteria 34% of subjects are frail, 41% are pre-frail, and 25% are non-frail. By FFP criteria, 55.3% are frail, 39.4% are pre-frail, and 5.2% are non-frail (Figure 2). The average LAS score is 44.2 (±14.2). Both the SPPB (r2=0.19, p = 0.01) and FFP (r2=0.33, p<0.01) are correlated with LAS score. 6 patients died on the waiting list. 16 candidates underwent transplantation.
*Conclusions: Although both physical frailty assessments correlated with LAS score, the FFP score is more strongly correlated. The SPPB and FFP assessments differed, resulting in discordant predictions of the prevalence of frailty in lung transplant candidates. Ongoing studies will determine whether SPPB data can add to the predictive value of LAS in terms of death on the waiting list and post-transplant outcomes for the growing numbers of older lung transplant candidates.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jaladanki S, Shih L, Kwon O, Ventigan N, Nanayakkara D, Weigt S, Singer J, Ardehali A, Biniwale R, Goldwater D, Schaenman J. Assessment of Physical Frailty is Positively Correlated with LAS Score in Lung Transplant Candidates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/assessment-of-physical-frailty-is-positively-correlated-with-las-score-in-lung-transplant-candidates/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress