Ambulatory Antibiotic Utilization and Outcomes in an Adult Kidney Transplant Population: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis.
Pharmacy, Ralph H Johnson VAMC, Charleston, SC
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 129
Keywords: Graft failure, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Clinical Complications 1
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Location: E354a
Antibiotics (abx) are commonly prescribed to kidney transplant (KTX) recipients in the outpatient setting. There is limited data assessing the safety and outcomes associated with outpatient abx prescribing in this population.
Methods: This longitudinal cohort study utilized detailed national VA data from the electronic data warehouse to conduct a pharmacovigilance assessment of abx prescribing. Adult veteran KTX recipients transplanted between 2001 and 2007 (follow up through 2010) were included. Pediatrics, non-renal transplants, <1 year follow up, intravenous abx, antifungals, antivirals and prophylactic abx were excluded. Descriptive, univariate statistics and Cox regression were utilized for analysis.
Results: A total of 5,392 KTXs were included, with a mean follow up of 5.6±2.5 years (30,233 patient years); 14,311 oral outpatient abx courses were assessed for a rate of 0.47 courses per patient year; 2,466 KTXs (45.7%) received at least one abx course during follow up, with only 24.8% prescribed by transplant/nephrology providers. Of the 14,311 courses assessed, 54 were documented as prescribed in the presence of a safer alternative, 18 with known significant drug interactions with immunosuppressive therapy without appropriate drug level monitoring, 6,519 without renal function measured, 138 without recommended renal dose adjustments, 198 without LFTs measured and 7,436 without WBC assessment. Overall, 390 courses (2.7%) in 296 patients (5.5%) were deemed as likely to be unsafe (better alternative, drug interaction, wrong dose based on renal function or lack of hepatic function monitoring). After adjusting for baseline characteristics, KTXs that received abx regimens deemed to be unsafe had a 32% higher risk of graft loss (aHR 1.32, 95% CI 1.05-1.67, p=0.019), as compared to those receiving abx regimens deemed to be appropriate (see Figure).
Conclusion: In this cohort, a majority of outpatient antibiotics were prescribed by non-transplant providers. Although unsafe abx prescribing was uncommon, it was associated with significantly higher risk of graft loss.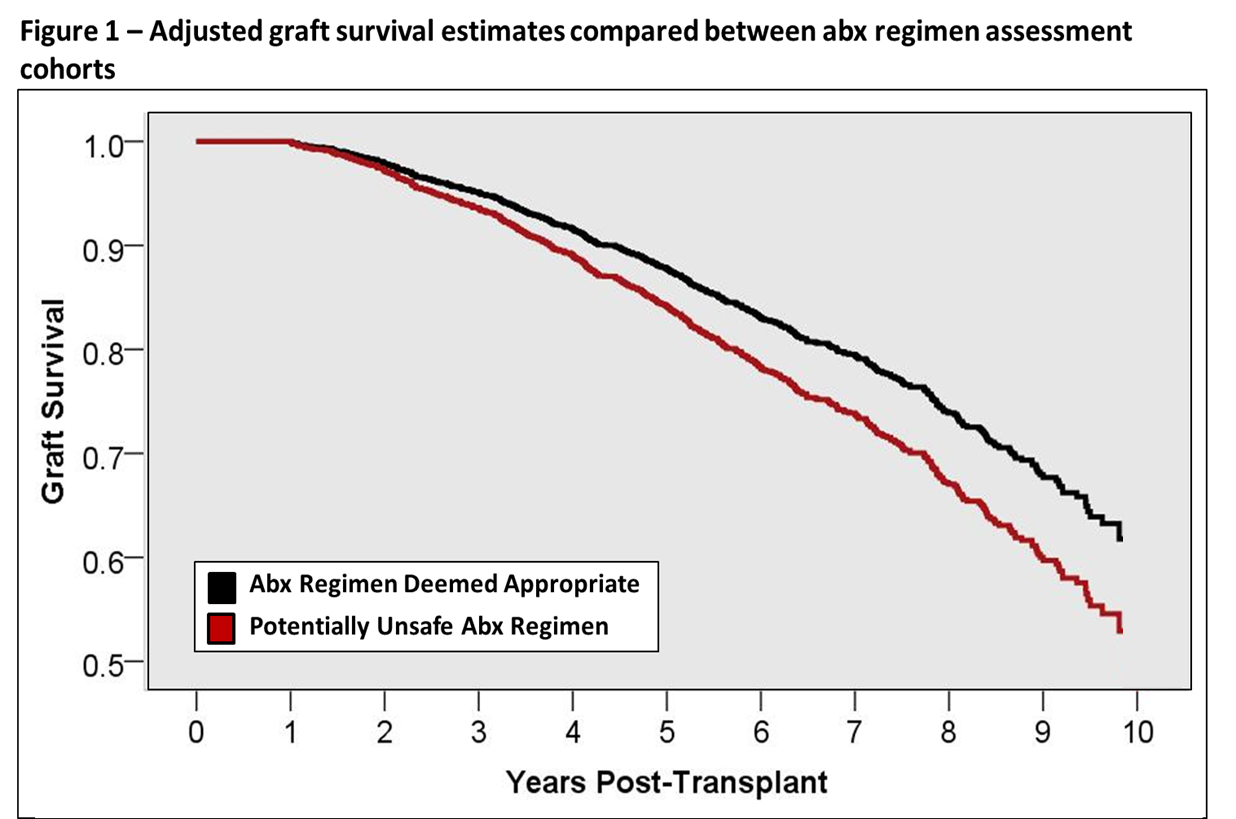
CITATION INFORMATION: Avery L, Fominaya C, Crawford R, Taber D. Ambulatory Antibiotic Utilization and Outcomes in an Adult Kidney Transplant Population: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Avery L, Fominaya C, Crawford R, Taber D. Ambulatory Antibiotic Utilization and Outcomes in an Adult Kidney Transplant Population: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ambulatory-antibiotic-utilization-and-outcomes-in-an-adult-kidney-transplant-population-a-pharmacovigilance-analysis/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
