Anti-HLA Antibodies Do Not Increase in Kidney Transplant Recipients During COVID-19 Infection
1Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 2Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, NY, 3University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 4Mount Sinai, New York, NY, 5Emory University Hospital, Atlanta, GA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 848
Keywords: Alloantibodies, COVID-19, Graft function, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 47 - Kidney Complications: Immune Mediated Late Graft Failure
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Complications: Immune Mediated Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: To determine if HLA allo-antibody levels are affected by COVID-19 in renal transplanted patients and to compare the immunoglobulin class and subclass profiles as well as the epitope binding patterns of anti-HLA and anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
*Methods: A cross-sectional study of 46 kidney transplant recipients diagnosed with PCR+ SARS-CoV-2 infection was conducted. Serum samples were collected at the time of infection. For 21 patients, we obtained historical anti-HLA antibody information before COVID-19. Using a single-antigen bead Luminex assay, we determined IgG, IgG1/2/3/4, IgM, and IgA antibodies against Class I and Class II HLA, as well as against five SARS-CoV-2 (Wuhan strain) protein fragments: nucleocapsid, whole spike (S), spike S1, spike S2 and spike receptor binding domain (RBD).
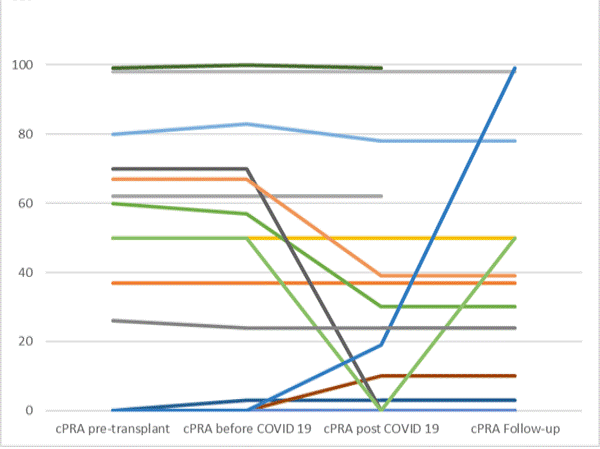
*Results: 26/46 subjects had anti-HLA antibodies of which fourteen had donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies (DSA) compared with 45/46 had anti-SARS-CoV2 antibodies. The majority of DSA were specific to HLA-DQ (10/14), with a dominant IgG/IgG1/IgG3 subclass prevalence. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies exhibited stronger reactivity towards S and RBD and had increased IgM (38/43, 79%) and IgA (41/42, 85%) prevalence when compared to DSAs (5/14, 35% and 2/14, 14%, p<0.001).Out of 21 patients with pre-COVID-19 data available, calculated panel antibody reactivity (cPRA) levels did not change after COVID-19 in 14 cases (67%); cPRA increased in two cases (10%), both of them with allograft nephrectomy and immunosuppression discontinuation, and decreased in five patients (20%) (from 65.4±12.6% before COVID-19, to 29.4±33.6% after COVID-19) (Figure 1). Patients with DSA exhibited significantly lower anti-S IgG (9453±9945 vs 17975±12792; P=0.001), anti-RBD IgM (4464±3693 vs 8751±6468; P=0.03) and anti-nucleoprotein IgA (998±835 vs 5476±6895; P=0.001) anti-SARS-CoV2 antibody MFI values than patients without DSA.
*Conclusions: cPRA values did not increase following PCR confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis in renal transplant recipients and those subjects with pre-existing DSA had lower antibody strength directed at SARS-CoV-2 antigens. The lack of increase in alloantibody response is quite remarkable, since over 80% of the patients underwent either significant reduction or withdrawal of mycophenolate mofetil after COVID-19 diagnosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Girnita A, Wang L, Ahearn P, Colovai A, Fernandez-Vina M, Woodle E, Yalamarti T, Menon M, Azzi Y, Melcher M, Bray R, Gebel H, Cravedi P, Maltzman J, Akalin E. Anti-HLA Antibodies Do Not Increase in Kidney Transplant Recipients During COVID-19 Infection [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/anti-hla-antibodies-do-not-increase-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-during-covid-19-infection/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress