Apolipoprotein L1 & Chronic Kidney Disease Risk in Young Potential Living Kidney Donors.
1University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham
2University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
3Vanderbilt University, Nashville
4Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 254
Keywords: Donation, Gene polymorphism, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Living Kidney Donation: Post Donation Issues
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Location: E450b
Background: Living kidney donor selection practices have evolved from examining individual risk factors to a risk calculator incorporating multiple characteristics. Due to limited long-term data and lack of genetic information, current risk tools lack precision among young potential living kidney donors, particularly African Americans (AAs).
Methods: We identified a cohort of young adults (18-30 years) with no absolute contraindication to kidney donation from the longitudinal cohort study CARDIA. Risk associations for CKD (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73m2) were identified and assigned weighted points to calculate risk scores.
Results: 3,438 healthy adults were identified; mean age 24.8 years; 48.3% African American; median follow-up 24.9 years (IQR: 24.5-25.2). For 18-year-old adults, 25-year projected risk of chronic kidney disease varied by ethnicity and gender even without baseline clinical and genetic abnormalities; risk was 0.30% for European American (EA) women, 0.52% for European American men, 0.52% for African American women, 0.90% for African American men. Among 18-year-old African Americans with two apolipoprotein L1 gene (APOL1) renal-risk variants without baseline abnormalities, 25-year risk significantly increased: 1.46% for women and 2.53% for men; among those with two APOL1 renal-risk variants and baseline abnormalities, 25-year risk was higher: 2.53%-6.23% for women and 4.35%-10.58% for men. 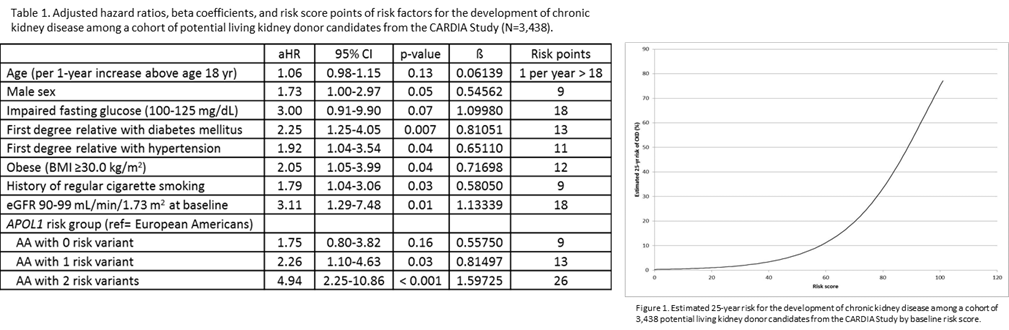 Conclusion: Young AAs were at highest risk for chronic kidney disease, and APOL1 renal-risk variants drove some of this risk. Understanding the genetic profile of young African American potential living kidney donors in the context of baseline health characteristics seems prudent and may help to inform candidate selection and counseling.
Conclusion: Young AAs were at highest risk for chronic kidney disease, and APOL1 renal-risk variants drove some of this risk. Understanding the genetic profile of young African American potential living kidney donors in the context of baseline health characteristics seems prudent and may help to inform candidate selection and counseling.
CITATION INFORMATION: Locke J, Sawinski D, Reed R, Shelton B, MacLennan P, Kumar V, Mehta S, Mannon R, Gaston R, Julian B, Carr J, Terry J, Kilgore M, Massie A, Segev D, Lewis C. Apolipoprotein L1 & Chronic Kidney Disease Risk in Young Potential Living Kidney Donors. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Locke J, Sawinski D, Reed R, Shelton B, MacLennan P, Kumar V, Mehta S, Mannon R, Gaston R, Julian B, Carr J, Terry J, Kilgore M, Massie A, Segev D, Lewis C. Apolipoprotein L1 & Chronic Kidney Disease Risk in Young Potential Living Kidney Donors. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/apolipoprotein-l1-chronic-kidney-disease-risk-in-young-potential-living-kidney-donors/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
